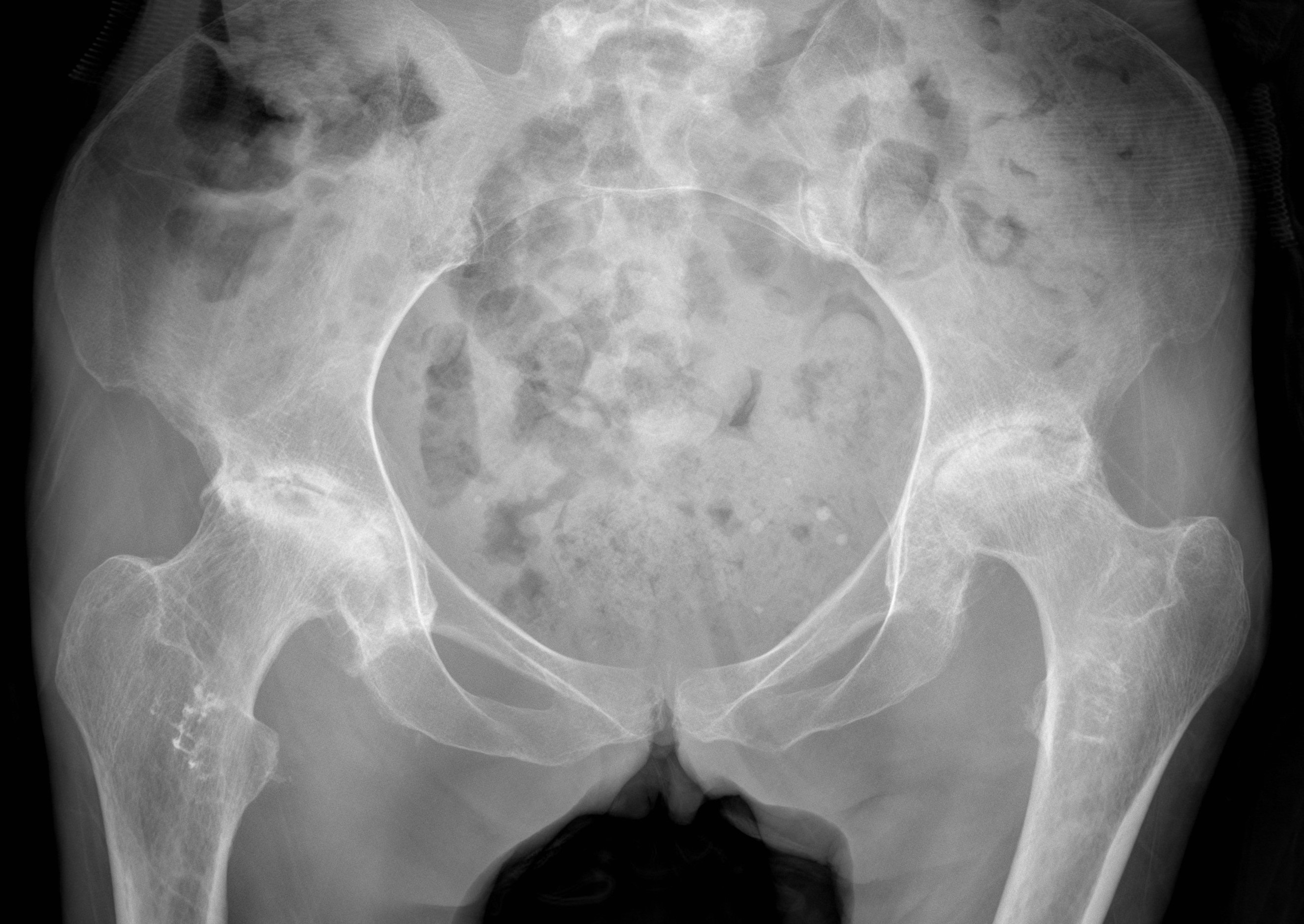
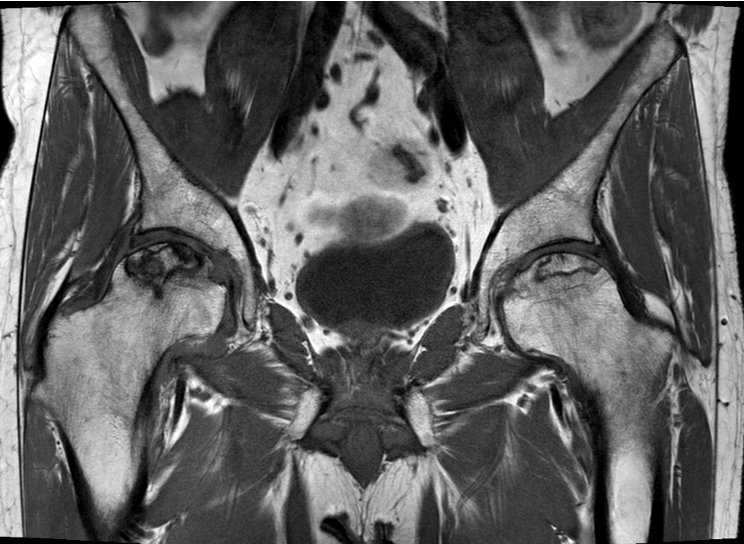
Definition
Lack of sufficient blood supply or oxygen leads to cell death, fracture, and collapse of the femoral head
Epidemiology
20 - 50 years old (average 38)
Male : Female 4:1
Etiology
AS IT GRIPS 3Cs
Alcohol - > 400 ml / week
Steroids - > 20 mg / day
Idiopathic - 20 - 40% of cases
Trauma - hip fracture / dislocation
Gout, Gaucher's, genetics (Factor V Leiden mutation)
Rheumatoid, radiation
Infection, increased lipids, inflammation (arteritis)
Pancreatitis, pregnancy
SLE, Sickle cell, smoking
CRF, chemotherapy, Caisson (decompression sickness)
Pathogenesis
Cell death caused by blood supply / oxygenation issues
Bone resorption by osteoclasts > bone formation osteoblasts
Trauma
- most common cause
- Garden III / IV subcapital 16% risk
- intertrochanteric 1% risk
Corticosteroids
- second most common cause
- postulated secondary to changes lipid metabolism / fat emboli
- increased risk with higher dose
- high incidence in children with ALL, transplant patients
Alcohol
- also postulated secondary to changes lipid metabolism / fat emboli
SLE
- independent of steroid use
- thought due to prothrombotic effects
- incidence 6-8%
Sickle cell disease
- due to precipitation of hemoglobin S in low oxygen conditions
- incidence 2 - 4%
Stages
1. Necrosis
2. Inflammation / Revascularisation / Resorption
3. Repair - osteoblasts, new bone on dead trabeculae
4. Remodelling
Pathology
Starts in Anterior / Superior / Lateral head
- wedge shaped area
Cysts - regions of bone reabsorption
Crescent Sign
- subchondral collapse of the necrotic segment
- separation of subchondral plate from necrotic cancellous bone
Collapse
Classification
Ficat - developed in 1985, no MRI
ARCO (Association Research Circulation Osseous)
- combines Ficat, Steinberg and JOA
Most important
- stage I/II: pre collapse
- stage III/IV: collapse, THA
| Stage | Ficat | ARCO |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Normal xray |
Normal xray Abnormal MRI |
| Stage II | Sclerosis with cysts |
Abnormal xray No flattening |
| Stage III |
Flattening femoral head Crescent sign |
Subchondral fracture IIIA: <2mm flattening IIIB: > 2 mm flattening |
| Stage IV | Collapse with osteoarthritis | Osteoarthritis |
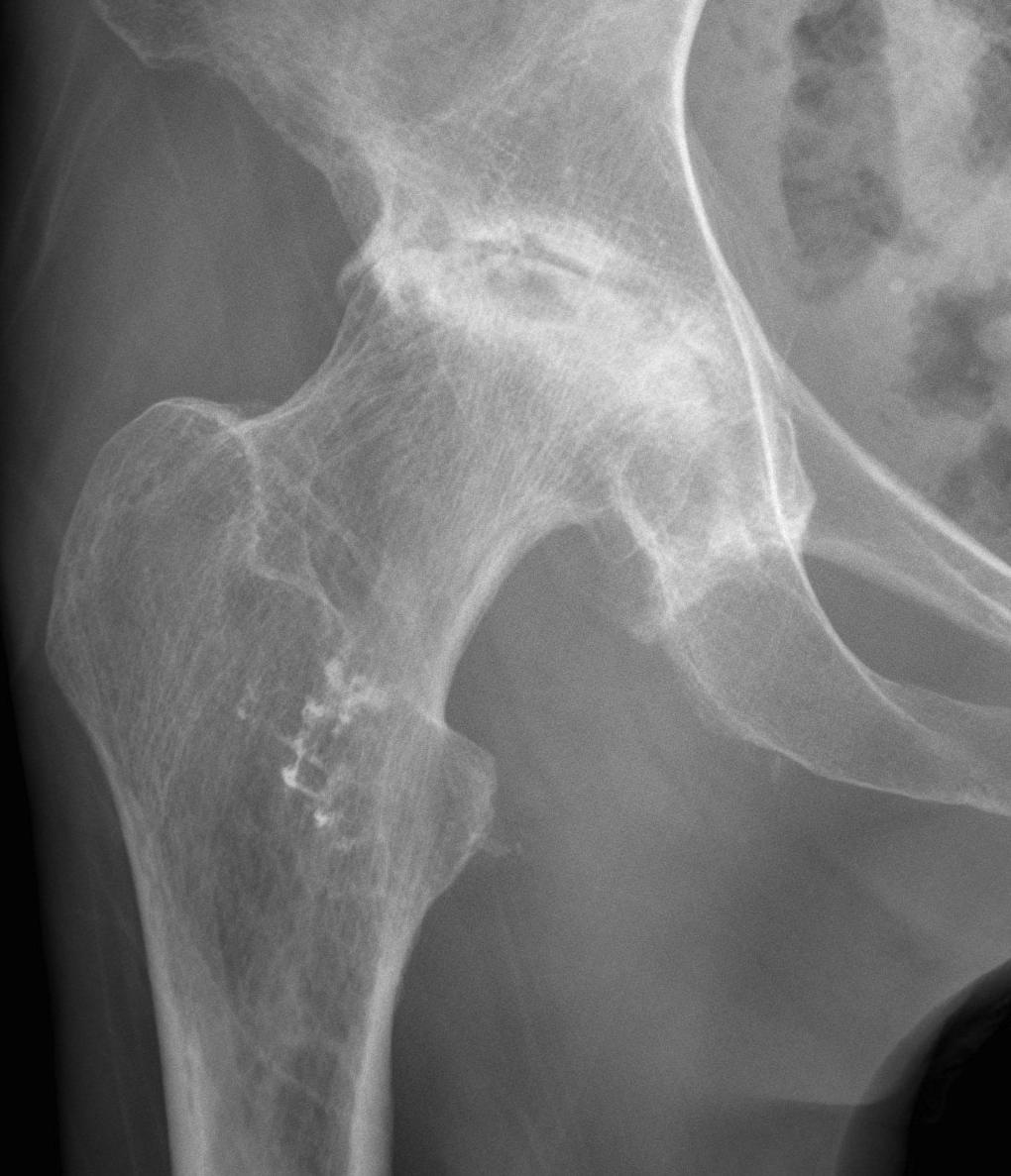
Xray
Stage II: sclerosis with cystic areas resorption, no collapse
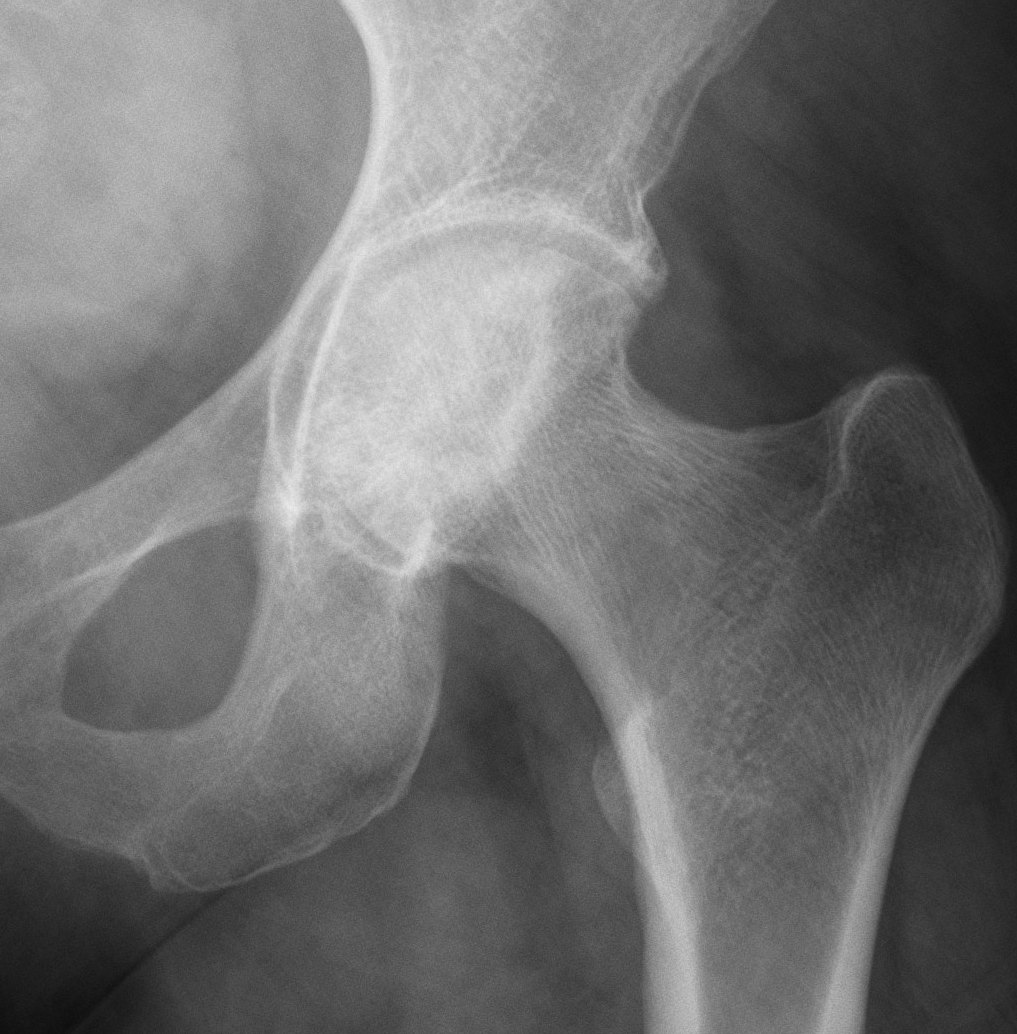
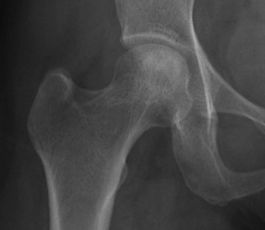
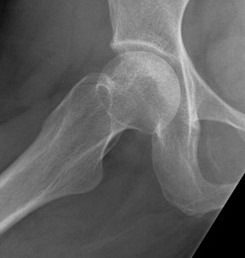
Stage III: collapse / flattening femoral head with preserved joint space

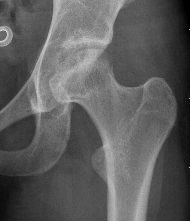
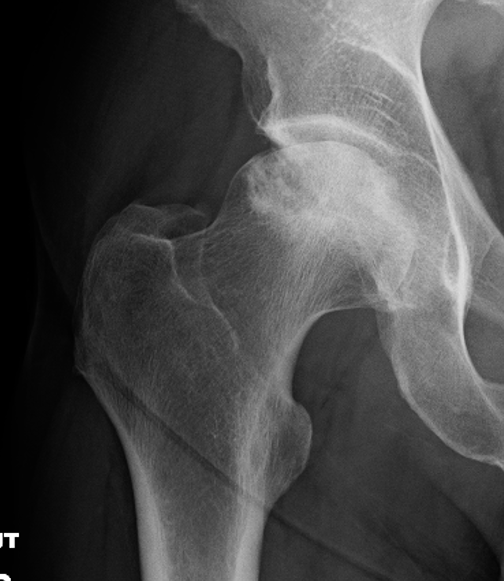
Stage IV: Collapse with osteoarthritis
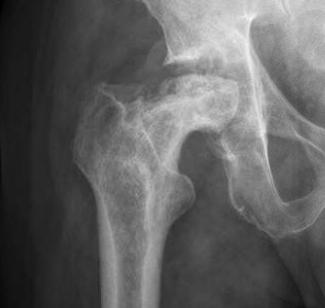

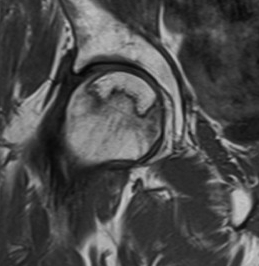
MRI
T1
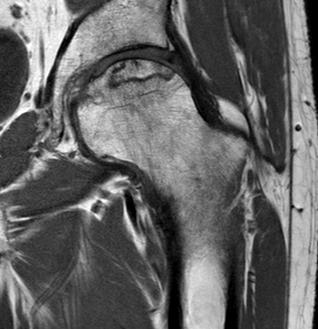
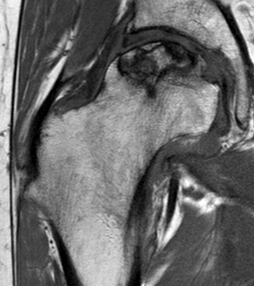
T2
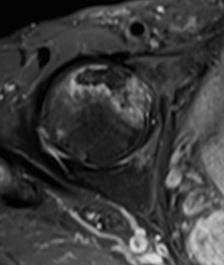
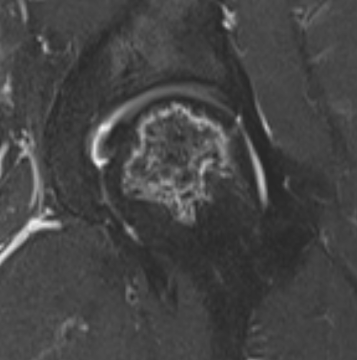
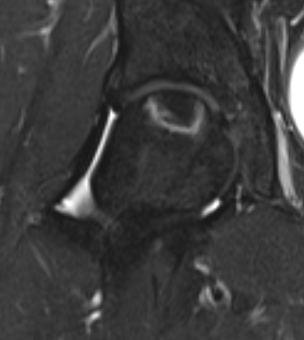
T2 Double Line Sign
Two lines virtually diagnostic of AVN
- outer line / low signa intensity
- inner line / high signal intensity / hypervascular granulation tissue
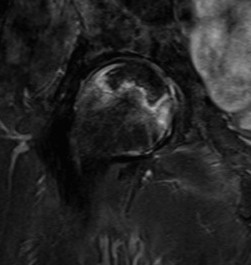
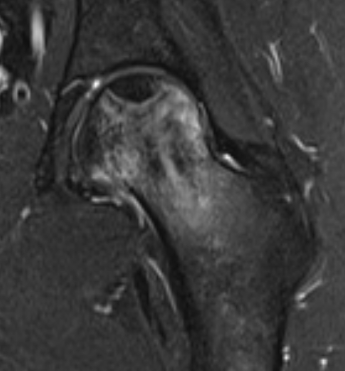
T2 double line sign
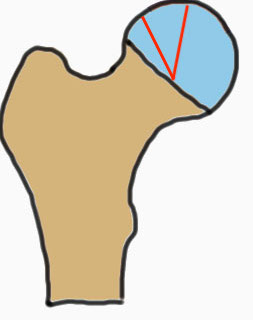
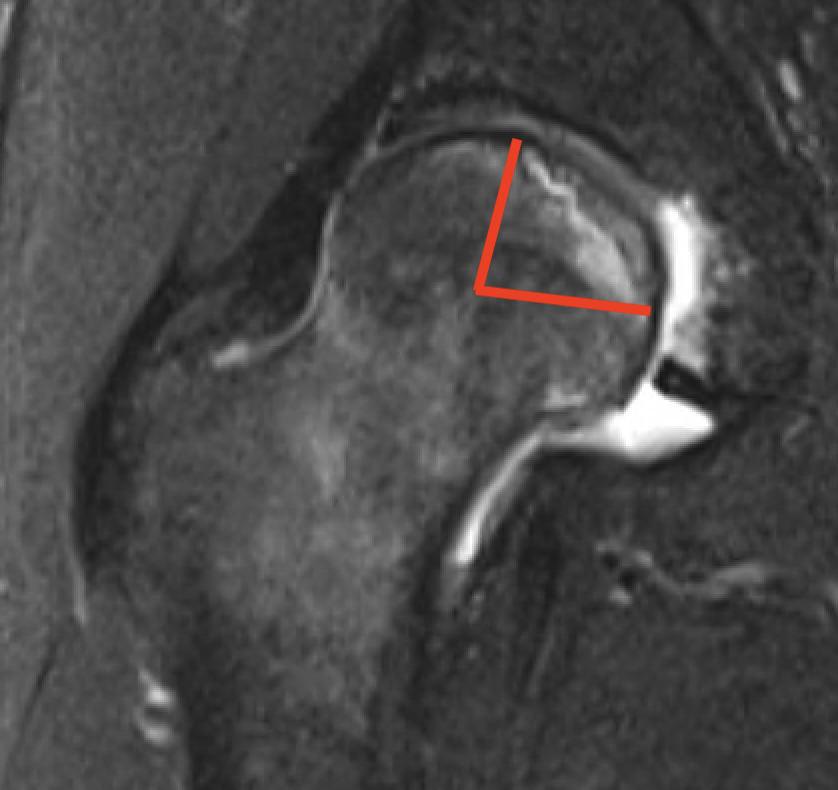
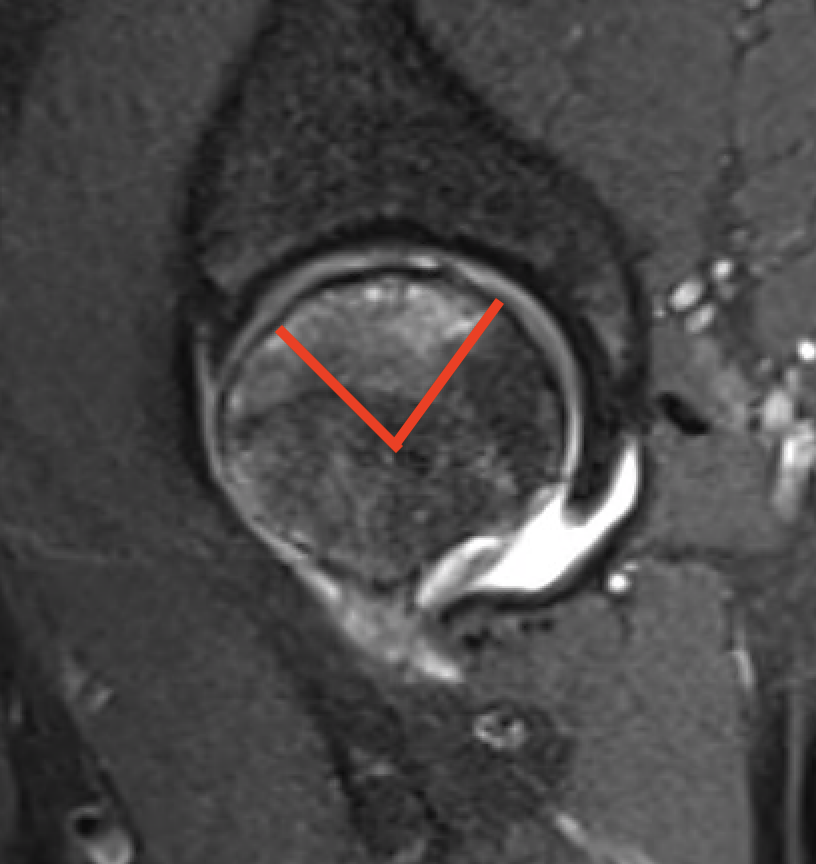
Modified Kerboul Combined Necrotic Angle (CNA)
Adding the arc of the femoral head necrosis
- mid-sagittal and mid-coronal MRI
- low risk collapse: < 190 degrees
- moderate risk collapse: 190 - 240 degrees
- high risk collapse: > 240 degrees

Natural history
Kerboul CNA
- CNA > 240: 100% collapse
- CNA 190 - 240: 50% collapse
- CNA < 190: 0% collapse

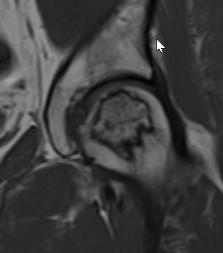
Asymptomatic Contralateral Hip
- systemic review of asymptomatic contralateral hips
- 59% progressed to symptoms or collapse
- small medial lesions progressed to collapse < 10%
- sickle cell high risk, SLE low risk
- 105 asymptomatic contralateral hips
- 59% became symptomatic within 5 years
- 1/21 with < 30% volume of femoral head AVN became symptomatic
- 11/24 with 30 - 50% volume of femoral head AVN became symptomatic
- 50/60 with > 50% volume of femoral head AVN became symptomatic
Differential diagnosis
Bone marrow edema syndrome
- diffuse edema throughout femoral head
- possible stress / overuse reaction / low Vit D in athletes
- possible early AVN
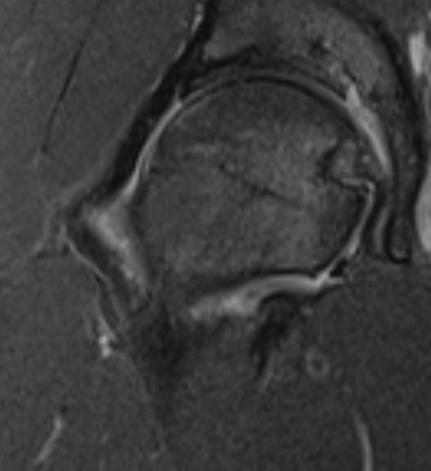

Subchondral insufficiency fracture
- trauma
- acute line
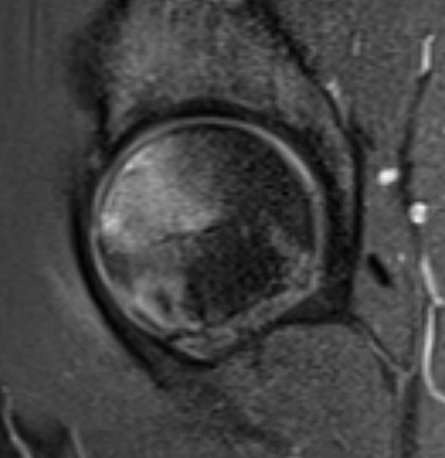
Transient osteoporosis of the hip
- third-trimester pregnancy
- edema into metaphysis or neck

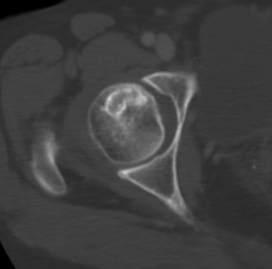
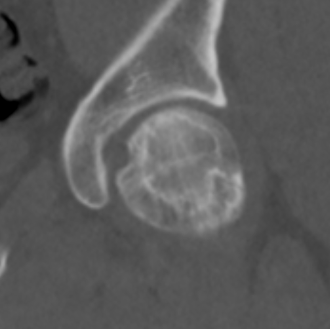
CT
Can diagnose early collapse & flattening
Bone Scan
Most useful to investigate if head vascular after subcapital fracture
