Types of Instability
1. AP Instability
2. Varus Valgus Instability
3. Global Instability
4. Frank Dislocation
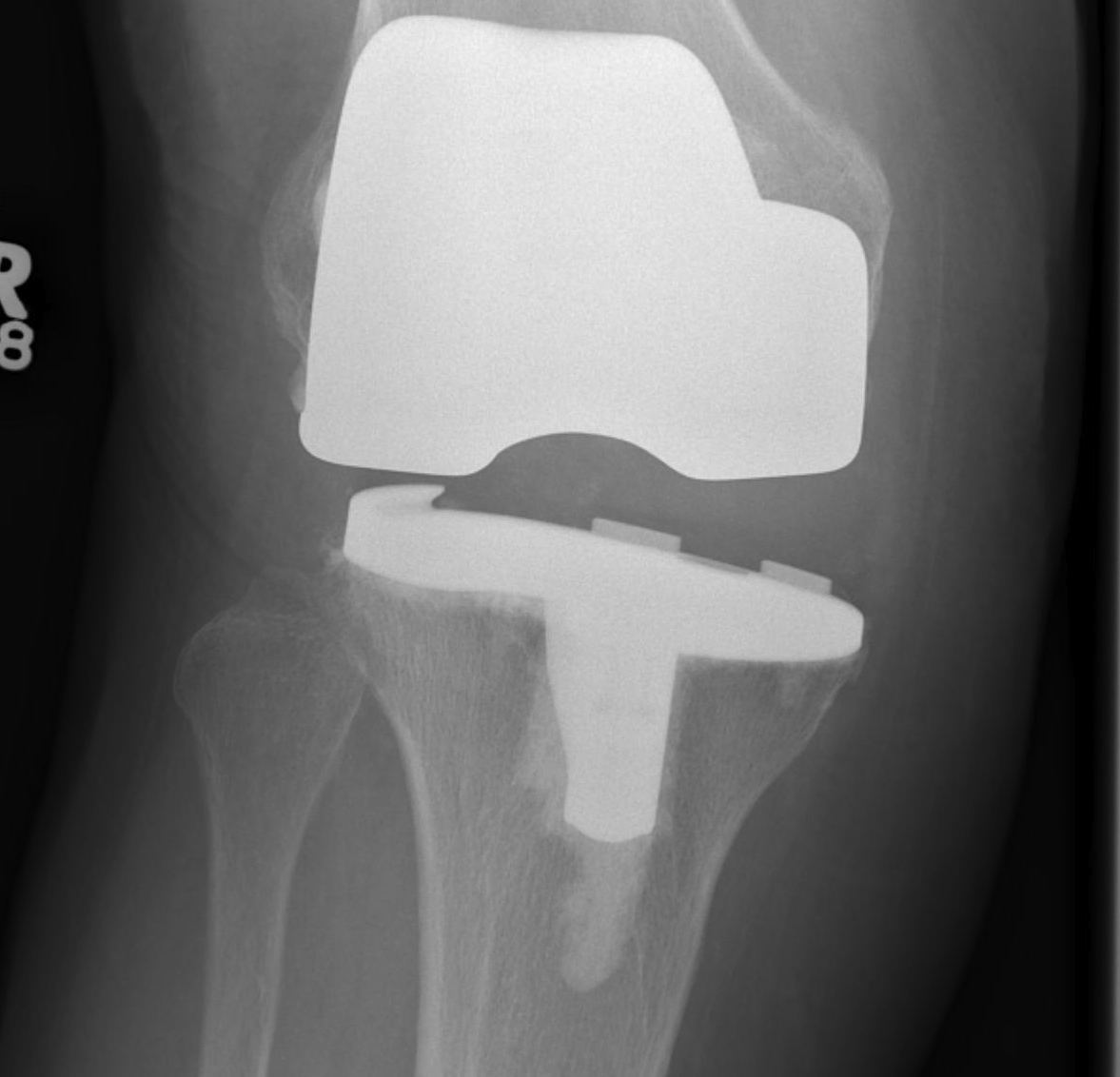
AP instability
A. Loose in flexion
Issue
- can get knee dislocation / post jump
Cause
- excessive posterior femoral resection
- PCL failure
A. Excessive posterior femoral resection
Revise femur
- posterior femoral augments + stem
B. Failure of PCL in CR knee
Revision femur and poly
- insert PS femur and poly
- need to have CCK revision equipment available
B. Loose in extension
Excessive distal femoral resection
- revise femoral component
- distal femoral augments + stem
B. Loose in flexion and extension
Insufficient poly thickness / wear
- insert larger poly
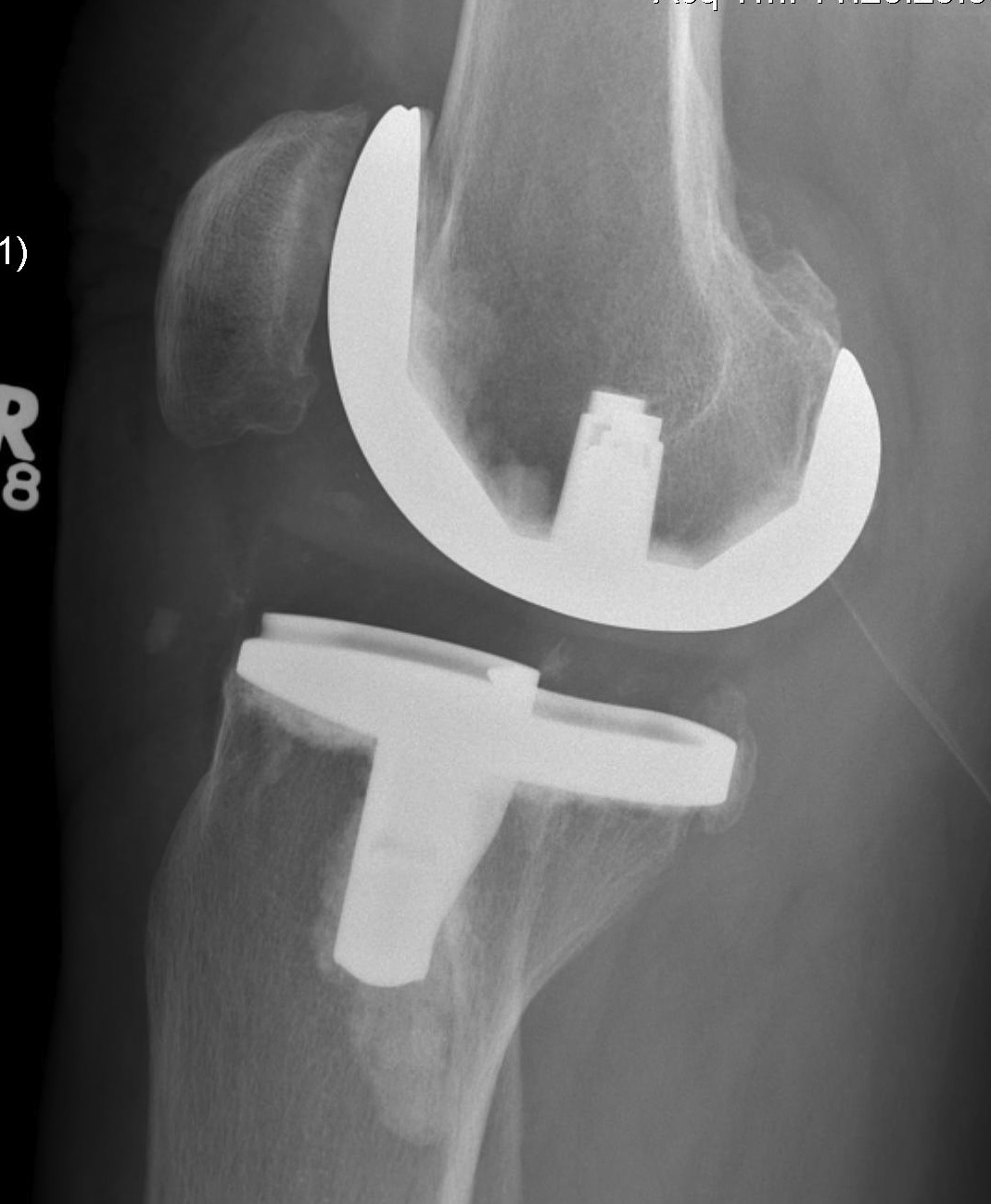
Varus-Valgus instability
Causes
A. Iatrogenic collateral ligament injury
Options
- advance / imbricate / augment / reconstruct collateral
- full revision to VVC / CCK constrained implant
B. Failure to balance knee
Cause
- under release deformity in the concavity
Management
- increase poly thickness, further releases in concavity
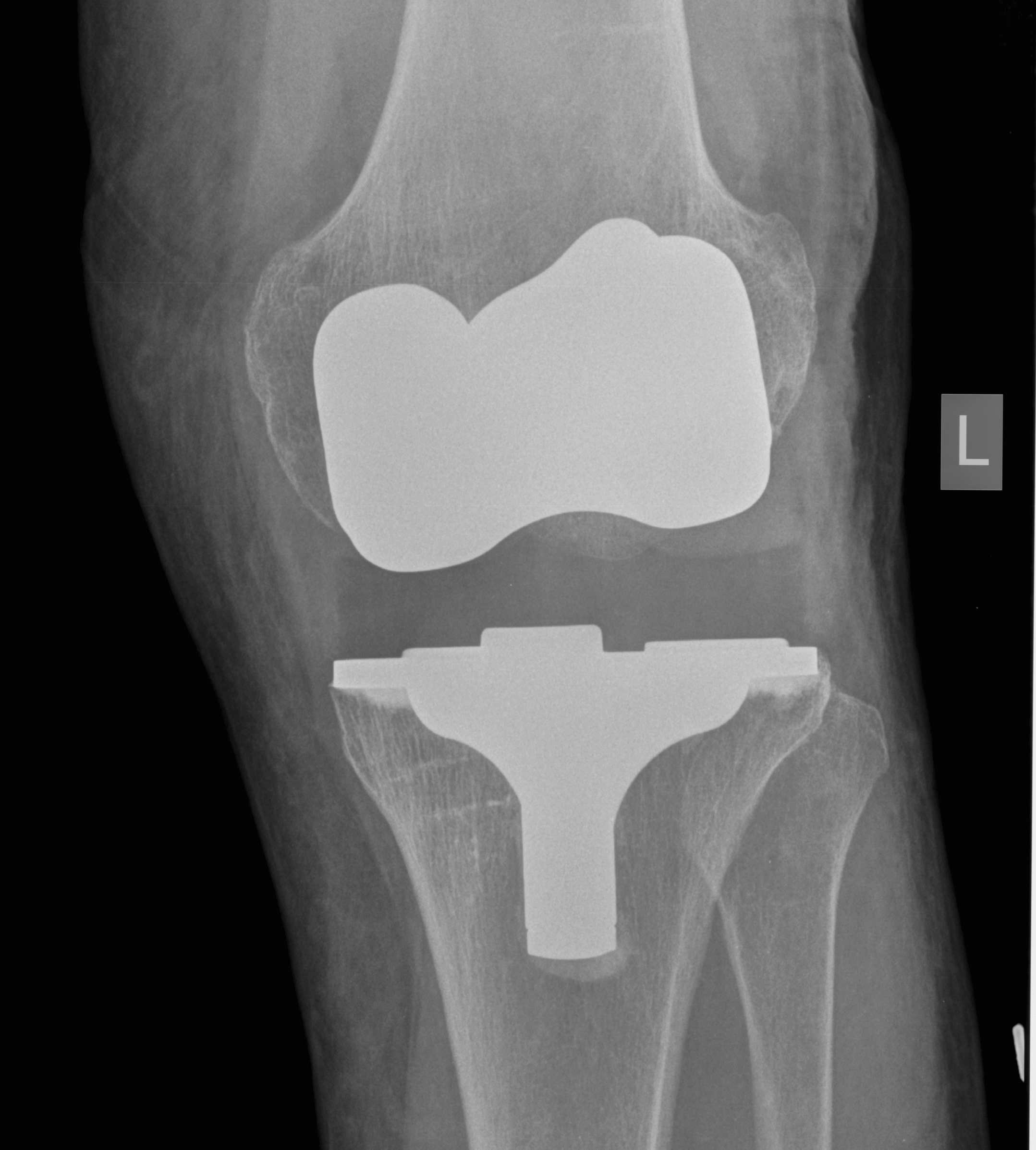
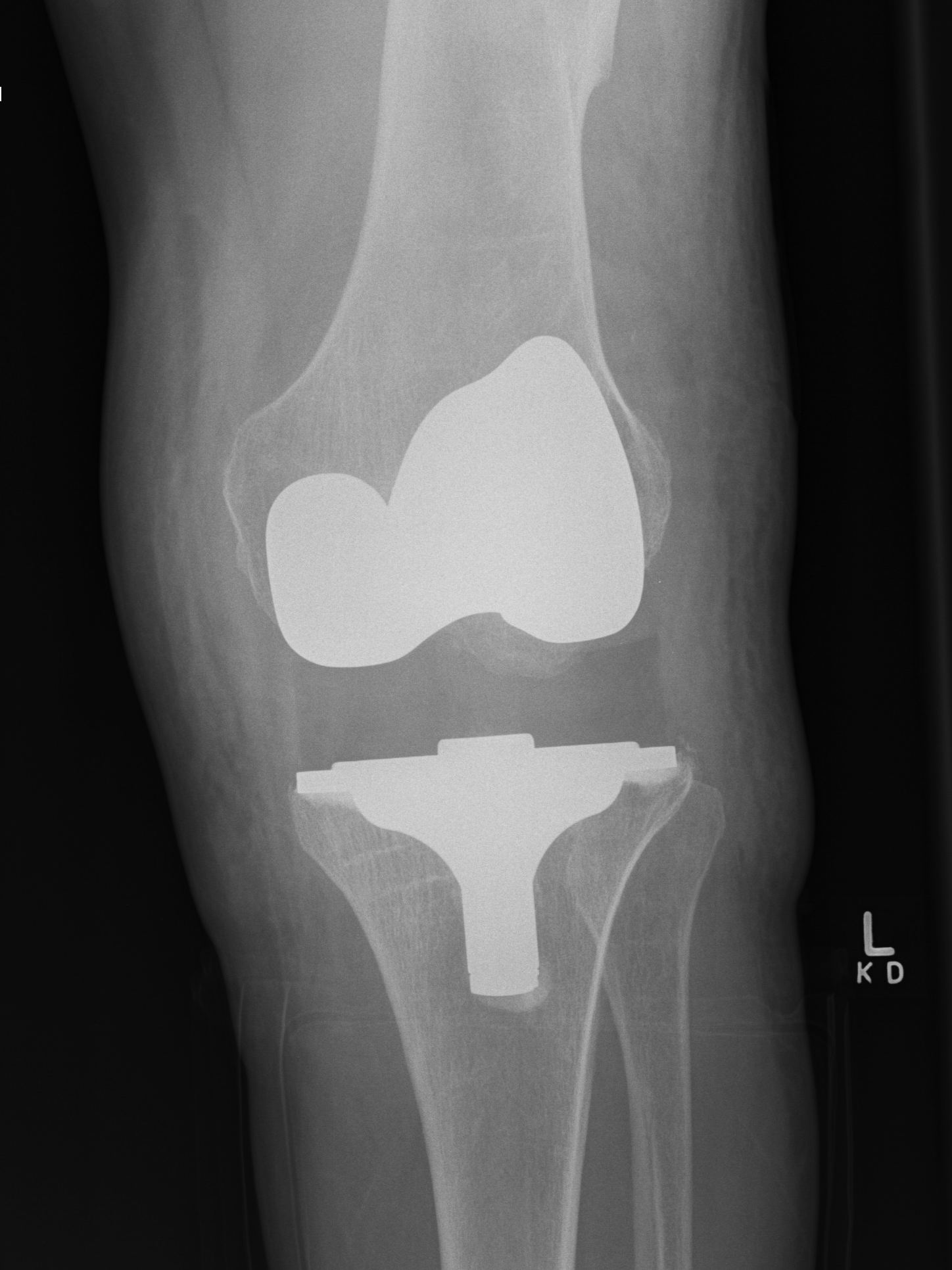
C. Insufficient poly / loosening over time
Diagnose
- equal varus and valgus instability
Management
- increase poly thickness
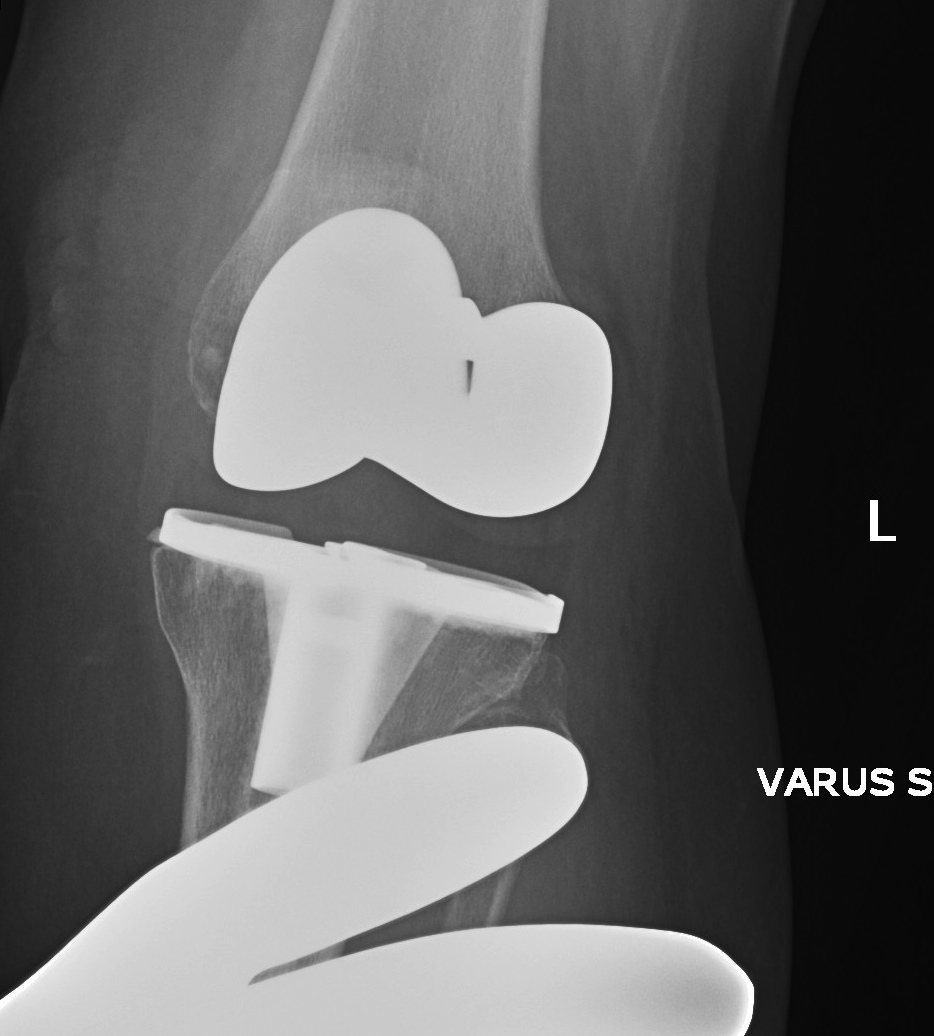
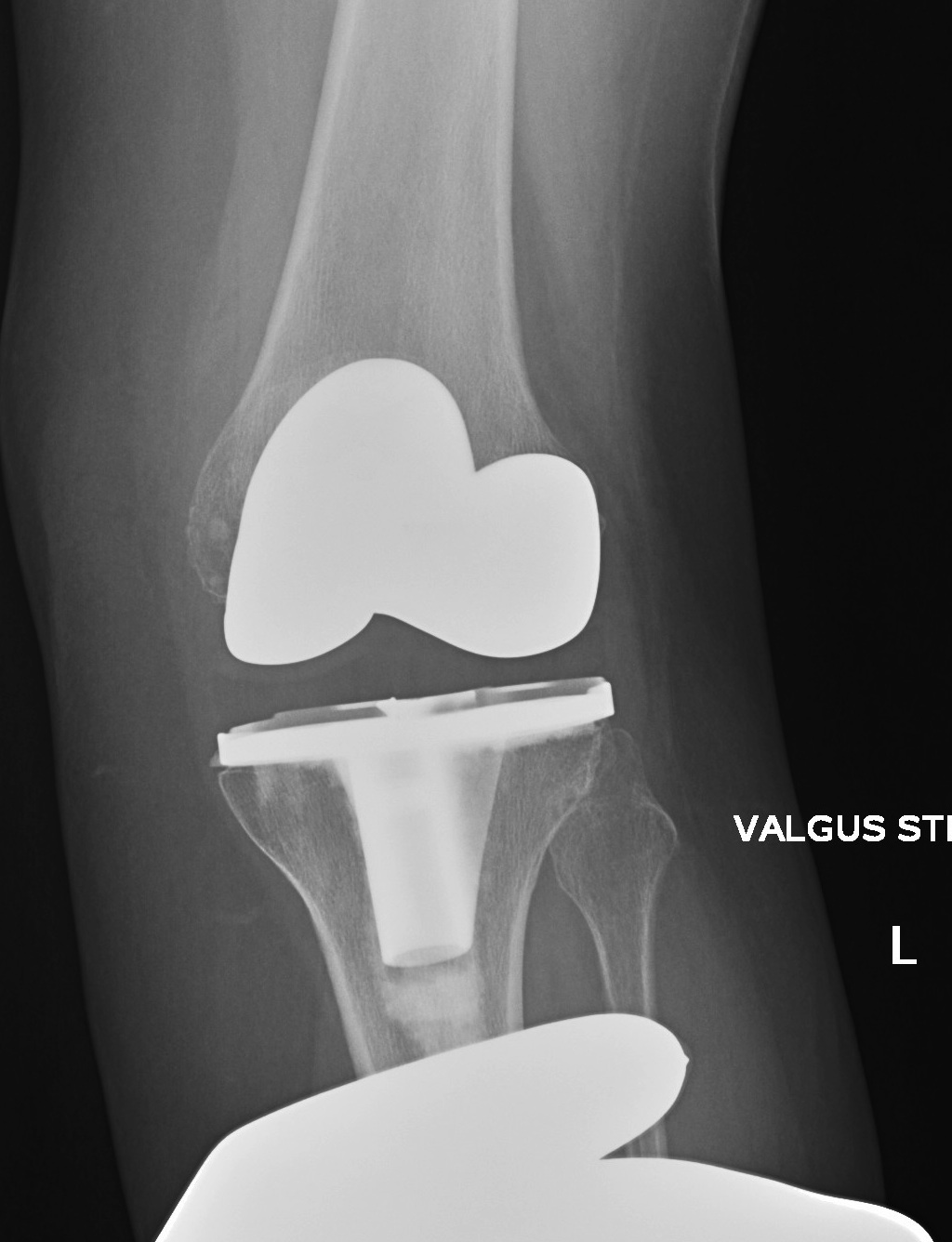
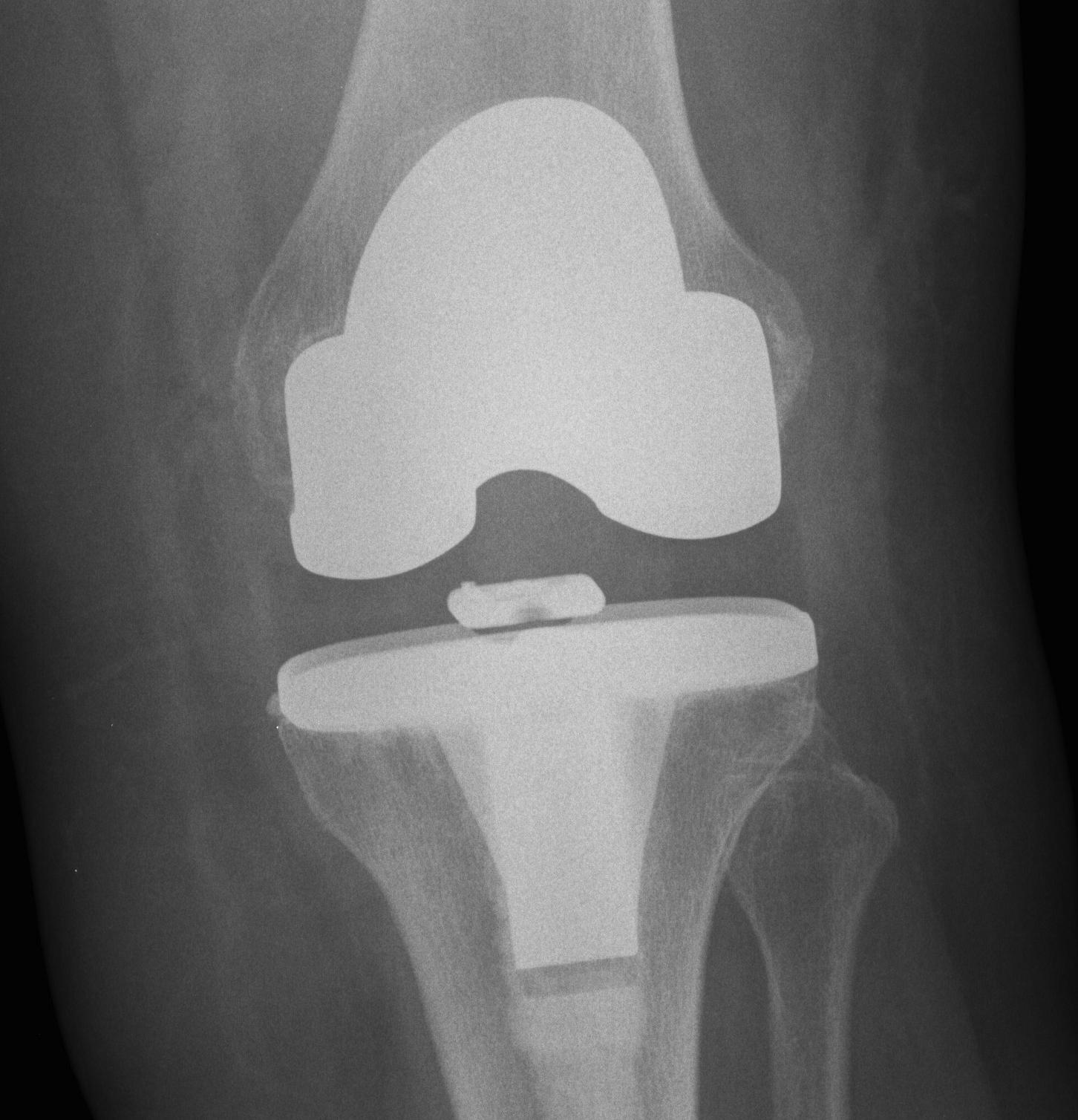
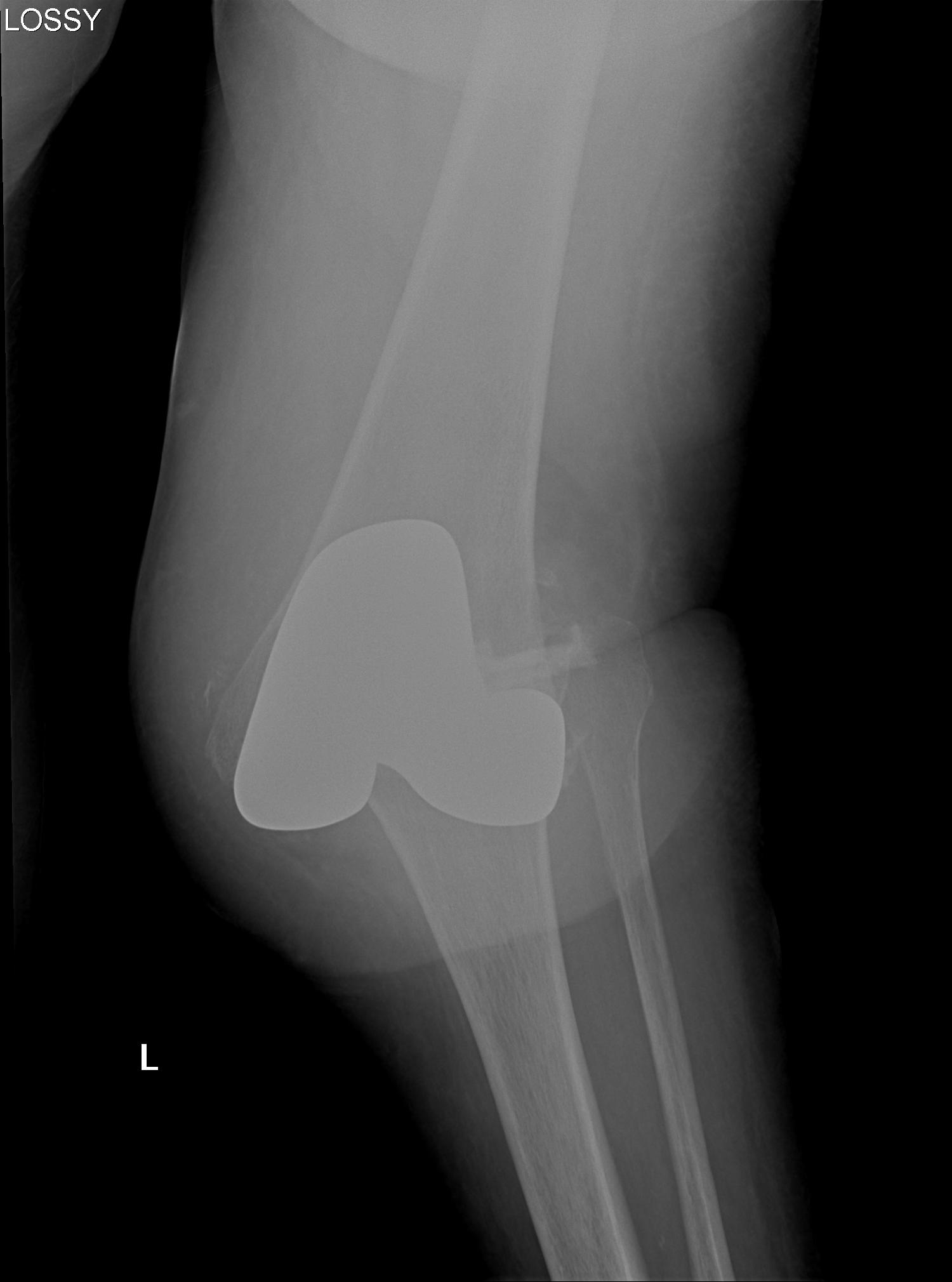
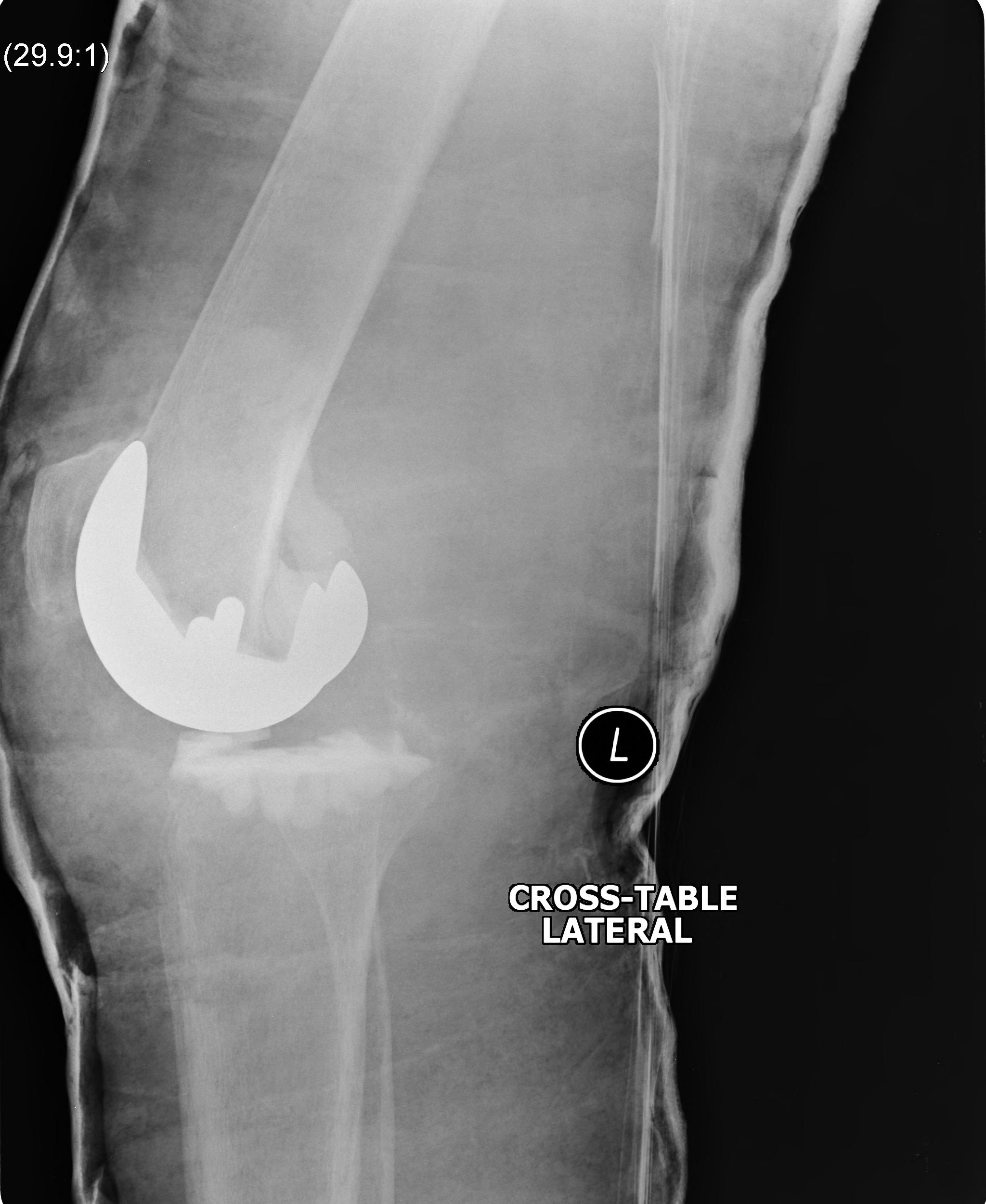
3. Global instability
Unstable in sagittal and coronal planes
1. Insufficient poly thickness / poly wear
Options
- increase poly thickness
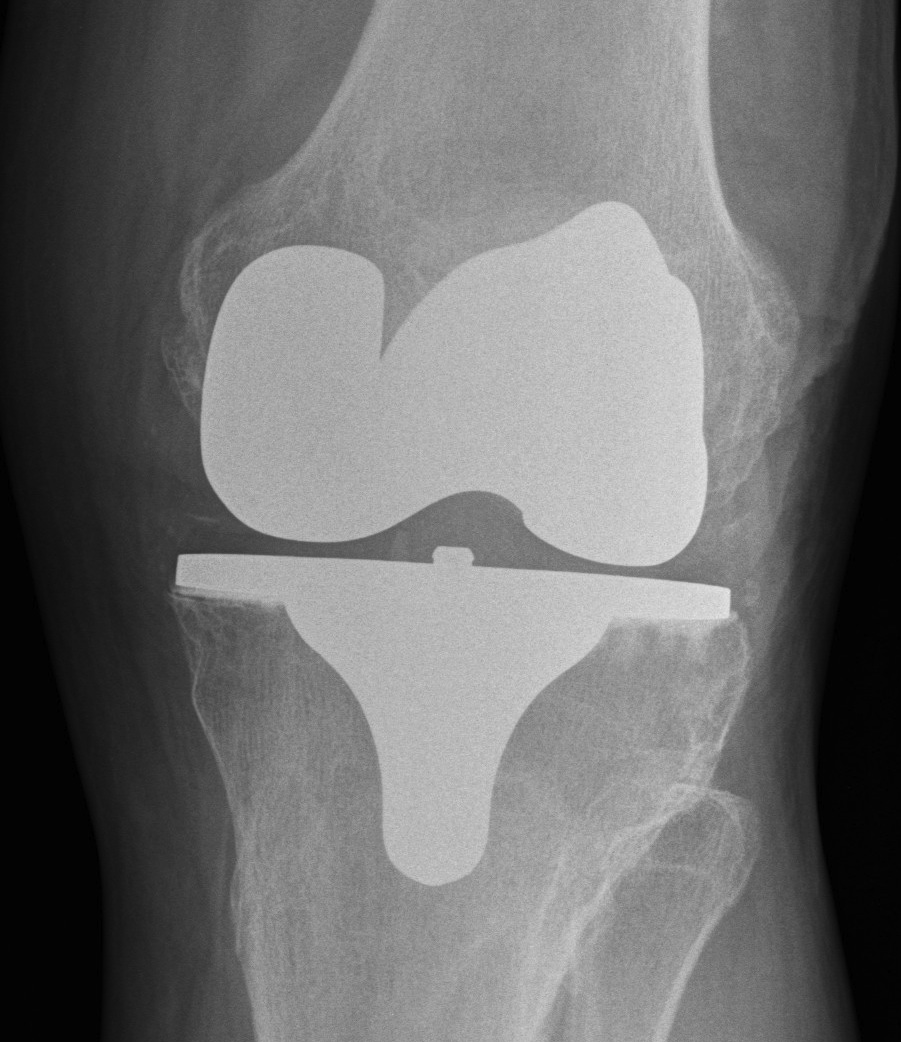
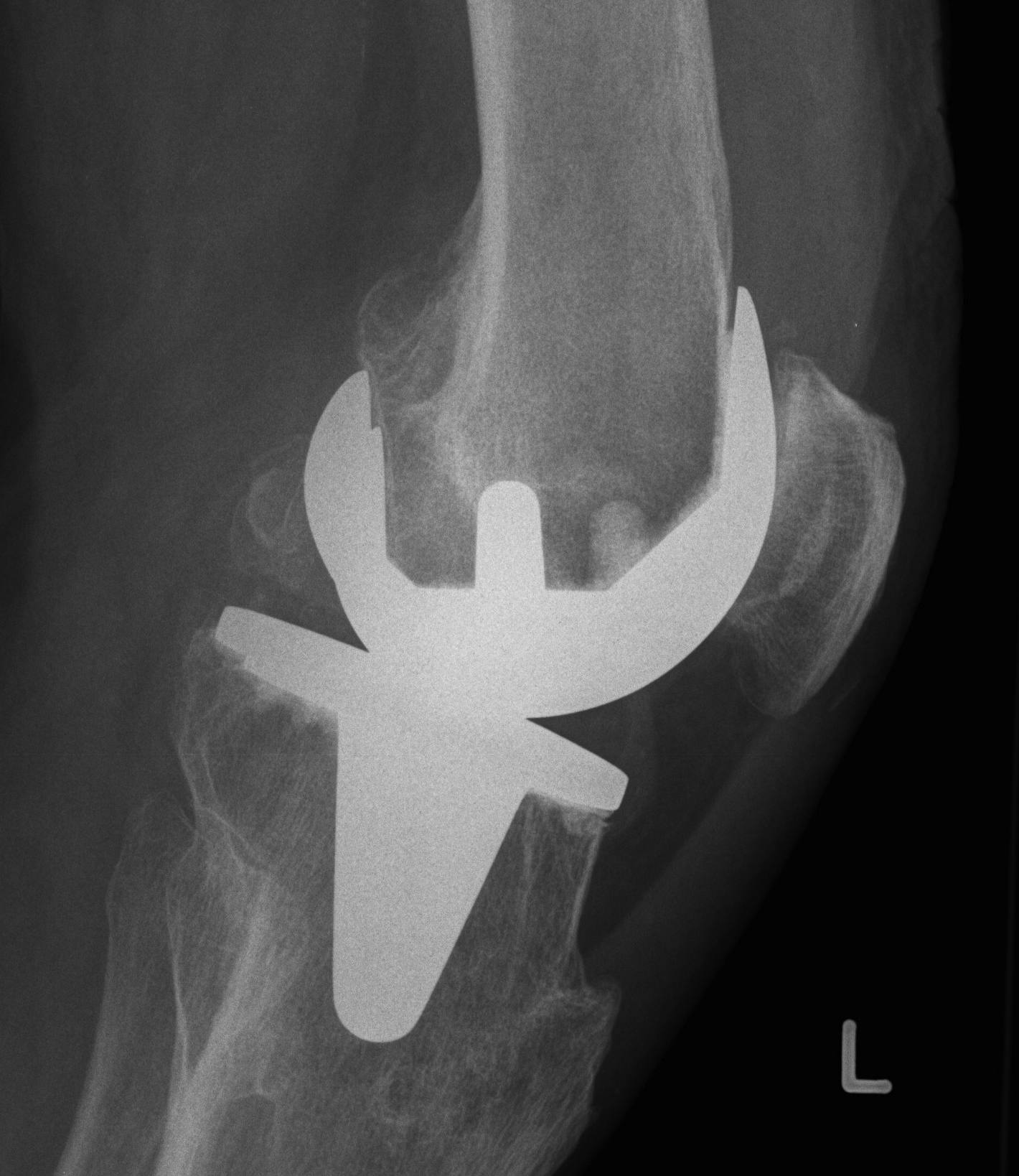
2. Loosening / collateral ligament damage
Options
- revise to highly constrained prosthesis