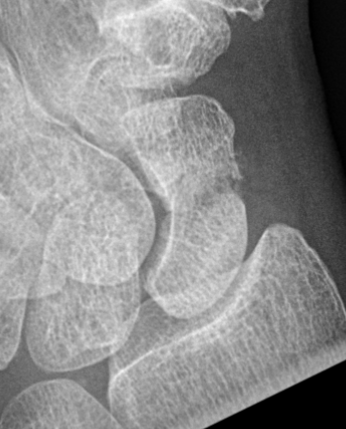
Epidemiology
- systematic review of scaphoid fractures
- majority in males
- peak incidence 20 - 29 years
- 70% in the mid third of the scaphoid
Etiology
FOOSH
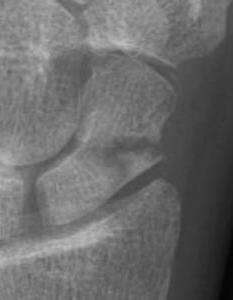
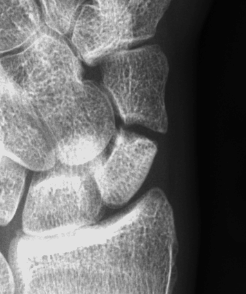
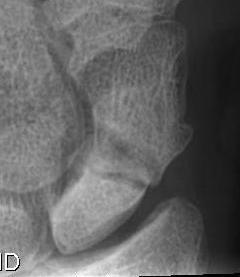
Herbert Classification
Type A: Stable acute fractures
- A1: tubercle
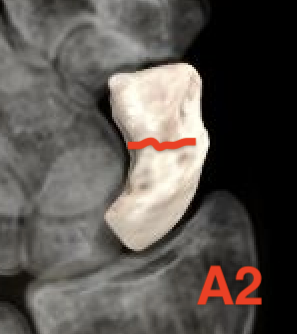
- A2: incomplete waist fracture
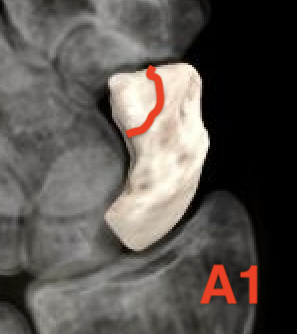
Type B: Unstable fractures
- B1: distal oblique
- B2: complete waist
- B3: proximal pole fractures
- B4: trans-scaphoid perilunate fracture
- B5: comminuted

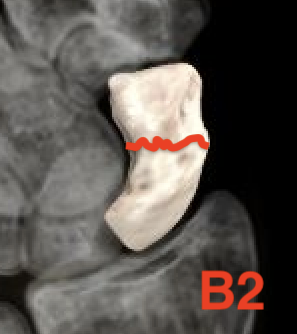
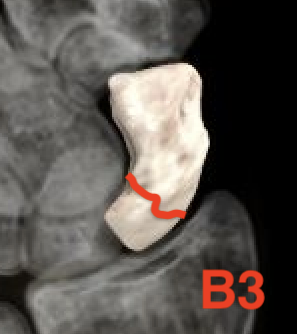

Type C: Delayed union
Type D: Nonuion
| A1: Tubercle fracture | A2: Incomplete waist fracture |
|---|---|
 |
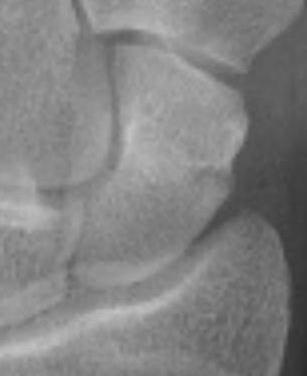 |
| B1: Distal oblique | B2: Complete waist | B3: Proximal pole | B5: Comminuted |
|---|---|---|---|
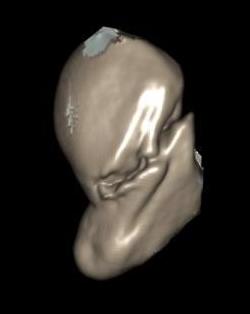 |
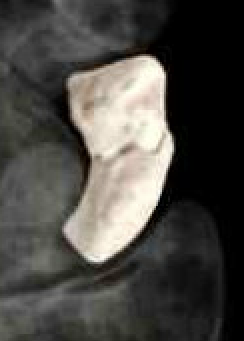 |
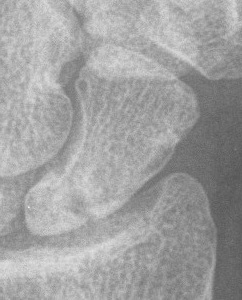 |
 |
Anatomy


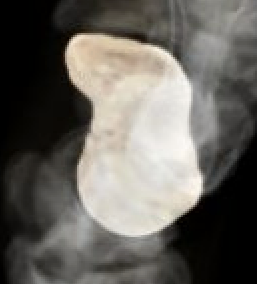
Scaphoid is greek for boat
- shaped more like a twisted peanut
- majority is articular cartilage except for dorsal ridge
- dorsal ridge is site of entry of majority of blood supply
Blood supply
1. Dorsal scaphoid branch
- dorsal ridge artery via branch of radial artery
- supplies 70- 80% scaphoid including proximal pole
- enters through the non articular dorsal ridge
2. Volar scaphoid branch
- superficial palmar arch via distal tubercle
- distal 20% to 30% of scaphoid
Complications of scaphoid fractures
| Nonunion | Avascular necrosis | Malunion |
|---|---|---|
|
Displaced fractures Proximal pole fractures |
Proximal pole fractures |
Flexion / increased intra-scaphoid angle Humback deformity DISI deformity / worse outcomes |
 |
 |
 |
Nonunion
Increased risk with displaced fractures
Increased risk with proximal pole fractures
Displaced fractures
- systematic review of scaphoid fractures displaced > 1 mm
- operative versus non operative management
- nonunion rate of displaced fractures 4X nondisplaced fractures
- nonunion rate of displaced fractures treated with cast: 18%
- nonunion rate of displaced fractures treated with surgery: 1%
Proximal pole fractures
Chong et al J Plastic Surg Hand 2022
- meta-analyis of proximal third fractures
- nonunion rates 2 - 3X higher than waist fractures
- nonoperative nonunion: 18%
- operative nonunion: 6%
Clinical
Tender anatomical snuffbox
Swelling
Reduced ROM
X-ray
5 images
- PA / lateral
- PA in 45° oblique pronation / PA 45o oblique supination
- PA in ulna deviation
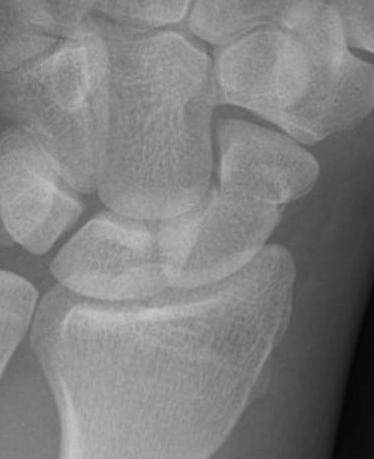
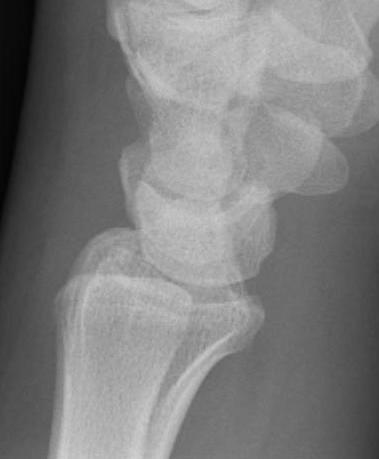
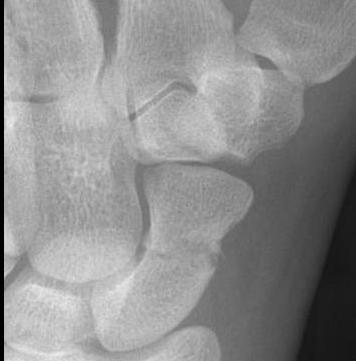
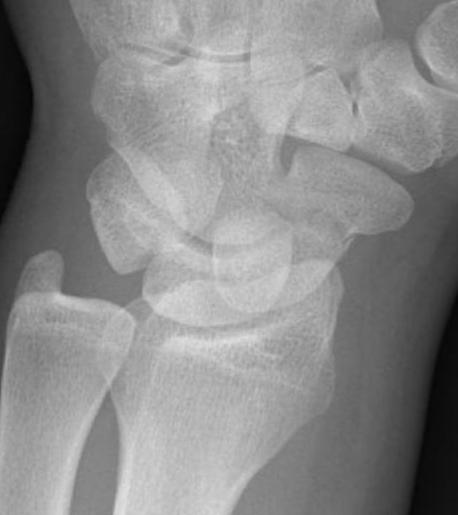
Occult scaphoid fracture
Issue
Tender in anatomical snuffbox with normal xrays
Occult fracture on delayed xrays / CT / MRI
Incidence
Cohen et al J Orthop Traumatol 2025
- 180 patients with normal xrays and suspected scaphoid fractures
- xrays at 2 weeks and 1 year
- 9% incidence of occult fracture
CT
Indication: any potential displacement
Position: patient prone with fully pronated hand over head
Instability
- displacement > 1mm on any film
- intra-scaphoid angle > 35o
- comminution
- proximal pole fractures
- perilunate trans-scaphoid dislocation
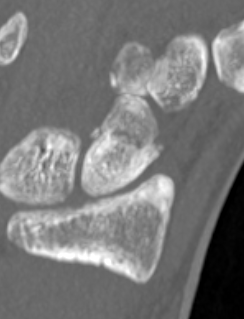
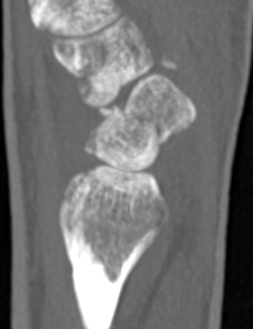
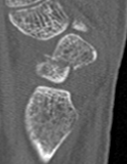
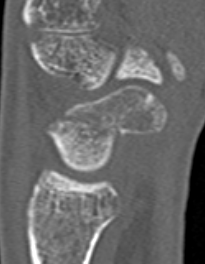
Scaphoid waist fracture 1 mm displaced
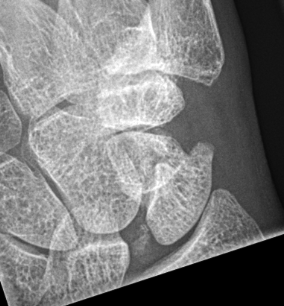
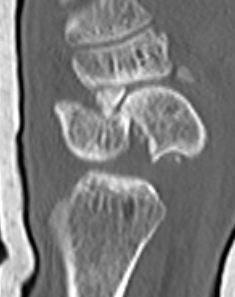
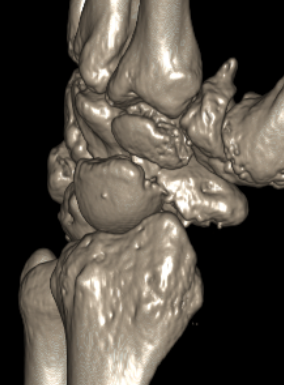
Scaphoid fracture with significant displacement
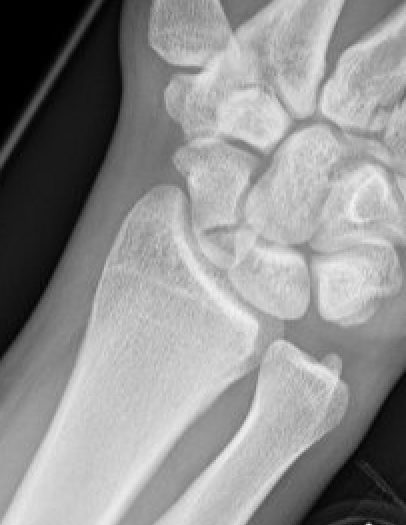


Scaphoid proximal pole fracture
MRI
Indications
- occult fractures
- diagnosis of AVN
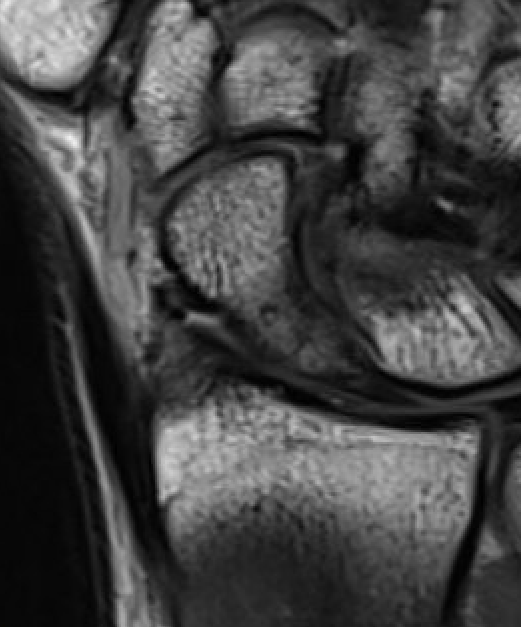
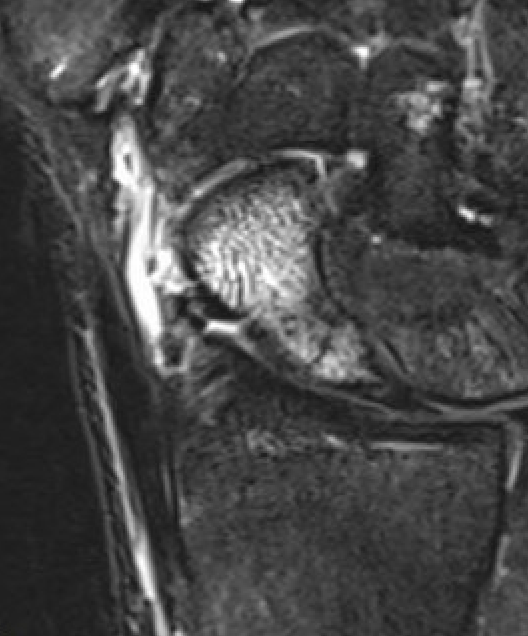
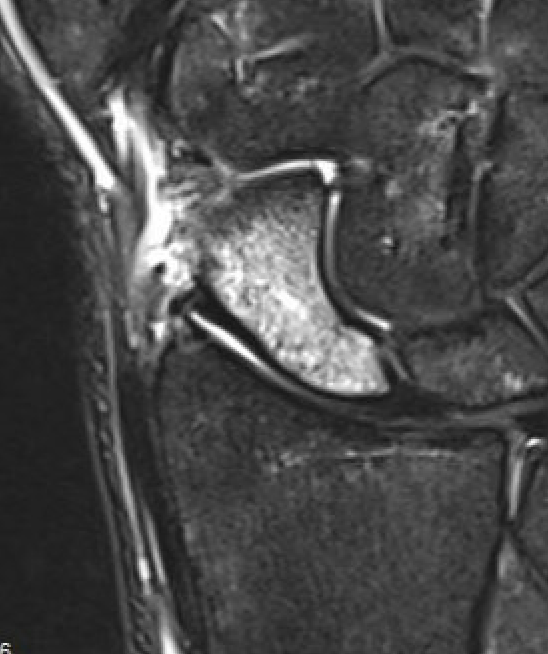
Occult scaphoid fracture on MRI
- 67 patients with normal xray and suspected scaphoid fracture
- 10% had scaphoid fracture on MRI
Dean et al Bone Joint Open 2021
- 258 patients with normal xray and suspected scaphoid fracture
- 13% had scaphoid fracture on MRI, 6% scaphoid contusion
Nonoperative management
Indications
Minimally displaced stable fractures
- incomplete fractures
- waist fractures displaced < 1mm
- tuberosity fractures
Management
Thumb spica versus colles cast
Harper et al Hong Kong Occ 2025
- systematic review of 4 RCT
- no benefit of thumb spica with regards outcomes or union rates
Results
Occult scaphoid fractures
- 250 patients with scaphoid fracture diagnosed on MRI
- 3% delayed union
- 4% nonunion
Cohen et al J Orthop Traumatol 2025
- 180 patients with normal xrays and suspected scaphoid fractures
- randomized to 2 weeks cast versus bandage
- 9% incidence of occult fracture on xray at 2 weeks and 1 year
- no nonunions either group
Distal scaphoid fractures
Clementson et al J Hand Surg Am 2017
- 41 cases of distal scaphoid fracture
- nonoperative treatment followed up for 10 years with CT scan
- good functional outcomes
- asymptomatic STT OA in 17% on CT
Operative versus nonoperative minimally displaced complete scaphoid fractures
- RCT 83 minimally displaced scaphoid fractures
- cast versus screw fixation
- 10 year follow up
- all fractures united
- increased STT OA in the operative group
- meta-analysis of 7 RCTs
- operative v nonoperative < 1 mm displaced scaphoid fractures
- surgery faster time to union
- no difference in nonunion rates or outcomes
- RCT of operative v non operative 439 patients
- bicortical scaphoid fractures 2 mm displaced or less
- 1 year follow up
- surgery: 72% united, 3% nonunion, 25% unknown
- cast: 62% united, 9% nonunion, 32% unknown
Operative Management
Indications for Surgery
| Instability | Proximal pole fractures | Manual worker / athlete | Delayed diagnosis / treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Displacement > 1 mm Comminution Flexion - intra-scaphoid > 35o
|
High risk of nonunion High risk of AVN |
Avoid cast Percutaneous screw |
Increased risk of nonunion |
| Perilunate fractures / dislocatons |
Options
Volar versus dorsal approach
- volar preserves dorsal blood supply
- dorsal likely indicated for proximal pole fractures
Open versus percutaneous versus arthroscopic
- open generally indicated for displaced fractures
Screw versus two screws versus volar plate
- single screw usually indicated for acute fractures
- two screws / volar plate for nonunion surgery
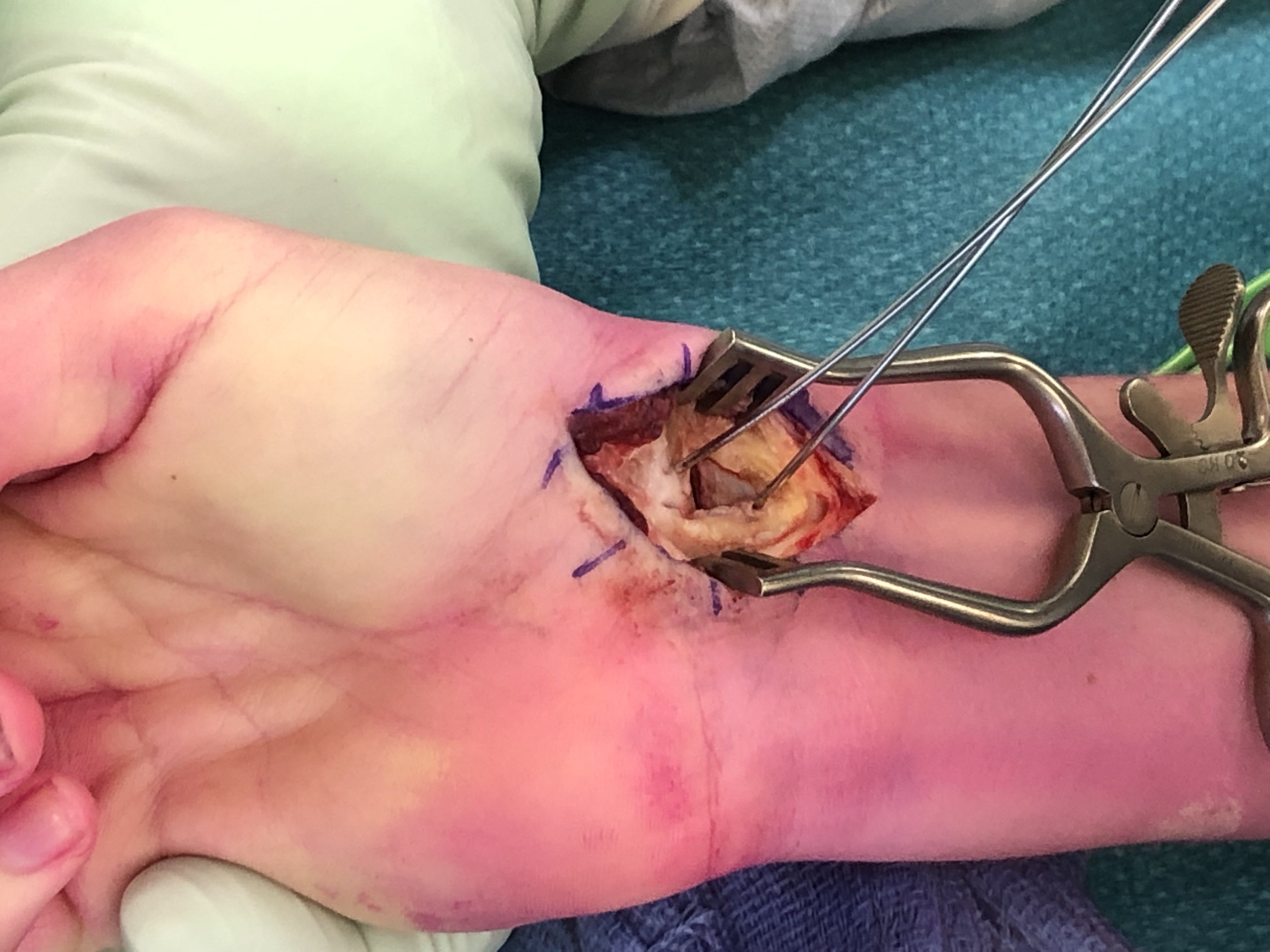
Open volar approach
Indication
Displaced scaphoid waist fractures
Scaphoid nonunion
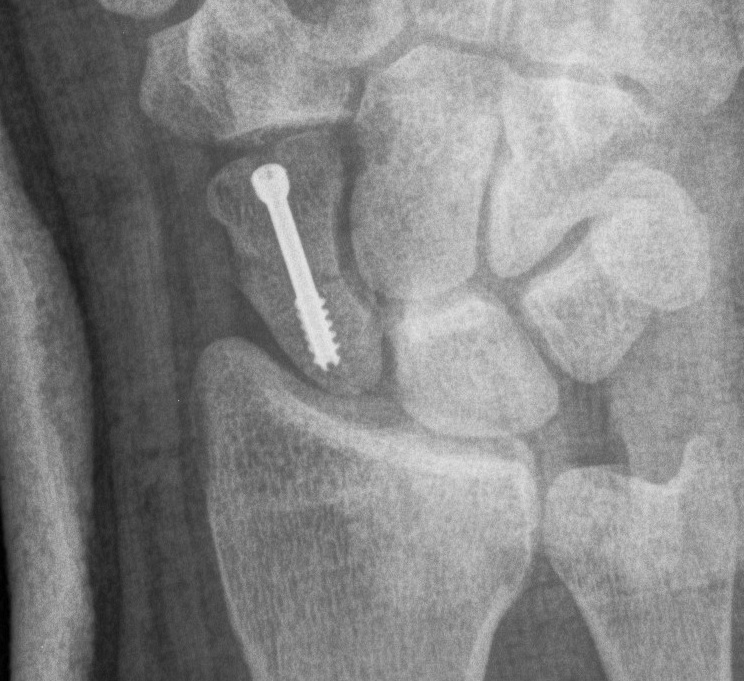

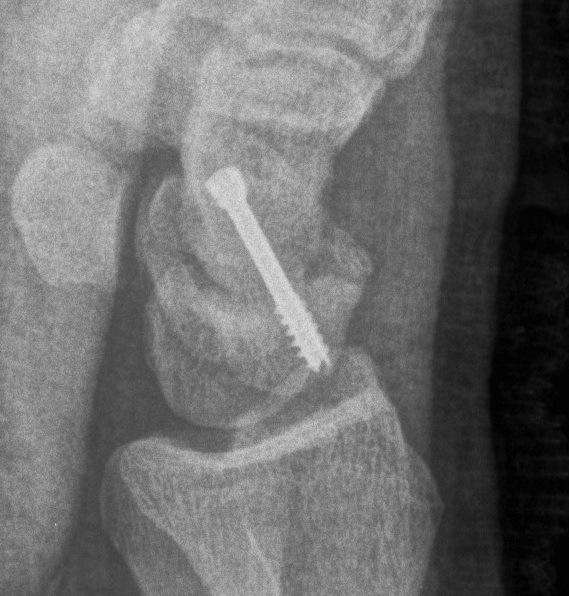
Technique

AO surgery foundation volar approach to scaphoid
Vumedi open volar approach illustration video
Vumedi open volar approach scaphoid video
Volar along distal FCR sheath
- deviate along thenar edge to scaphoid tubercle / STT joint
- open FCR sheath, may need to divide superficial branch radial artery
- retract FCR to ulna side
- elevate thenar muscles
- open capsule over scaphoid including over STT joint
Clean and reduce fracture
- K wires as joysticks
- pass cannulated screw wire central third of scaphoid
- can remove volar beak of trapezium
- consider use of additional anti-rotation K wire
- pass headless compression screw, bury head
- +/- bone graft
Bone graft
- comminuted fracture / unstable fractures / humpback deformity
- distal radius / iliac crest
Open dorsal approach
Indications
Displaced proximal pole fractures
Proximal pole nonunion
Waist fractures
Scaphoid fracture with perilunate dislocation / scapholunate ligament repair
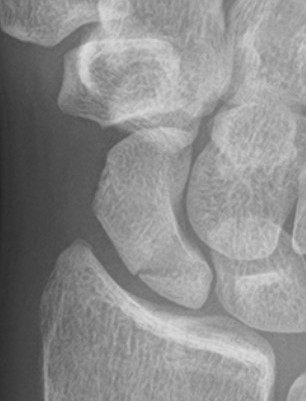
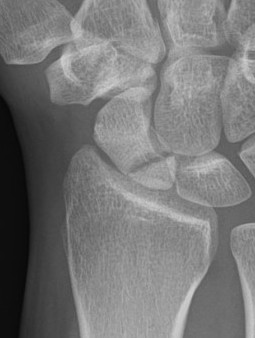
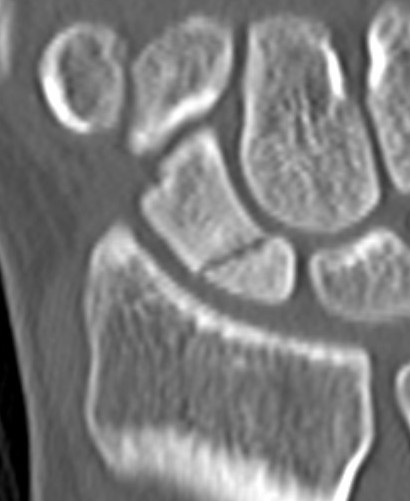
Technique
AO surgery foundation dorsal approach to scaphoid
Vumedi open dorsal approach to scaphoid video
Vumedi open dorsal approach 2 screw fixation proximal pole video
Dorsal approach
- incision centered on Lister's tubercle
- preserve superficial radial nerve
- open 3/4 extensor compartment
- reflect EPL radially, reflect EDC ulnarly
- open capsule
- preserve dorsal ridge vessels
Flex wrist and reduce fracture
- insert K wire
- proximal fragment into distal fragment
- entry point is just radial to SL ligament
- drive into trapezium / use additional anti-rotation K wire
- check position on multiple views
- insert headless compression screw
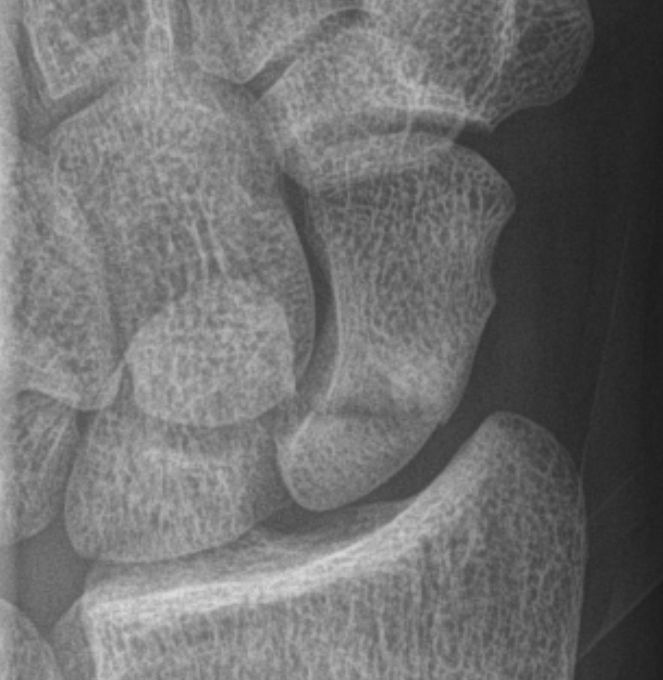
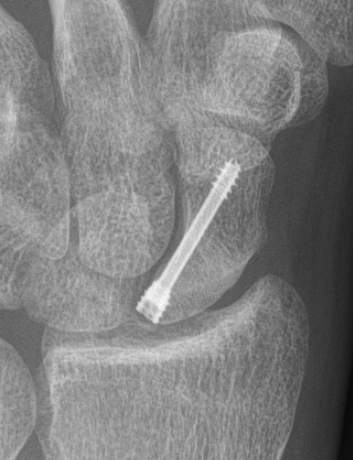
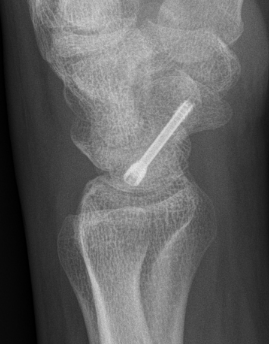
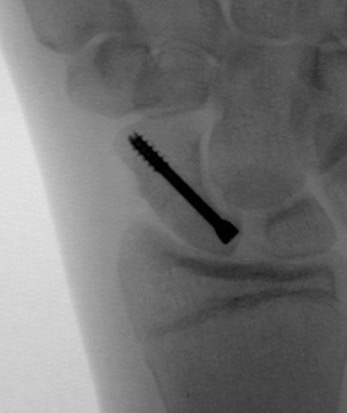
Percutaneous screw fixation
Indications
Minimally displaced fracture in acceptable position
Manual workers / athletes - limit time in cast
- meta-analysis of dorsal v volar percutaneous scaphoid fixation
- no difference in outcomes
Volar percutaneous screw technique
Vumedi volar percutaneous screw video
Dorsal percutaneous screw technique
Vumedi dorsal percutaneous screw video
Arthroscopic assist percutaneous technique
Vumedi arthroscopic assist scaphoid screw fixation
