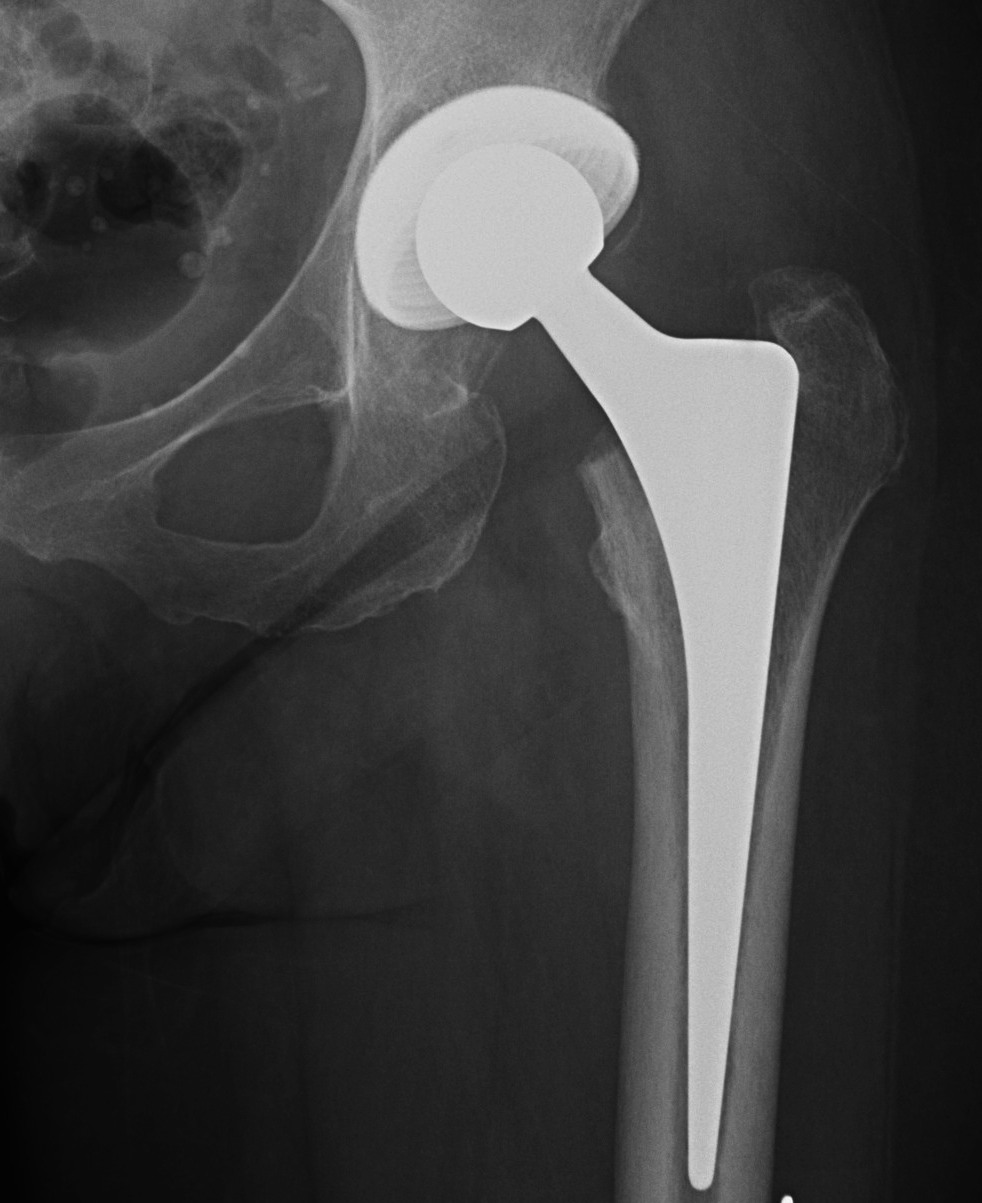
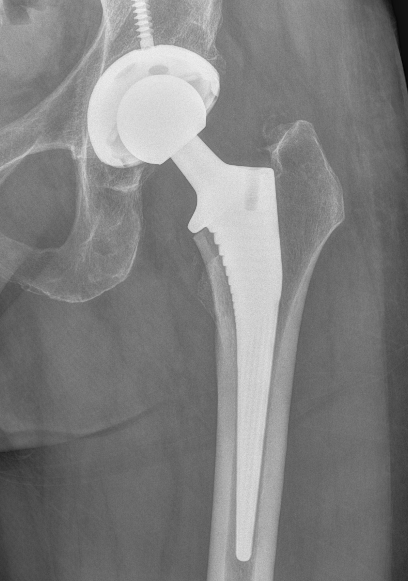
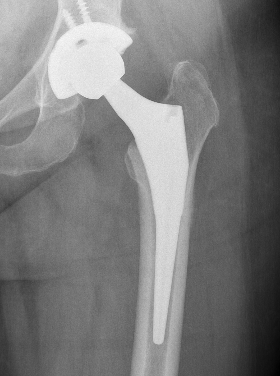
Concept
1. Initial press fit with mechanical stability
2. Osteoconductive surface to allow osteointegration
3. Contact viable host bone
Press fit
Goal
- tight peripheral press fit with complete seating
- < 0.5 mm gaps
- < 150 um of micromotion to limit fibrous ingrowth
Reaming
- 1-2mm undersize technique
- bone expands around prosthesis generating hoop stresses
Design
Material
- titanium
- low modulus of elasticity
- biocompatible
Porous coating
- titanium / hydroxyapatite coating
- pores allow bony ingrowth
- extensively coated prosthesis caused distal fixation and proximal stress shielding
- now typically proximal only to avoid proximal stress shielding
Shape
1. Proximal metaphyseal filling
- curved, anatomic stem to obtain tight proximal fit
2. Distal isthmus filling
- straight stem used more commonly in revision
Collars
- ? reduces early subsidence
Australian Joint Registry 2023
- 15 year revision rate
- collared 5.3%
- collarless 6.0%
Short stems
Australian Joint Registry 2023
- 9 year revision rate
- ministems: 2.7%
- conventional stems: 4.1%
Khunaja classification of uncemented femoral stems
| Type 1 | Single wedge |
Zimmer Taperloc Stryker Accolade |
| Type 2 | Double wedge | S&N Synergy |
| Type 3 | A Tapered round | Zimmer Mallory Head |
|
B Tapered splined /cone |
Zimmer Wagner | |
| C Tapered rectangular |
Depuy Corail Zimmer Alloclassic |
|
| Type 4 | Cylindrical fully coated | Depuy AML |
| Type 5 | Modular | Depuy S-Rom |
| Type 6 | Anatomic | Stryker ABG |
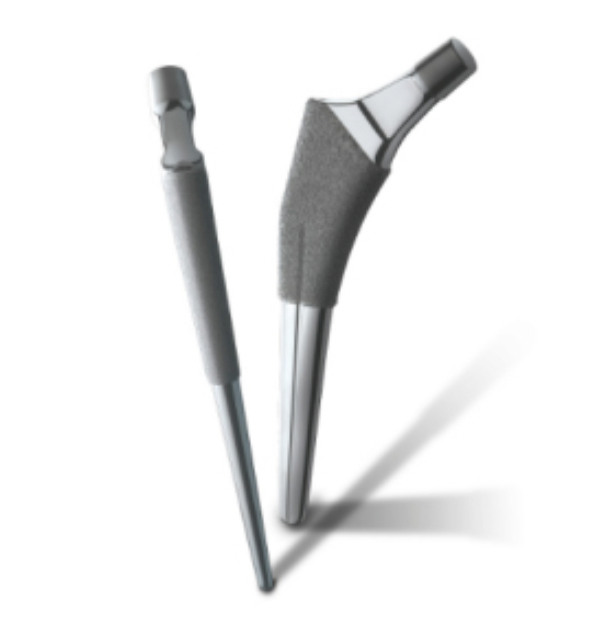
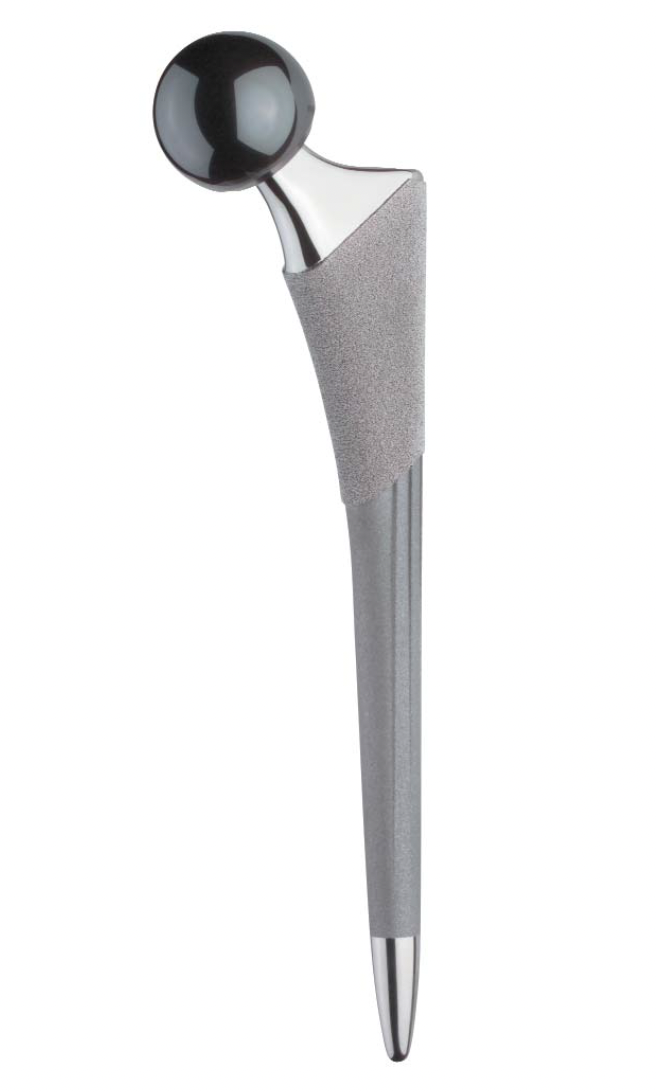


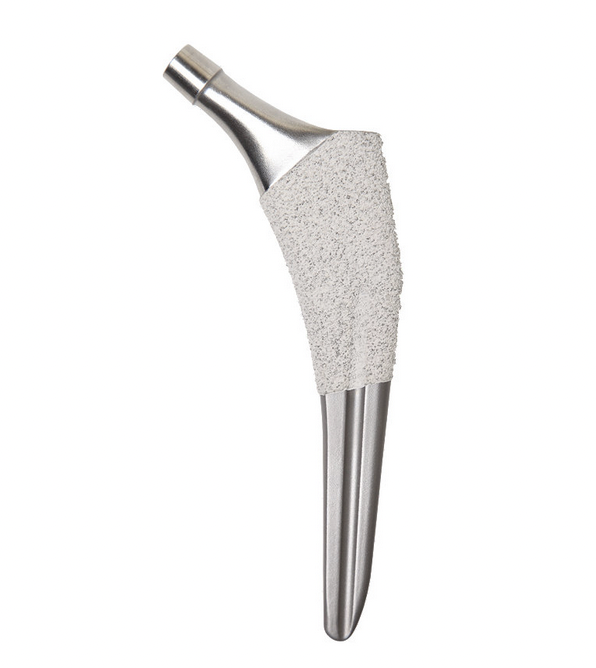
Zimmer Taperloc S&N Synergy Stryker Accolade
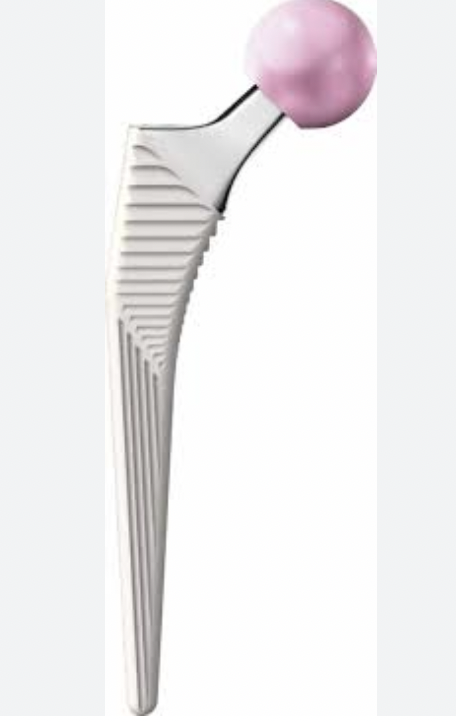
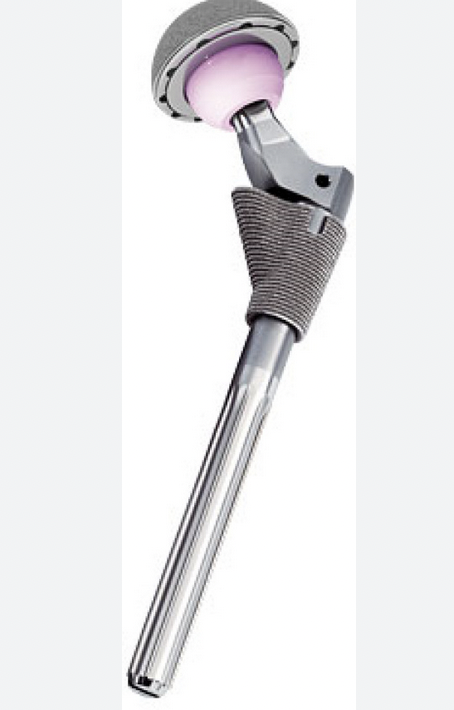


Corail tapered rectangular Depuy S-Rom Styker ABG
- review of 900,000 uncemented stems across joint registries
- most commonly used
- Type 3c: 61%
- Type 1: 21%
- Type 2: 8%
- no statistical difference in revision rates
Results
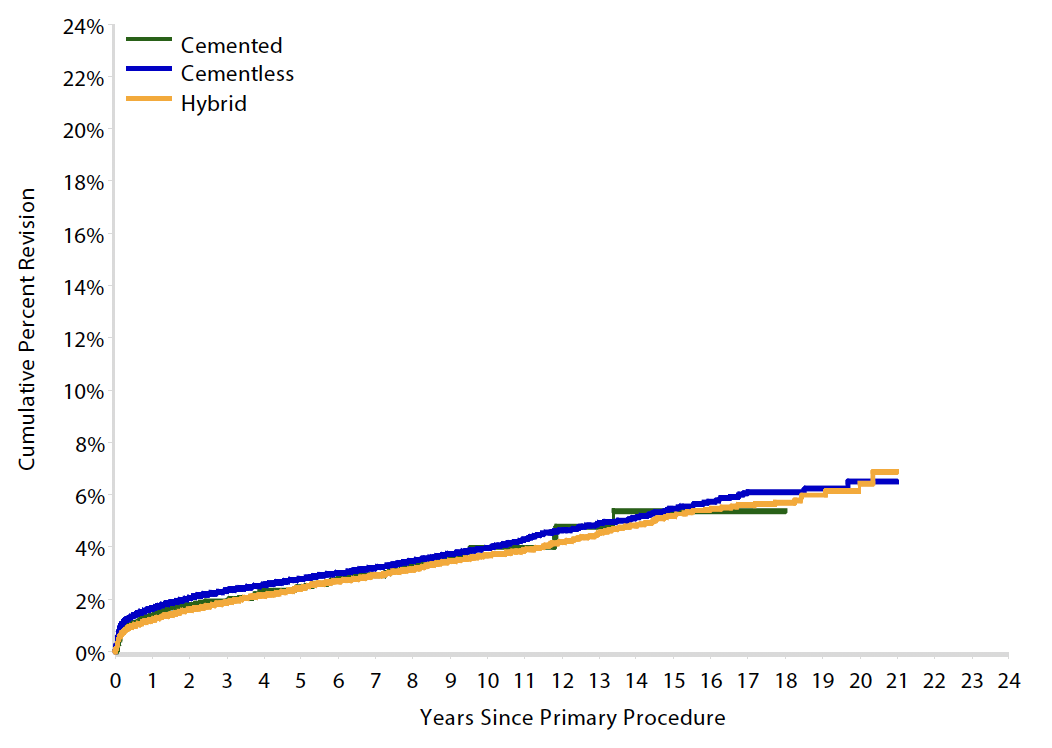
Australian Joint Registry 2023 Revision rates by fixation (400,000 THA)
| Cemented | Uncemented | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 year | 2.6 | 3.0 | 2.6 |
| 10 year | 3.8 | 4.3 | 3.9 |
| 15 year | 5.1 | 5.9 | 5.3 |
| 20 year | 7.0 | 6.7 |
15 year revision rate by age
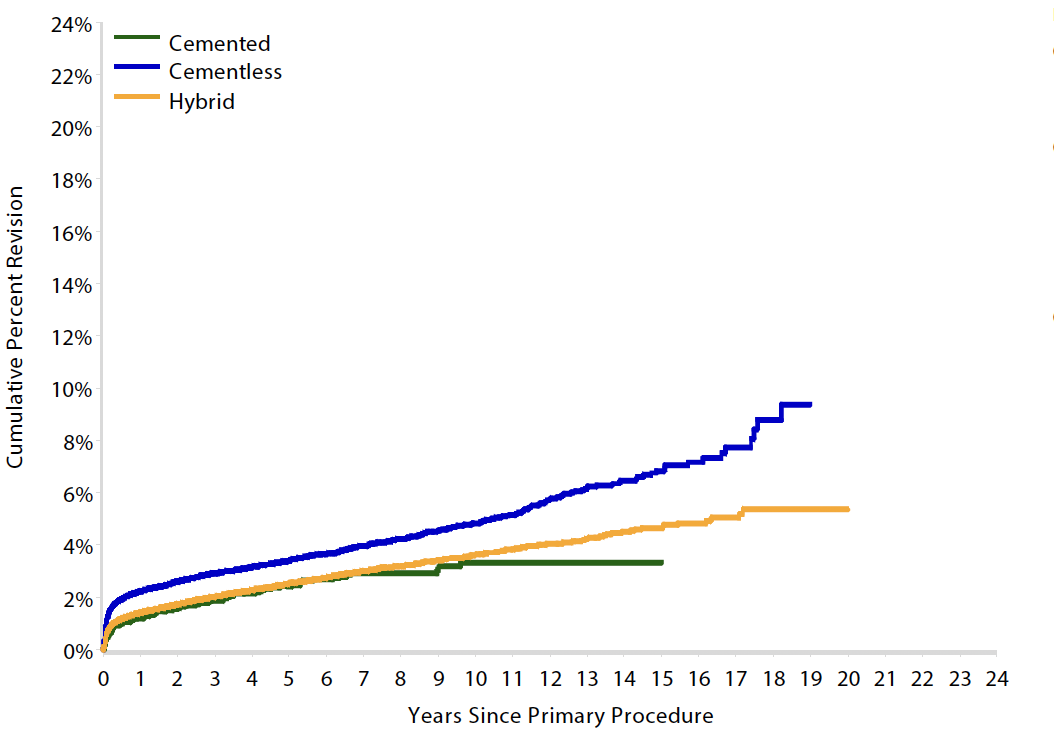
64 - 74 year > 75 years
| Cemented | Uncemented | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 55 | 6.4 | 7.2 | |
| 55 - 64 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 6.1 |
| 65 - 74 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 5.2 |
| > 75 | 3.3 | 6.8 | 4.7 |
Contraindications
Stove pipe femurs
Poor bone stock / osteoporosis
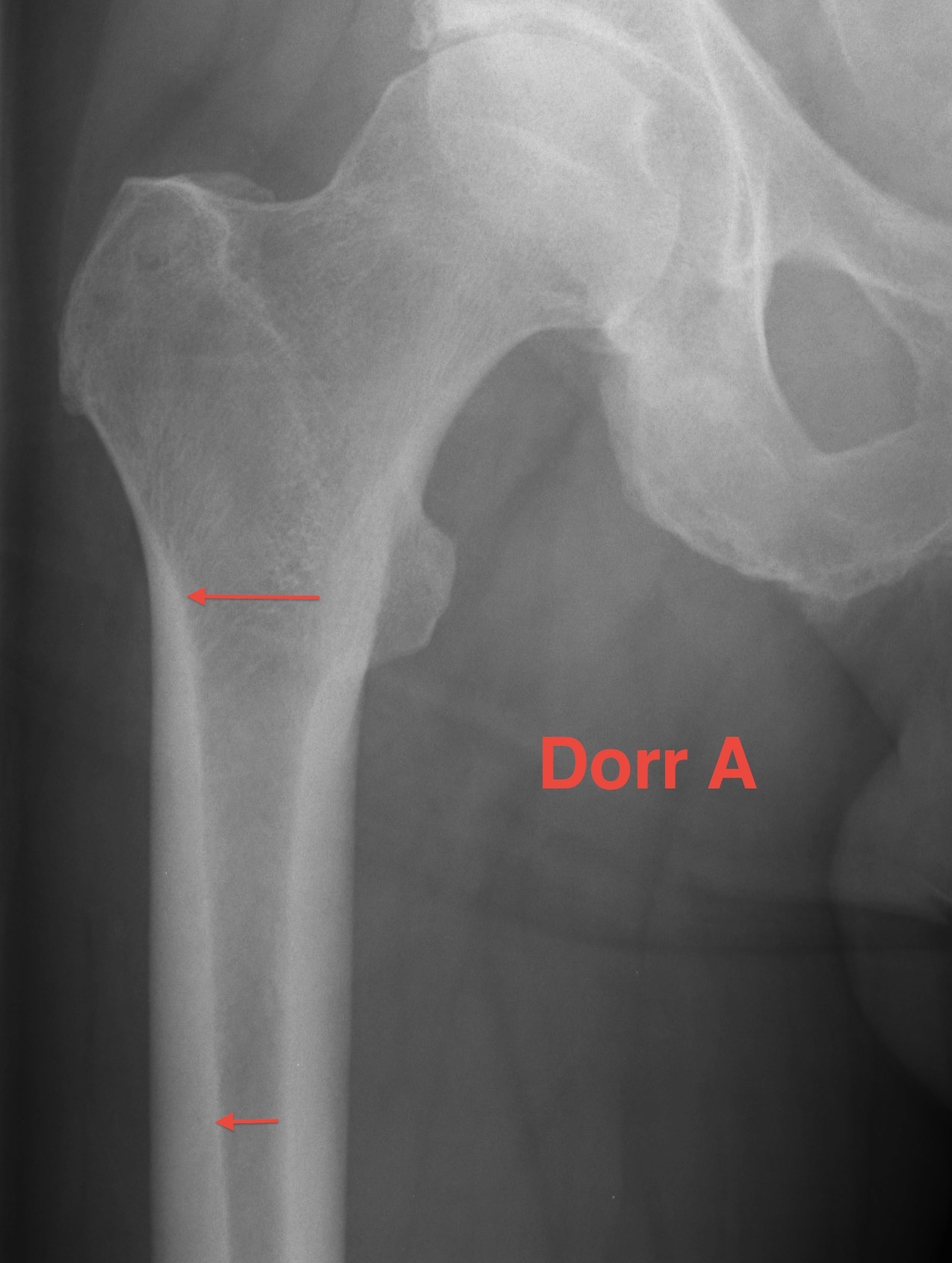
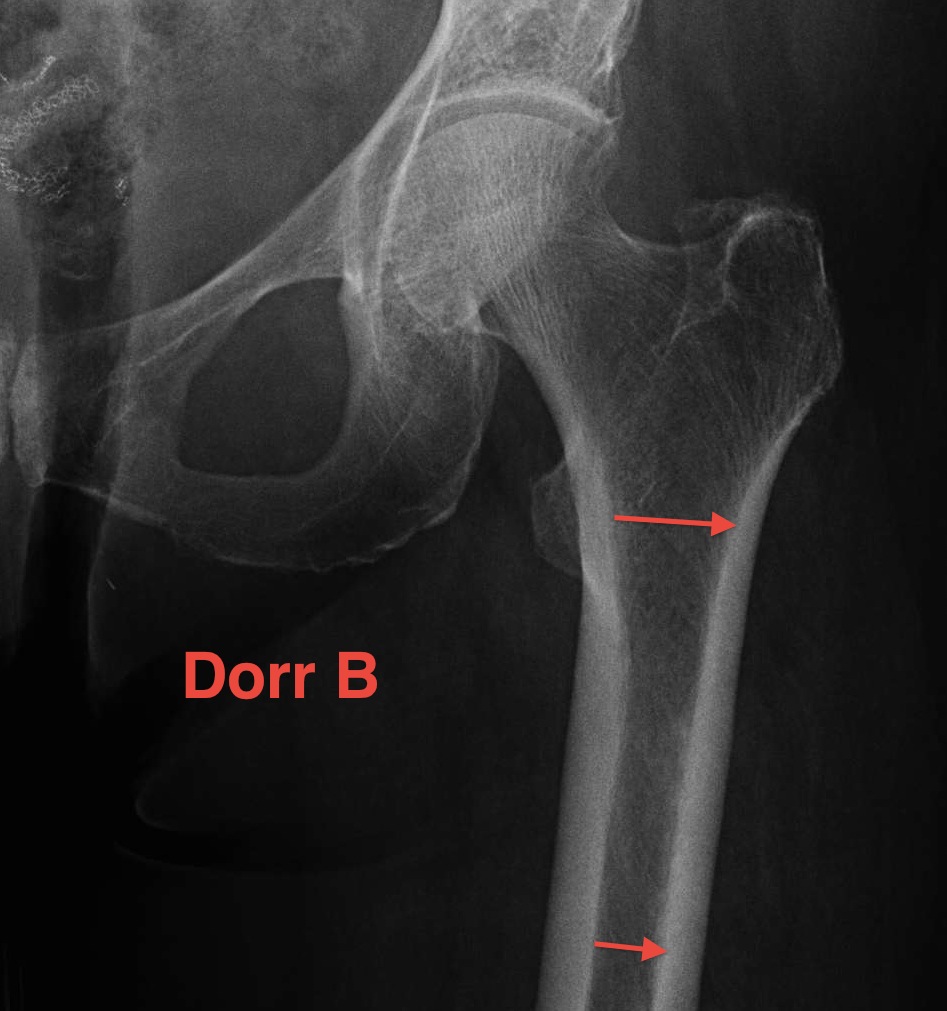
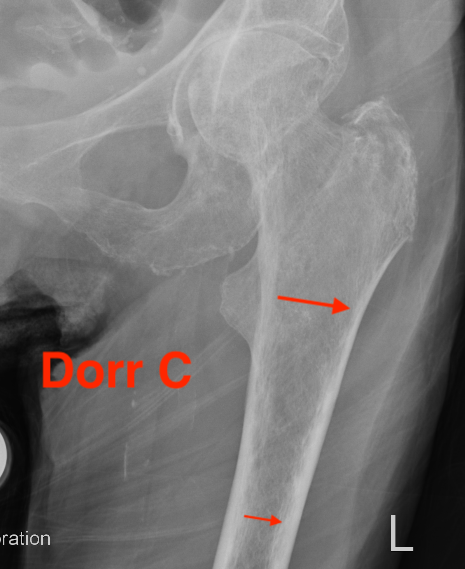
Dorr Classification of Proximal Femoral Geometry
Technique
- measure intra-medullary canal at lesser trochanter & 10cm below
- diameter 10 cm distal divided by inner diameter at midportion of lesser trochanter
- must be <75% for uncemented prosthesis
| Type A / Champagne Flute | Type B | Type C / Normal |
|---|---|---|
| Ratio < 0.5 | Ratio 0.5 - 0.75 | Ratio > 0.75 |
| Thick cortices | Wide canal diameter | |
| Young males | Elderly females | |
| Small diaphysis and thick cortex risks fracture | Cemented stem |
Signs of Osteointegration
1. Spot welds
- densification of endosteal bone
- usually in the region of termination of the porous coating on the implant
2. Absence of any radiodense reactive lines around porous coating
3. Calcar atrophy
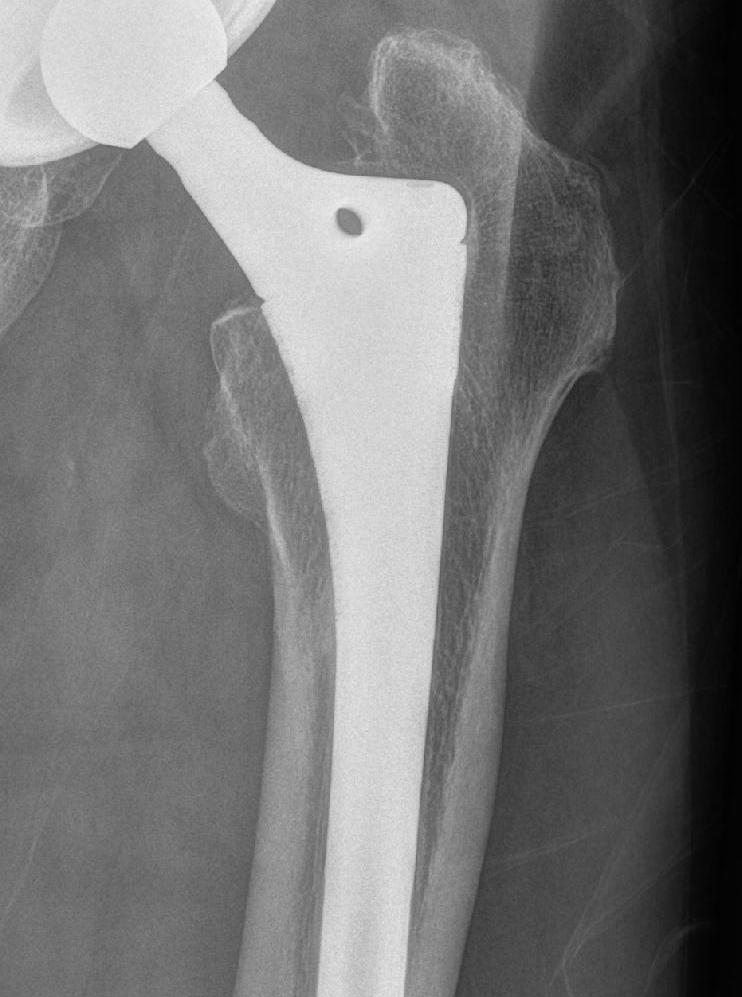
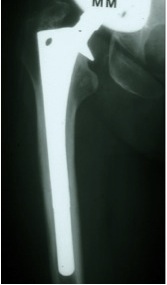
Spot weld Calcar atrophy
Failed bone ingrowth but successful stabilization by fibrous tissue ingrowth
- parallel sclerotic lines secondary to remodelling signs around the porous surface
- minimal atrophy of the medial femoral neck
- no progressive migration
- no local cortical hypertrophy / spot welding
Complications
Intra-operative fracture
Factors
- increasing age
- osteoporosis
- previous ORIF
- Type 2 (double wedge) and Type 6 (anatomic) prostheses
Prevention
- slow careful insertion
- make sure is advancing with each blow
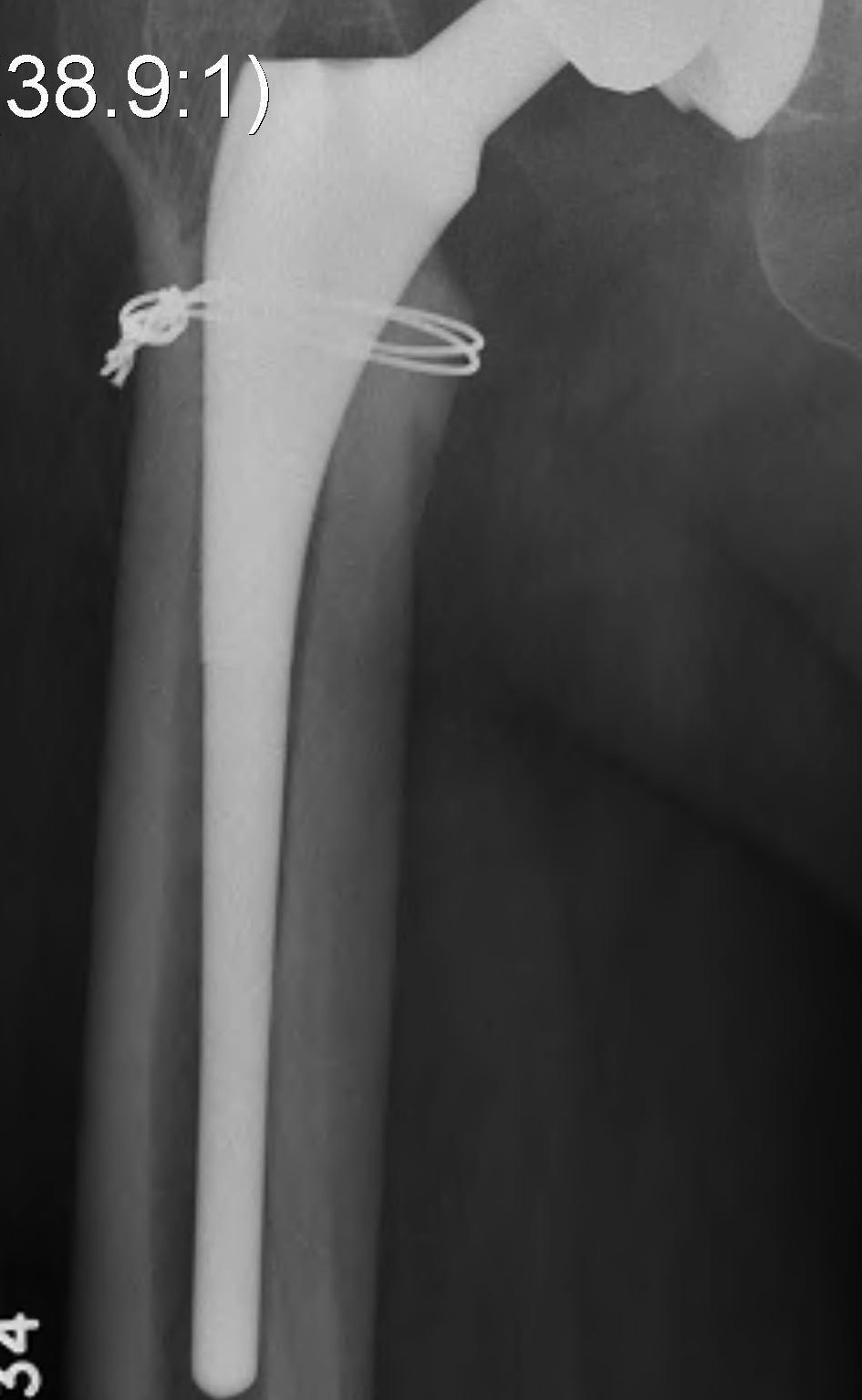
- +/- cerclage wire
Management
- cerclage wire / plate
- revision stems
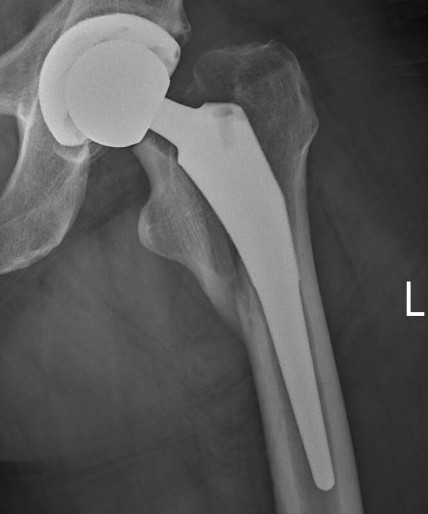
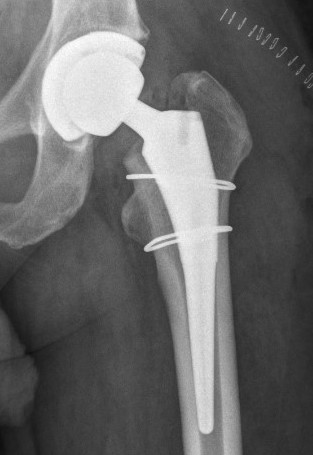
Thigh pain
Causes
- initial instability (lack of press fit)
- late instabiity (failed bony ingrowth)
- micromotion at distal stem with proximal coated stem
- osteoporotic bone
- mismatch between bone and prosthesis stiffness
- increased risk with short stem implants
Xray
- distal cortical hypertrophy
Bone scan / SPECT
- increased distal signal
Treatment
- cerclage wire + cortical strut grafts
- improve bony rigidity over distal stem
Stress shielding
Fully coated / diaphyseal fit prostheses
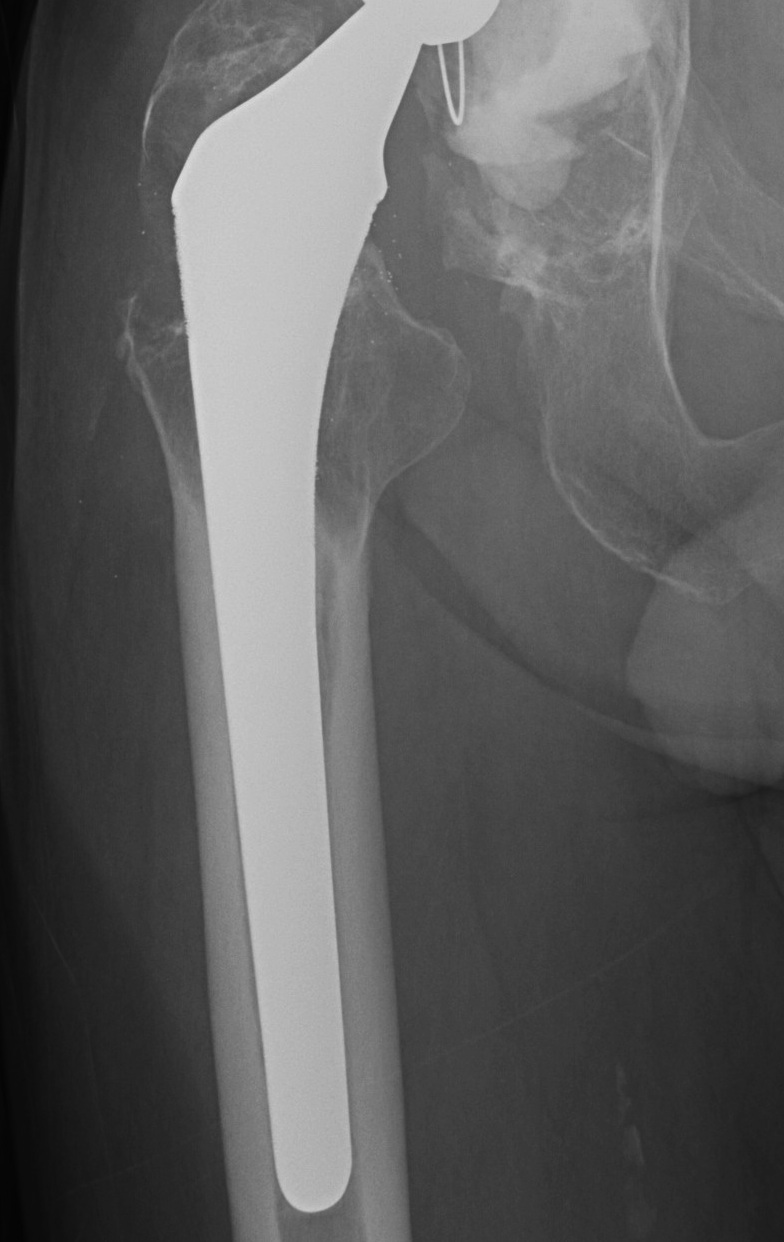
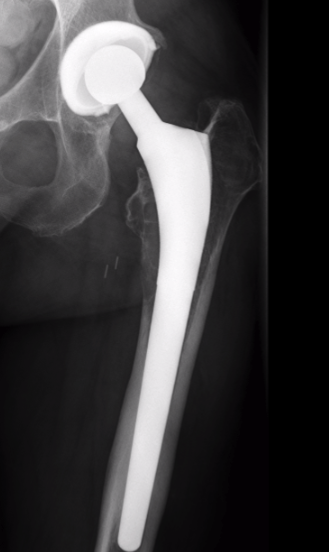
Stress shielding
Loosening
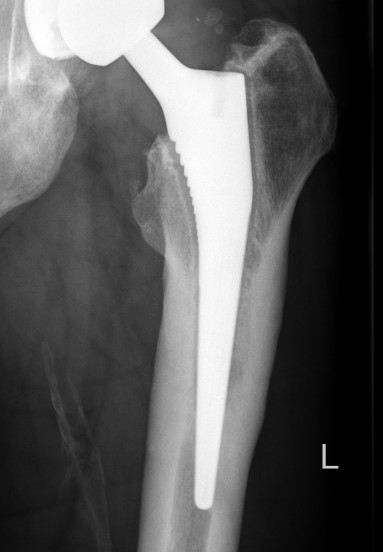
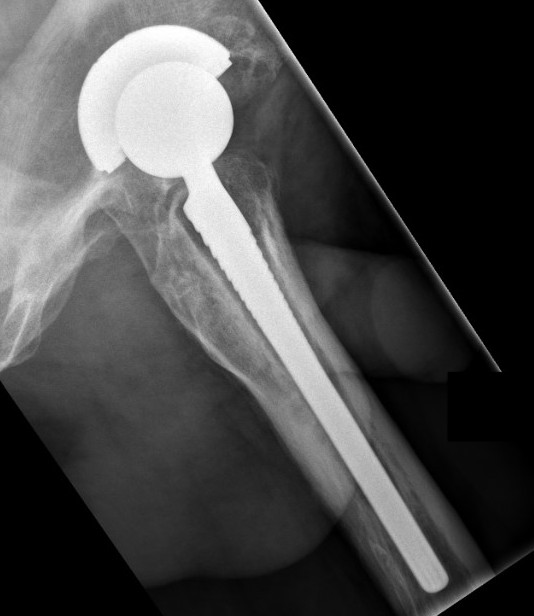
Lucent lines
Signs of frank implant instability
- component migration - subsidence and varus tilt
- progressive luceny on serial radiographs
- development of inferior pedestal
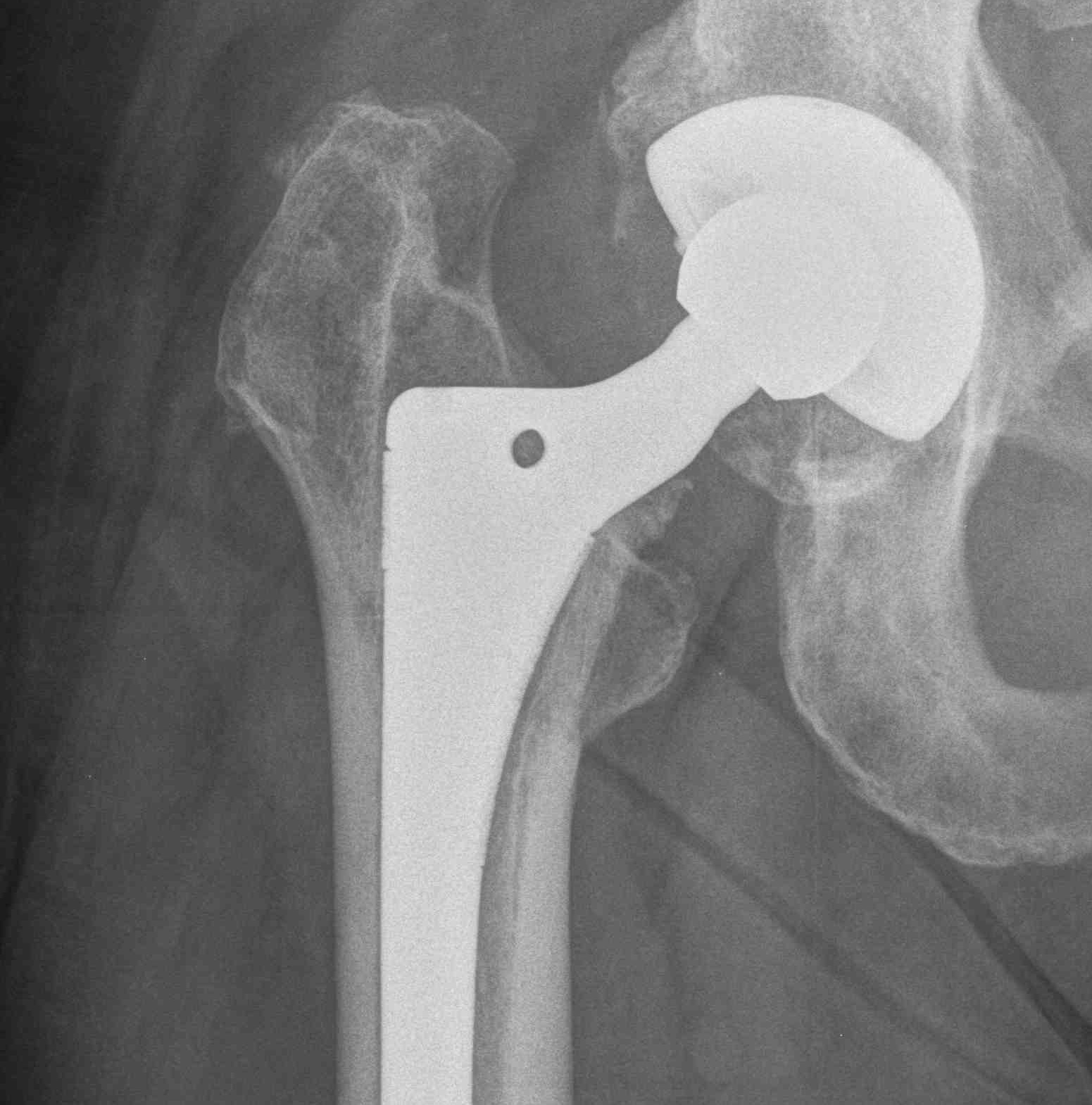
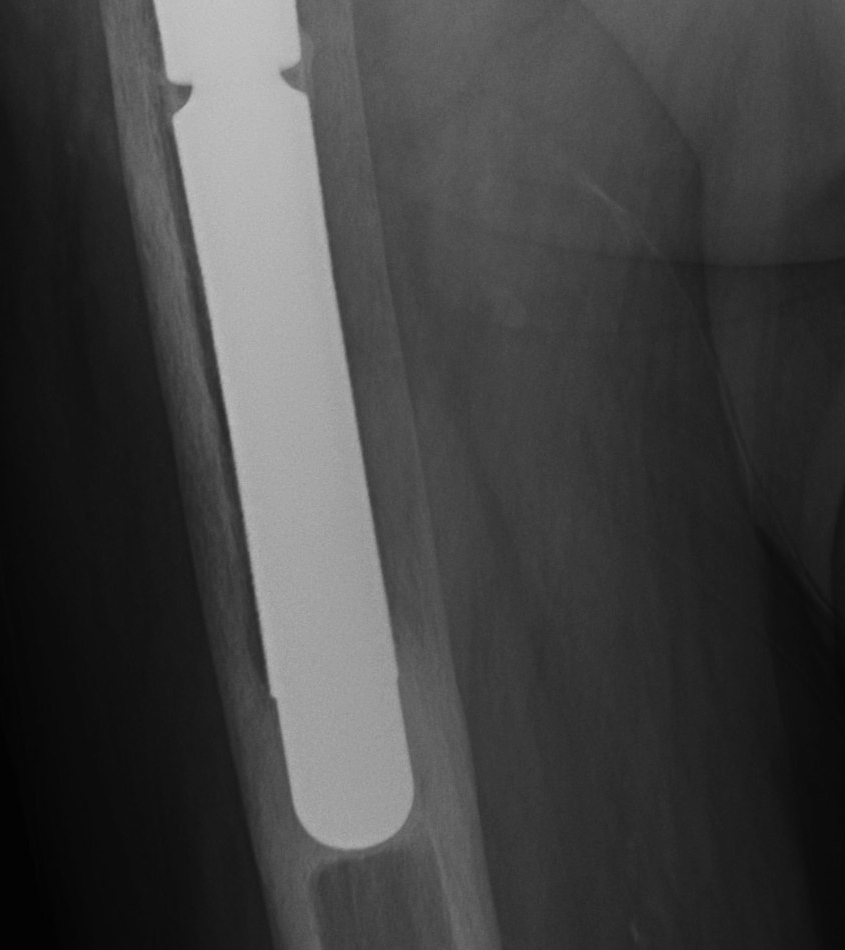
Stem migration Pedestal
