Definition
Avascular necrosis / osteonecrosis of the lunate
Epidemiology
Rare
Men 20 - 40
Anatomy
Half moon shape
- concave distally: articulates with the capitate
- convex proximally: articulates with the radius and the TFCC
Etiology
Predisposing conditions: SLE, sickle cell, Caison's
Vascular theory: repetitive micro trauma disrupting fragile vascularity of lunate
Mechanical theory: ulna minus variance causes increased radioulnar load on lunate
Clinical
Pain dorsal mid wrist
- stiffness
- lunate tenderness
- reduced grip strength
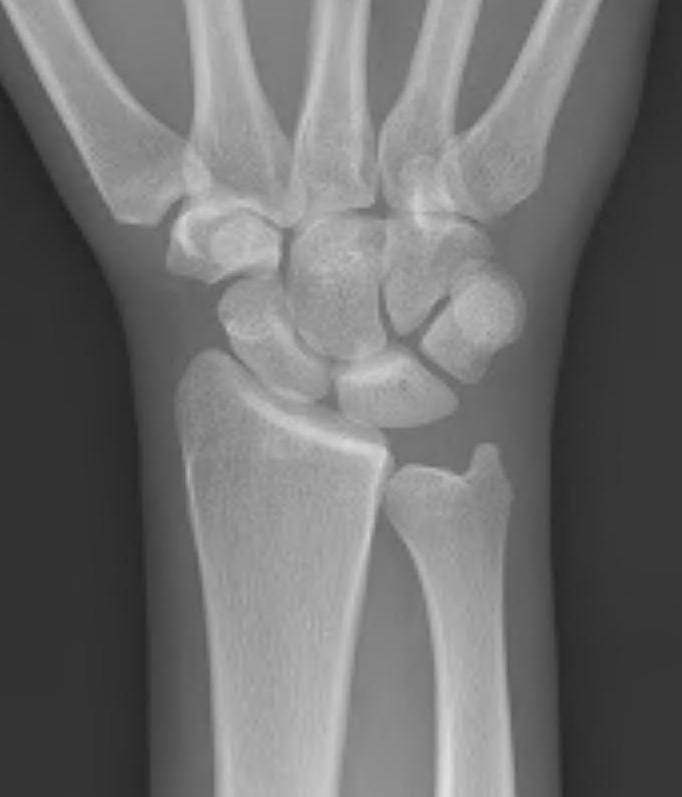
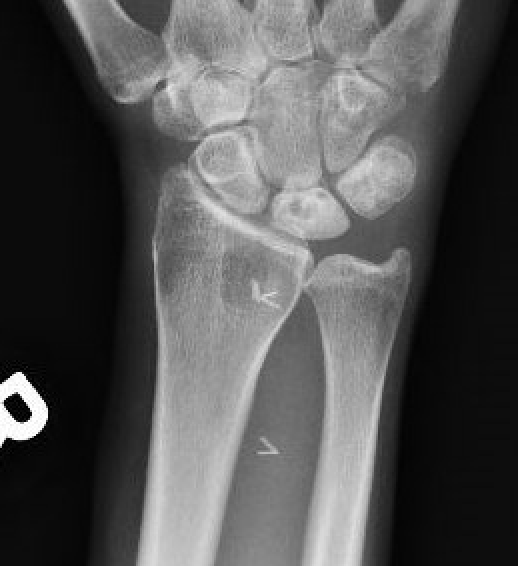
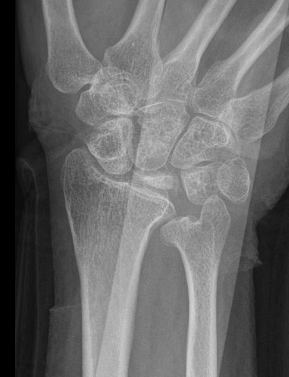
Xray
Progressive changes of AVN
- sclerosis
- fragmentation / fracture / flattenging
- midcarpal collapse: scaphoid flexion / capitate descent
- radiocarpal and midcarpal osteoarthritis
Lichtmann Classification
Stage I
- xray normal
- diagnosed on MRI
| Stage II | Stage IIIA |
|---|---|
| Sclerosis |
Collapse / fragmentation Normal carpal height |
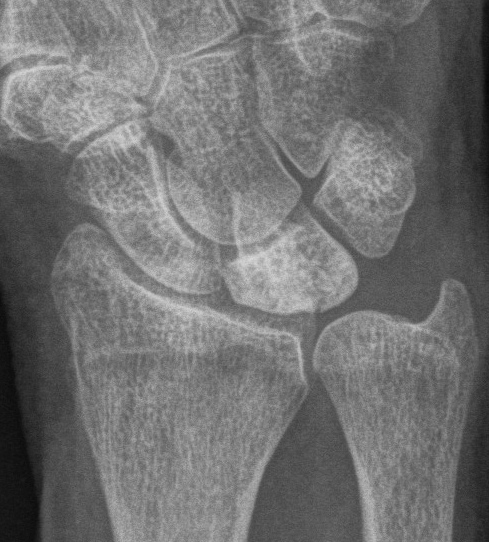 |
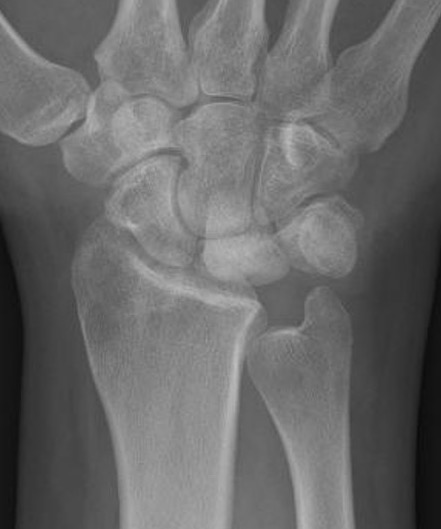 |
| Stage IIIB | Stage IV |
|---|---|
|
Collapse / fragmentation Scaphoid flexed / Capitate migrates proximally |
Pancarpal osteoarthritis |
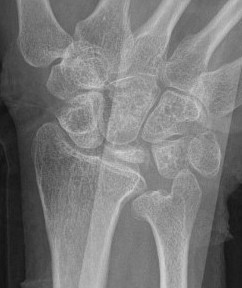 |
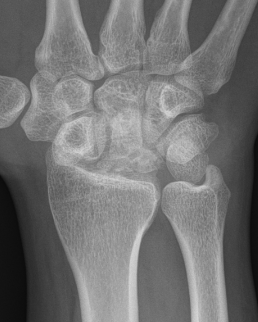 |
Ulna Variance
Supination and pronation alter variance
90 / 90 view (elbow 90° / shoulder abducted 90°)
- neutral supination / pronation
- PA film with wrist in neutral
- line from lunate fossa and ulna head
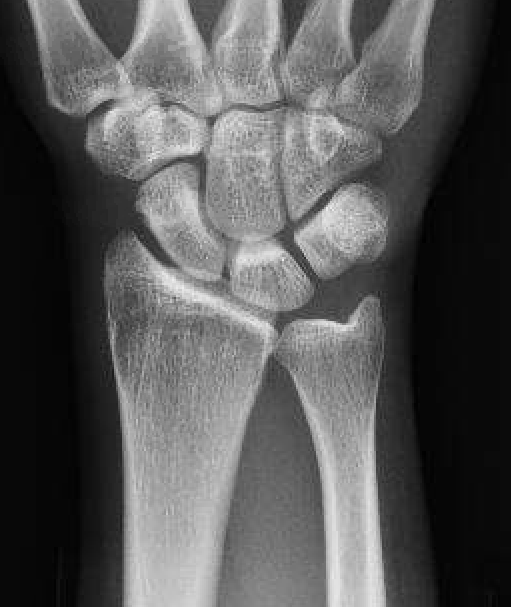
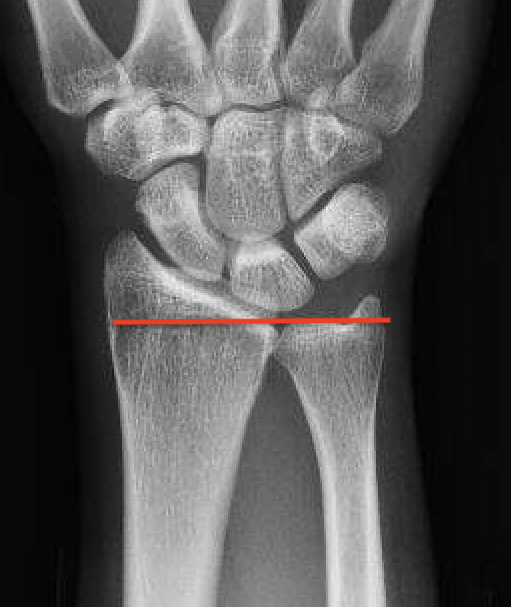
Ulna neutral
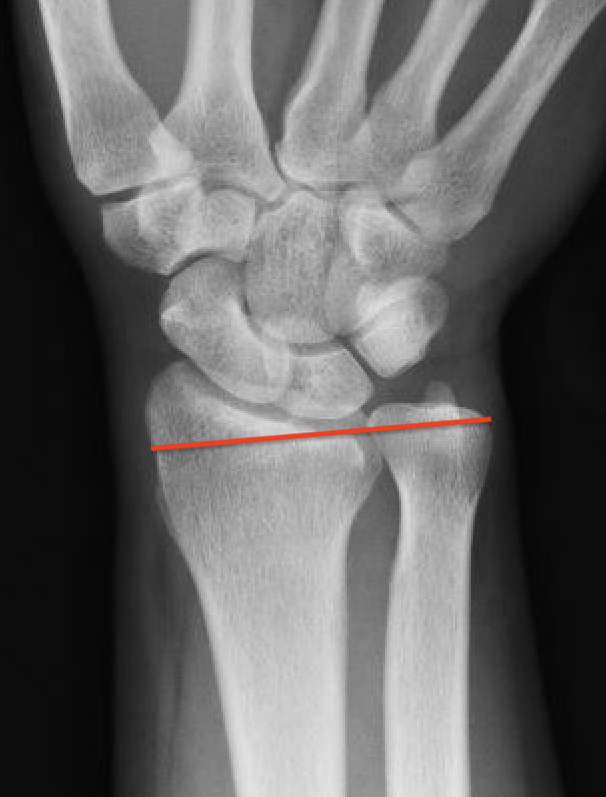
Ulna positive

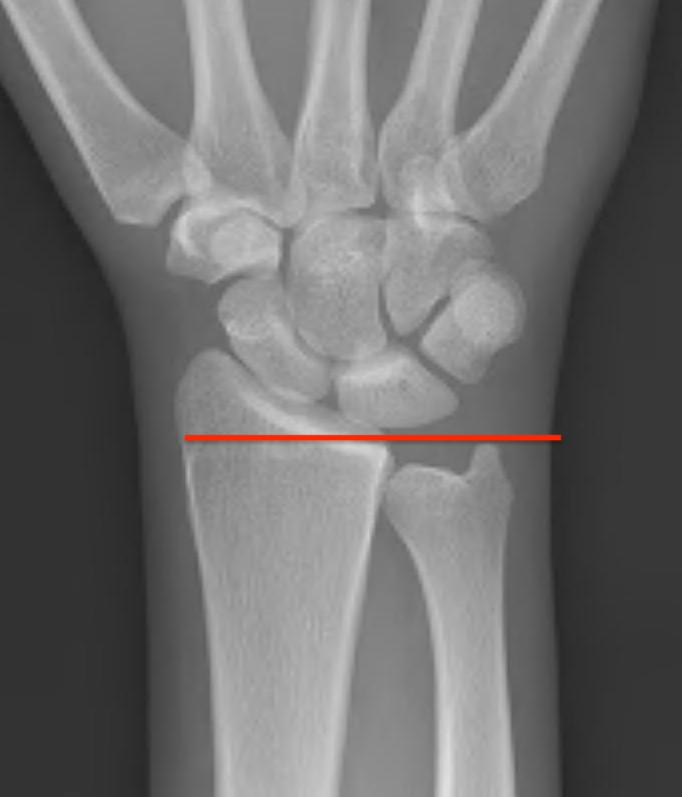
Ulna negative
MRI
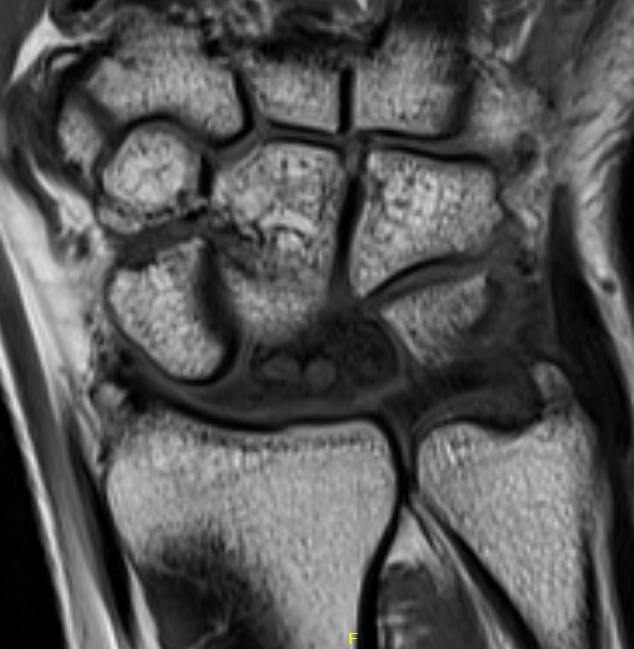
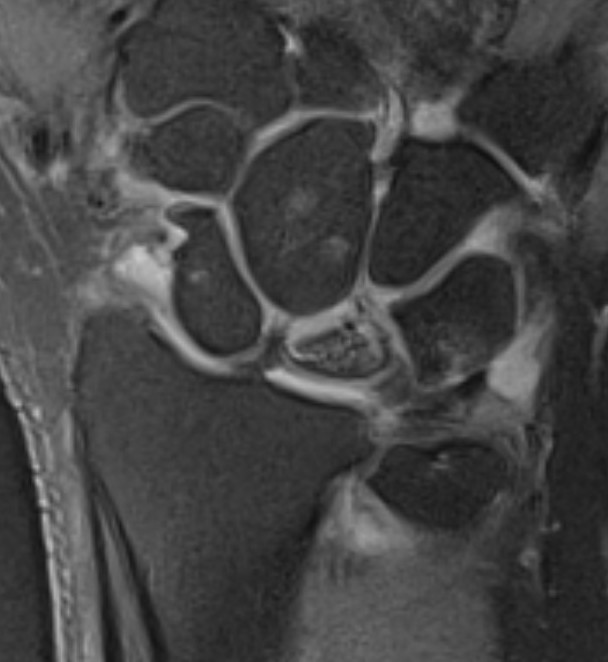
Avascular lunate on MRI
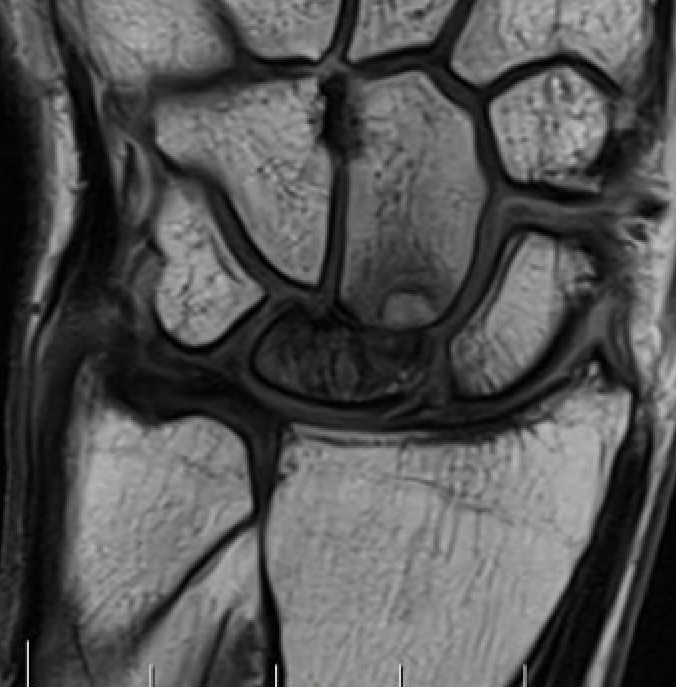
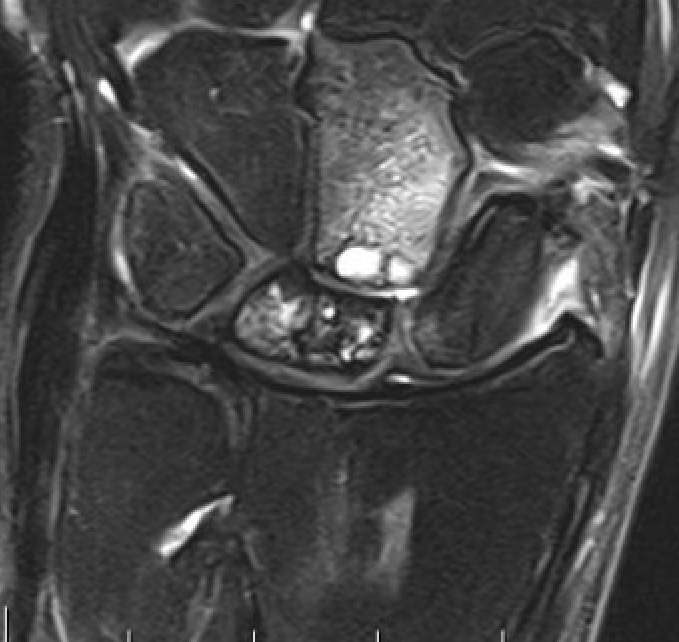
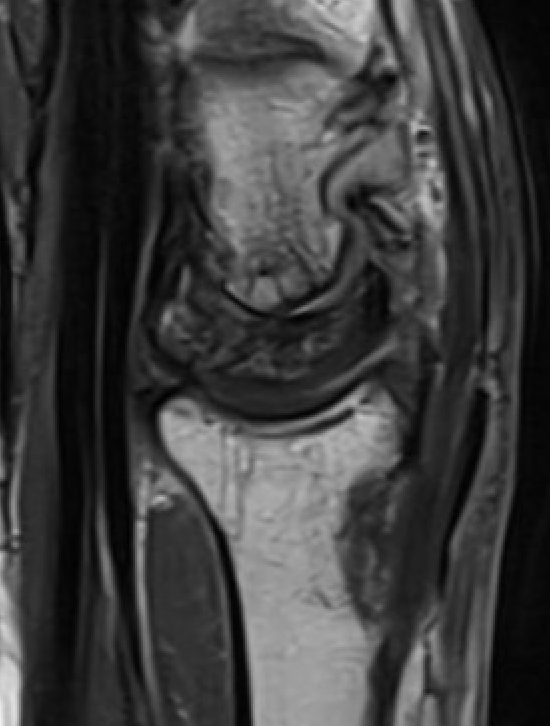
Avascular lunate with some cystic change on the capitate
CT
Hesse et al J Hand Surg Eur 2025
- CT more accurate at gauging Kienbock's
- disease frequently worse on CT than assessed on xray
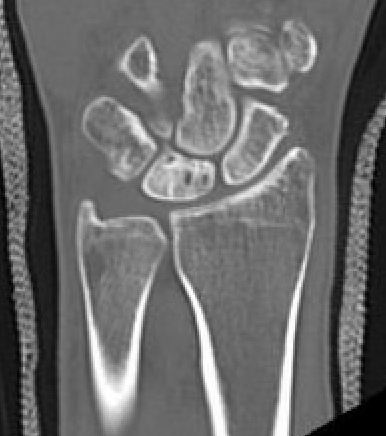
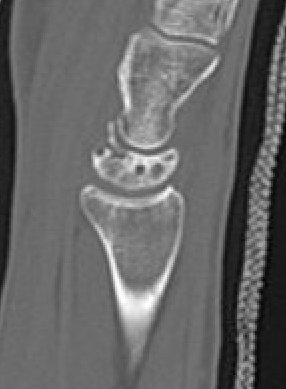
Lunate precollapse
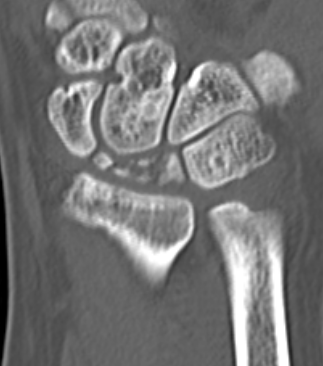
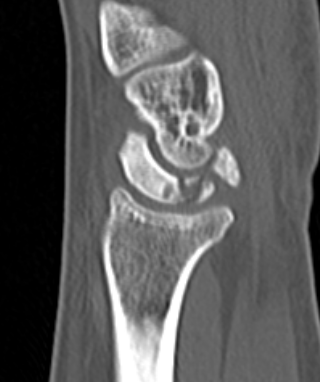
CT demonstrating lunate fragmentation and collapse
Natural history
Usually one of progressive collapse
Prognosis better in adolescents
Nonoperative management
Splint
Stage I
- trial of immobilization
- 3 months to aid revascularization
- most effective in adolescents
Operative management
Options
| Stage II / IIIA | Stage IIIB: midcarpal collapse | Stage IV: osteoarthritis |
|---|---|---|
|
Radial shortening - ulna negative
Capitate shortening - ulna neutral / positive
Vascularized bone graft
|
Limited fusions - STT fusion - scapho-capitate fusion
Proximal row carpectomy |
Wrist arthrodesis
Wrist arthroplasty |
Stage II / IIIA
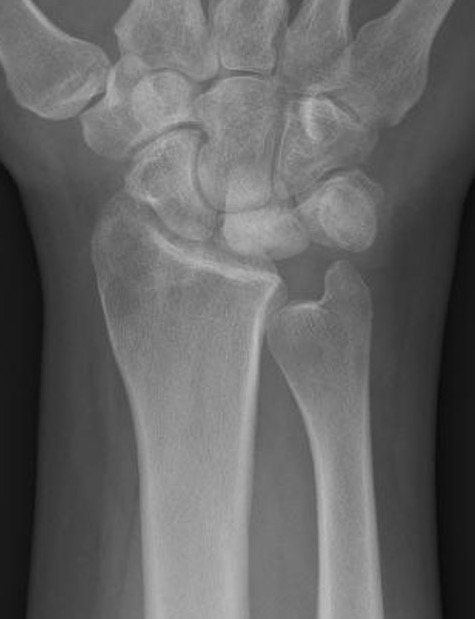
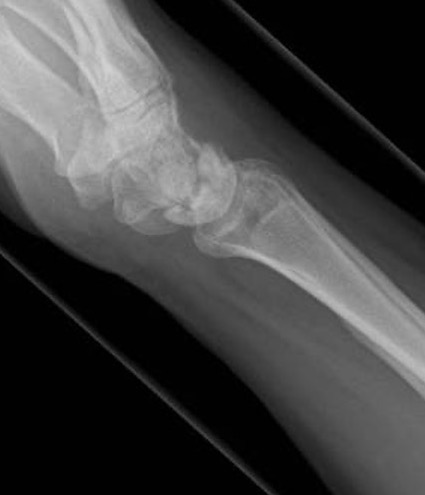
Radial Shortening +/- vascularized bone graft

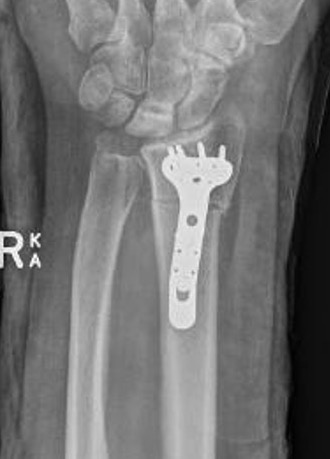
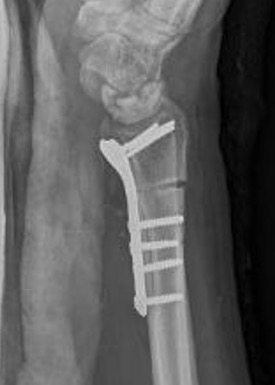
Indication
Stage II / IIIA
Negative ulna variance
Theory
Radius normally takes 80% of load
- with ulnar minus is increased to 96%
- 2mm radial shortening: 20% decrease radiolunate load
- 4mm radial shortening: 40% decrease in radiolunate load
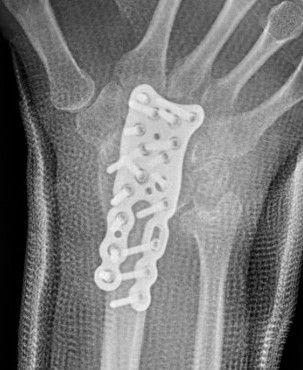
Technique
Trimed distal shortening osteotomy plate
Trimedi distal shortening osteotomy plate video
Vumedi radial shortening osteotomy video
Volar approach / bed of FCR
- osteotomy distal to DRUJ
- resection of desired amount
- aim for neutral or +1 mm ulnar variance
- usually 2 - 3 mm
- cutting guides available
- volar plate
Results
- systematic review of radial shortening and nonoperative treatment
- no difference in radiographic progression
- better pain relief and ROM in radial shortening group
Quenzer et al J Hand Surg 1997
- 68 patients with radial shortening osteotomy
- reduced pain in 93%
Capitate shortening +/- vascularized bone braft
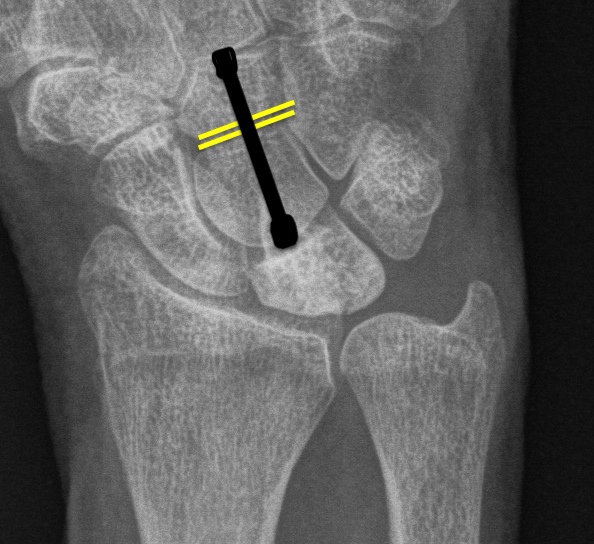
Indication
Stage II / IIIA
Neutral or positive ulna variance
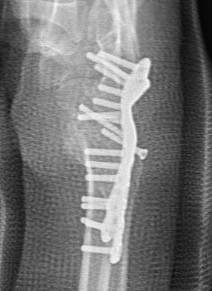
Technique
Bain J Wrist Surgery single cut capitate osteotomy PDF
Dorsal approach
- open capsule over wrist
- remove part of dorsal 3rd metacarpal to allow screw
- predrill screw into capitate distal to proximal with wrist flexed
- osteotomy distal to waist of capitate at level of STT joint
- remove 1 mm of bone
- insert compression screw
Result
Motaghi et al Hand Surg Rehab 2025
- systematic review of Stage IIIA Kienbocks without ulna minus
- capitate shortening in 125 patients
- persistent pain 10%
- revision surgery 6%
- 24 stage IIA treated with capitate shortening +/- vascularized bone graft
- isolated capitate shortening: failure rate 28%
- capitate shortening + vascularized bone graft: failure rate 8%
Vascularised bone graft (VBG)

Indications
Stage II
- precollapse / no fragmentation
- can be combined with radial or capitate shortening
Technique of 4th/5th extensor compartment artery VBG
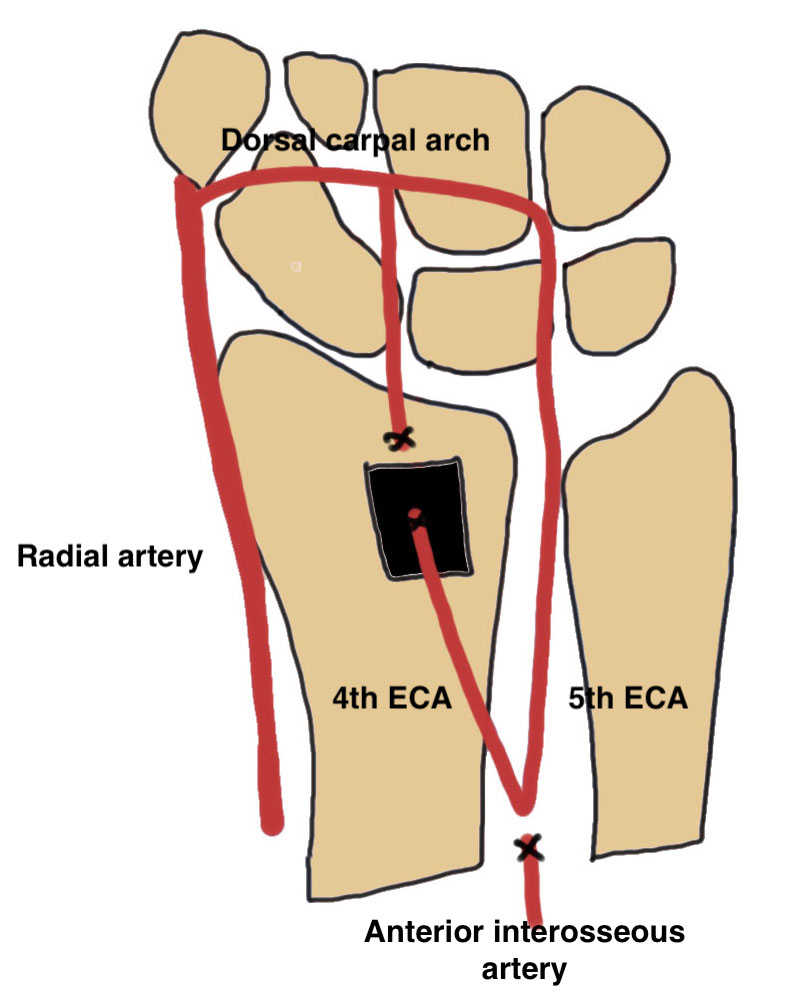
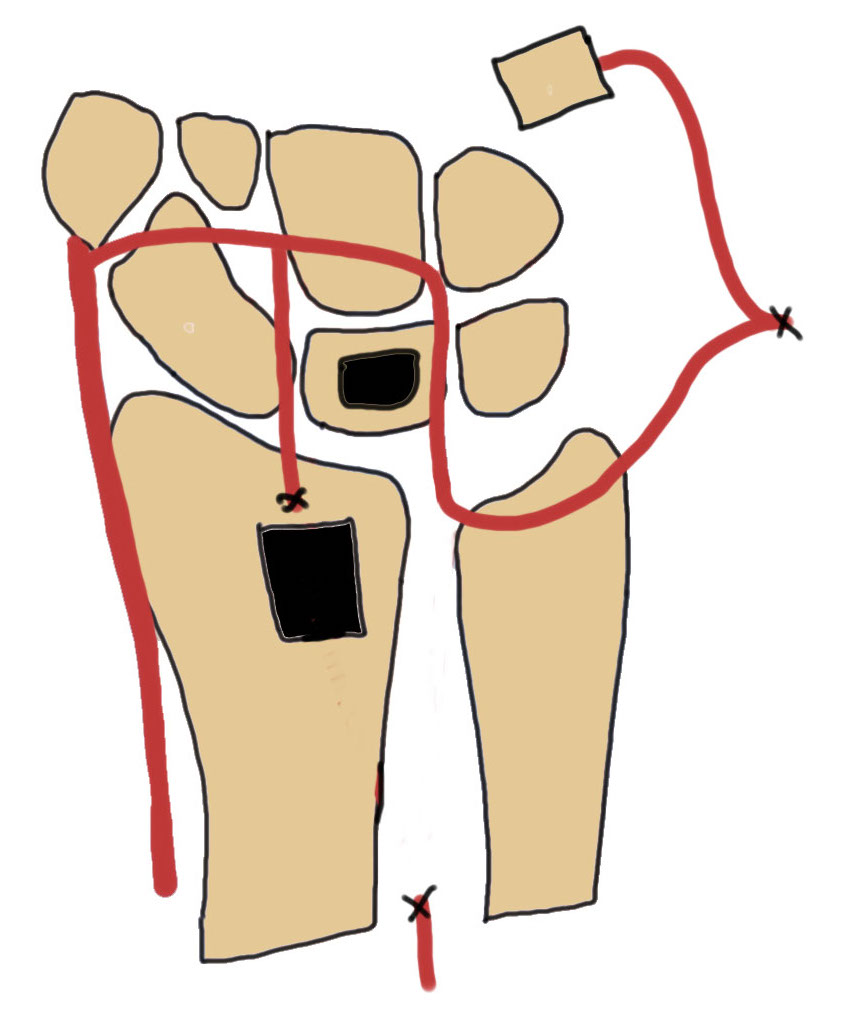

Dorsal approach
- based on Lister's tubercle
- divide extensor compartment and mobilize EDC
- identify 4th extensor compartment artery pedicle next to posterior interosseous nerve
- dissect origin from anterior interosseous artery proximally
- preserve 5th extensor compartment artery (bed of EDM) and ligate the anterior interosseous artery
- dorsal distal radius bone graft taken on pedicle
- reverse flow vascularized bone graft
Open wrist capsule over lunate
- open dorsal lunate and debrided necrotic tissue
- insert cancellous bone + VBG
Results
Park et al Clin Orthop Surg 2023
- systematic review of nonoperative treatment v VBG
- reduced progression and better long term outcomes in VBG
- 21 stage II Kienbock's treated with capitate shortening versus vascularized bone graft
- no difference in outcome
Stage IIIB
Limited fusions: Lunate excision + scaphocapitate fusion

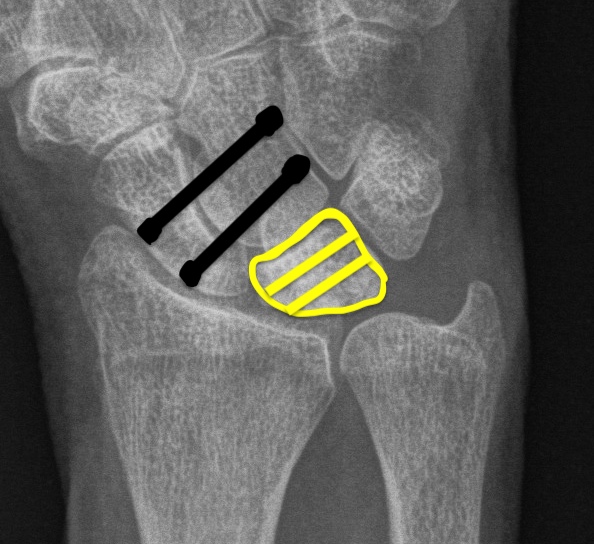
Indications
Stage IIIB
- lunate collapse with midcarpal collapse / scaphoid flexion
- limited capitate degeneration
Technique
Youtube lunate excision and scapho-capitate fusion video
Dorsal approach 3/4
- resect lunate
- resect scapho-capitate cartilage
- take scaphoid out of flexion / extend
- K wire into position
Results
Emanuels et al Plast Recon Surg 2025
- 78 scaphocapitate fusion v 64 proximal row carpectomy
- no difference in ROM or grip
- reduced pain in laborers with scaphocapitate fusion
- increased need for secondary procedures with scaphocapitate fusion
Proximal Row Carpectomy
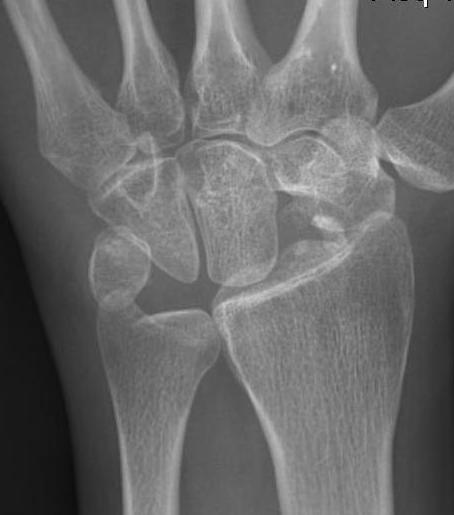
Indication
Stage IIIB
Minimal capitate degeneration
Technique
Vumedi proximal row carpectomy video 1
Vumedi proximal row carpectomy video 2
Stage IV

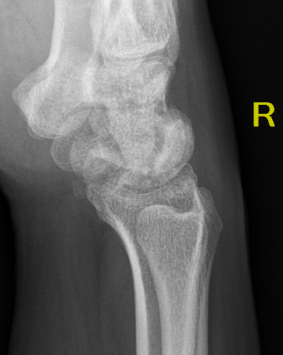
Arthrodesis
Indication
Stage IV
Stage IIIA / IIIB in manual worker