
Epidemiology
50% rheumatoid patients have elbow pathology
Pathology
Synovitis
- swelling and pain
- may develop FFD due to holding in flexed position
Annular ligament may rupture
- anterior displacement of radial head due to pull of biceps
Collateral ligaments may rupture
- medial-lateral instability
Ulna nerve neuropathy
- synovitis
- rheumatoid nodule
Cartilage and bone destruction
- severe cartilage damage
- instability
- bony destruction
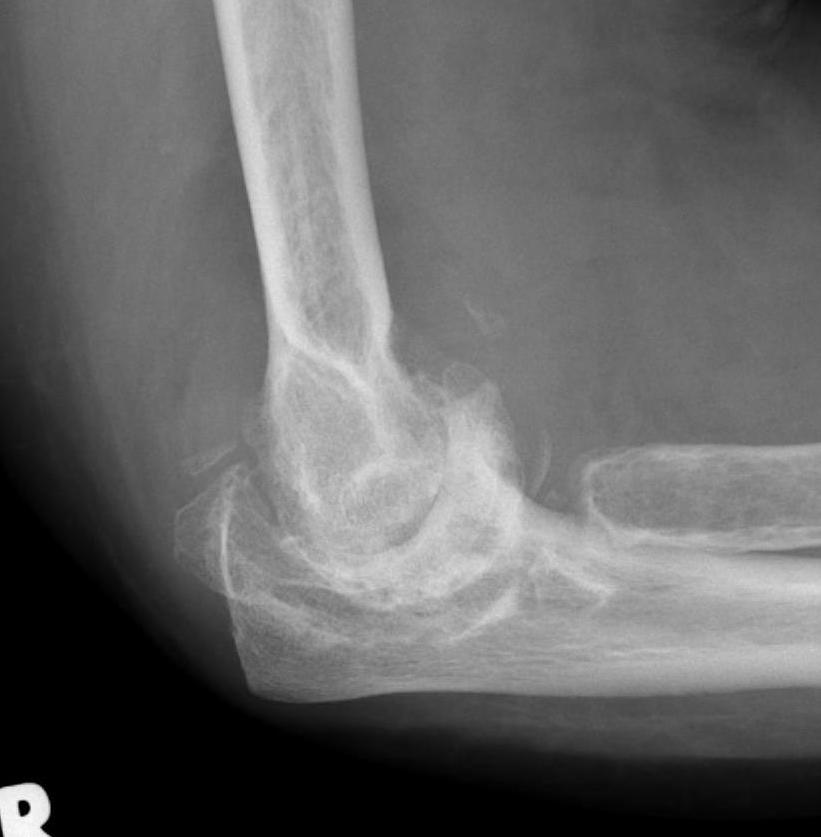
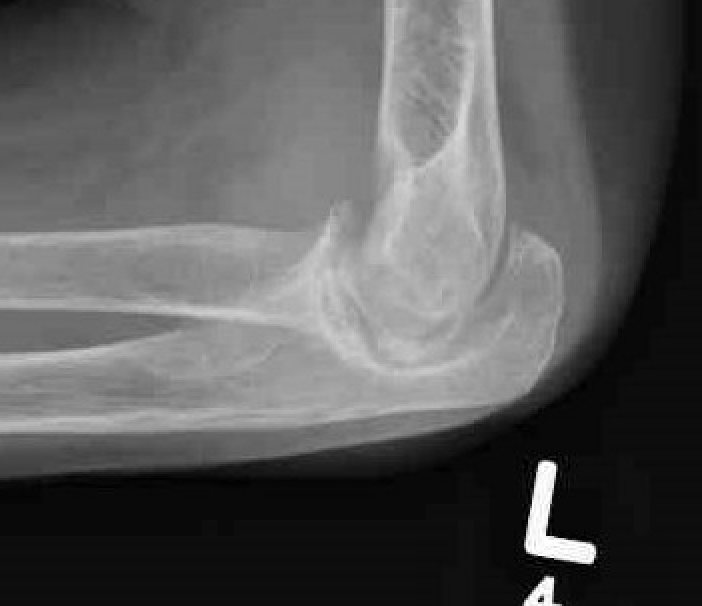
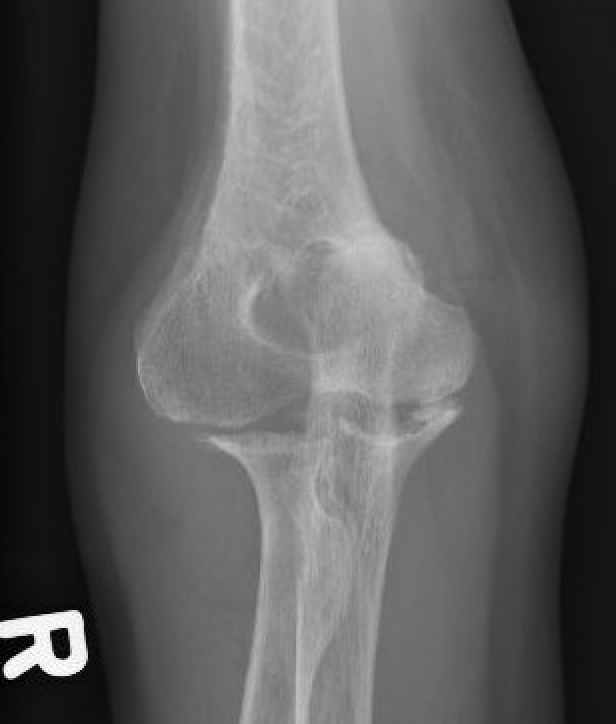
Xray
Articular destruction/ cysts / osteopenia /structural bone loss
Management
Non Operative
Medications
SMARD - symptom modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
DMARD - disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
1. Conventional synthetic: methotrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, and leflunomide
2. Biological synthetic:
a. (TNF) inhibitors - etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, certolizumab pegol, and golimumab
b. target other molecules: abatacept, rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, and anakinra
Cortisone injections
Operative
Options
Synovectomy
Interposition arthroplasty
Total elbow arthroplasty
Synovectomy
Indications
- minimal OA
- significant synovitis
- young patient
- failure medications
Options
1. Open
Extended Kocher
- limited access to posterior olecranon
- limited access to medial side
Universal Posterior approach
2. Arthroscopic
Results
- 171 open synovectomies
- 81% survival at one year
- 54% survival at 6 years
Maenpaa et al J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2003
- 103 open synovectomies via Kocher approach
- 5 year survival (reoperation / TEA) 77%
- no improvement in ROM but good pain relief
- best with early OA
- 26 elbows underwent arthroscopic synovectomy
- at 30 months, 73% had good or excellent results
Interposition Arthroplasty
- interposition arthroplasty in 35 RA elbows
- at 6 years 3 required TEA
Total Elbow Arthroplasty
Issues
Infection
Triceps - must preserve triceps insertion
Bone stock - deficient humeral columns
Intra-operative fracture - ulna at risk
Constraint
- unlinked require collateral and triceps integrity
- semiconstrained - linked pin and bushing with anterior humeral flange
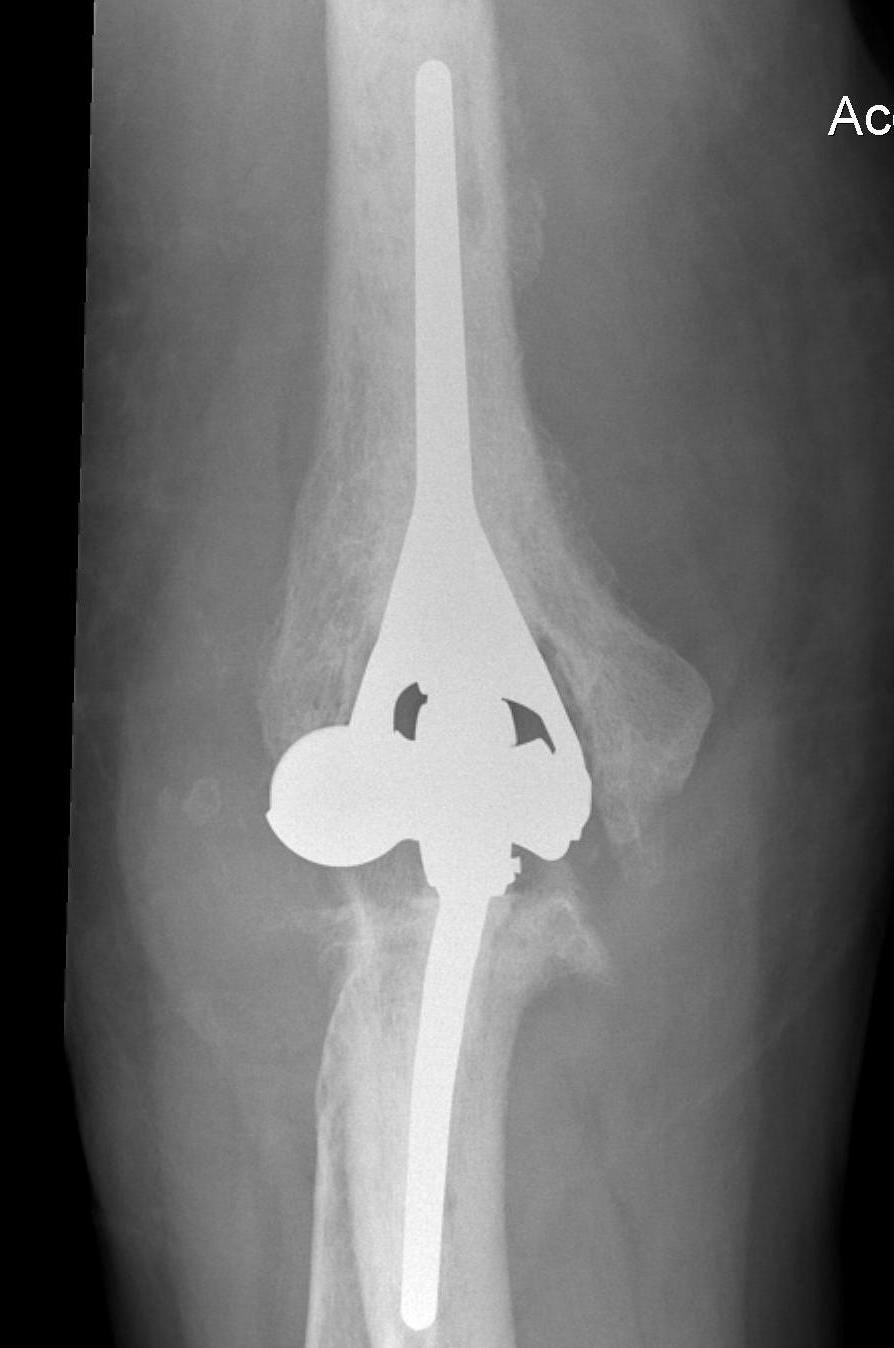
Results
- systematic review of 38 studies and 2118 patients with TEA for RA
- 7 year follow up
- implant failure 16%
- complication rate 25%
- young patients and unlinked design of TEA most at risk of aseptic loosening
Technique
