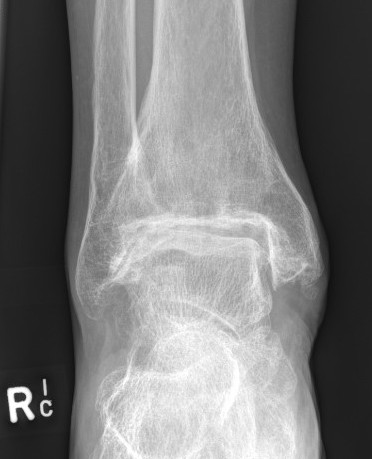
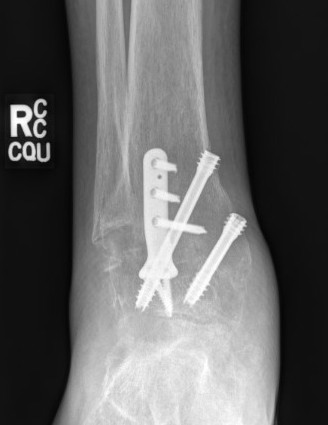
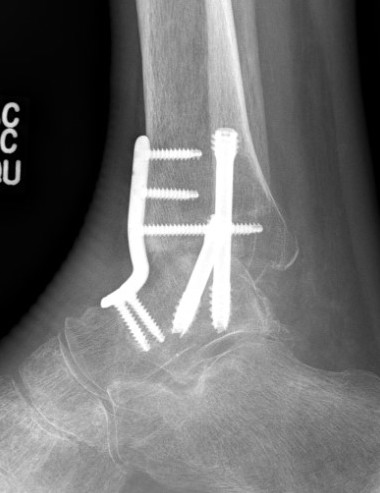
Disadvantages of Arthrodesis
Non union rates
ROM loss / decreased gait speed / poor mobility over uneven surfaces
Arthritic degeneration in subtalar joint
Types of Tibiotalar Arthrodesis
1. Intra-articular
A. Open - indicated with significant deformity / malalignment
B. Arthroscopic - indicated with minimal deformity
2. Extra-articular / External fixation
Sepsis
Ankle fusion position
1. Neutral Dorsiflexion - if fused in plantar flexion develop genu recurvatum to put foot on floor
2. Valgus 5° - excess varus causes cavovarus locking subtalar joint during gait
3. External rotation 5-10° - normal foot progression angle
4. Talus posterior on tibia - preserves heel and decreases lever arm = less energy required for toe-off
Surgical Techniques
Options
Open - anterior / transfibular
Arthroscopic
Issues
Open versus arthroscopic ankle arthrodesis
- systematic review of 18 studies and 1100 patients
- arthroscopic associated with increased union rates / faster union / lower pain scores
- arthroscopic with fewer complication / blood loss / hospital stay
Number of screws in crossed screw fixation
Izzo et al Foot Ankle Spec 2023
- systematic review of 15 studies and 670 patients
- 2 vs 3 screws
- non-significant difference in non-union and complication rates
Anterior plate augmentation
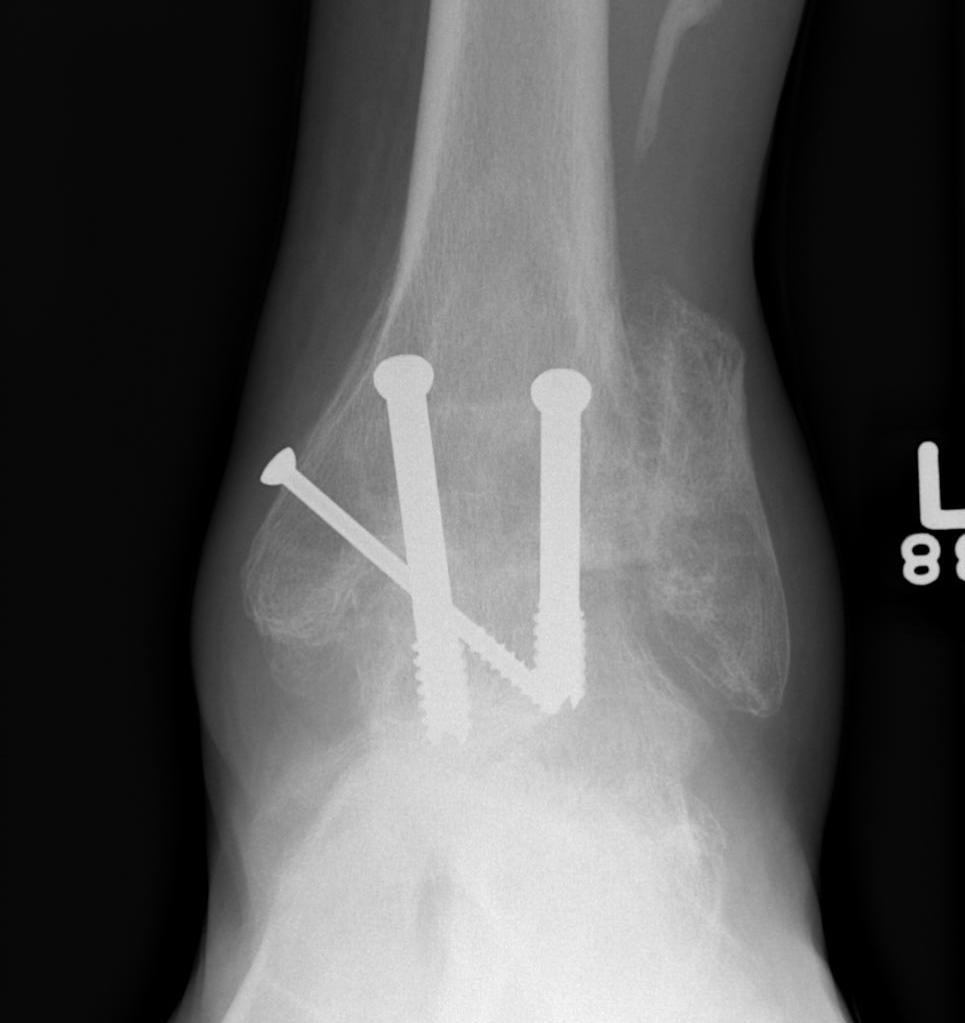
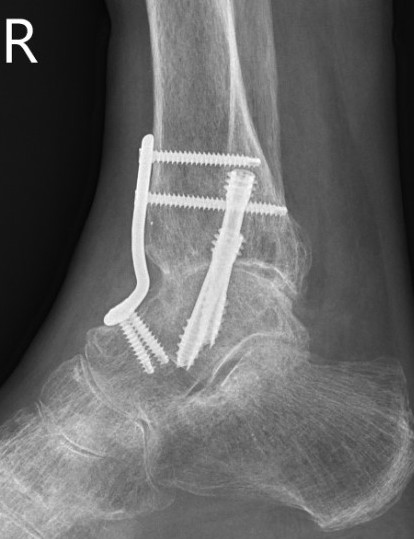
Mitchell et al Foot Ankle Int 2017
- comparison of 26 compression screws versus 39 with anterior plate + crossed screws
- nonunion screws v plate augmentation: 15% v 8%
- revision rate screws v plate augmentation: 8% v 3%
Bone grafting
Heifner et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review of role of bone grafting in open ankle fusion fixed with screws
- no bone graft v fibular onlay graft v bone grafting
- 95% union rate for all three groups
Open Intra-articular Technique
Indication
Malalignment > 15 degrees
Approaches
Transfibular
Anterior
Transfibular

Technique
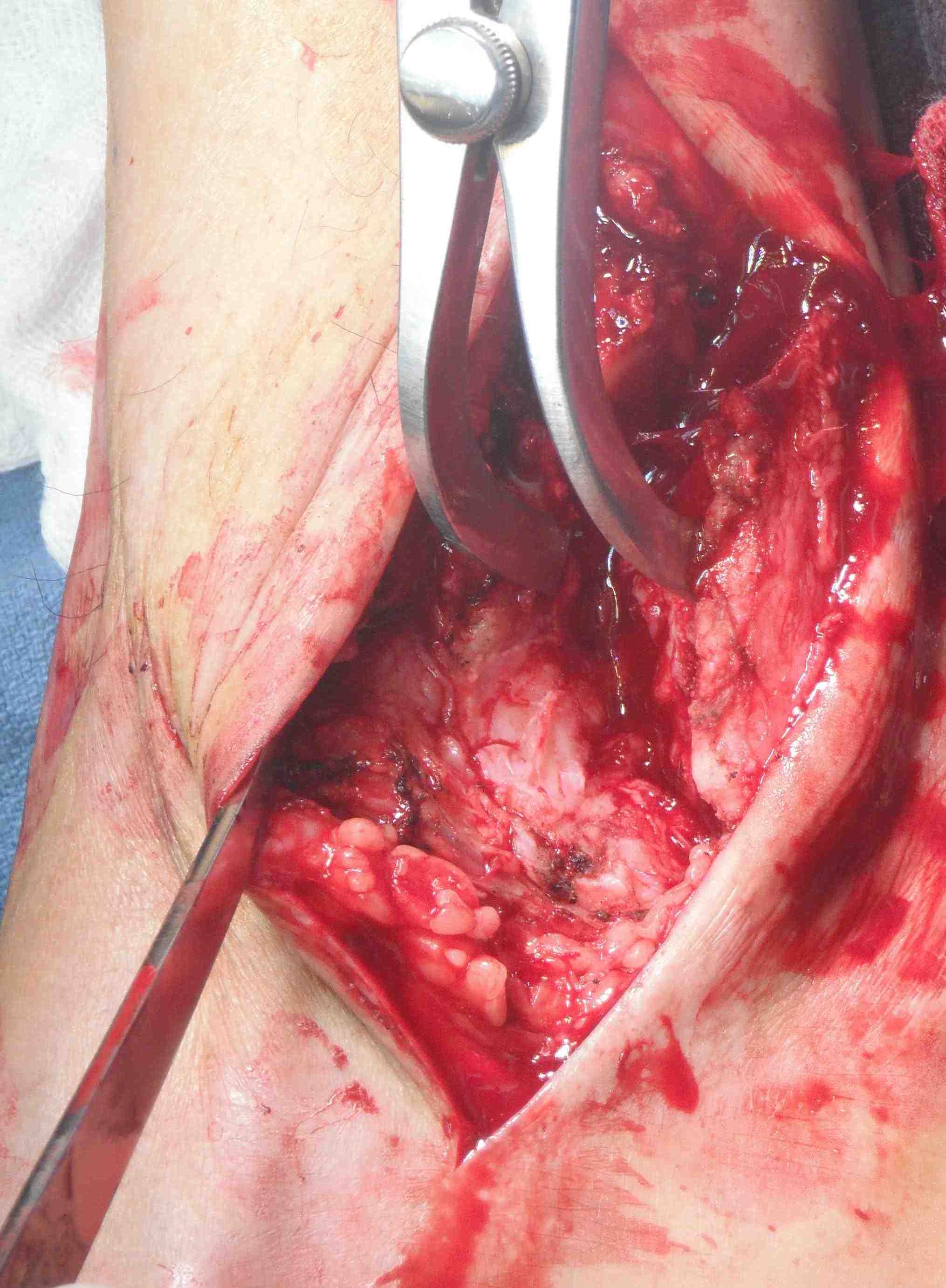
Incision over distal fibula, curved forward over subtalar joint
- subperiosteally expose distal fibula
- protect peroneal tendons posteriorly
- oblique osteotomy 6 cm above joint
- can externally rotate fibula +/- remove medial half +/- resect distal fibula
- insert lamina spreader / distractor into joint
- use oscillating saw / burr to prepare joint surfaces
- protect medial malleolus
+/- Anteromedial incision to prepare medial gutter
- medial to tibialis anterior, protect saphenous nerve and vein
- protect deltoid ligament (provides blood supply to talus)
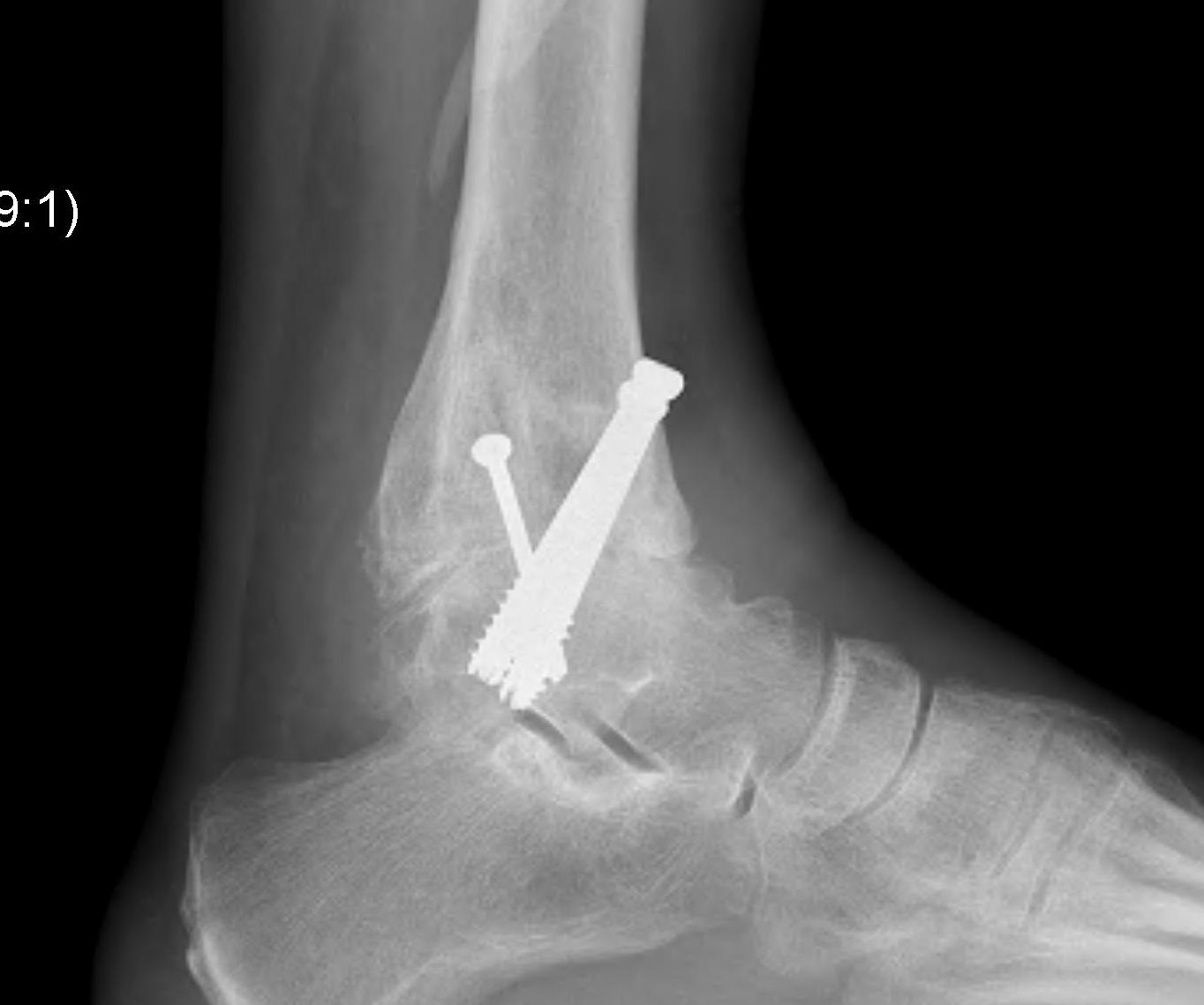
Fixation
- position foot, check with image intensifier
- +/- bone graft
- two cannulated screws from medial tibia to talus dome / neck
- +/- screw medial malleolus to talus
- +/- screw fixation fibular / onlay graft
Anterior approach


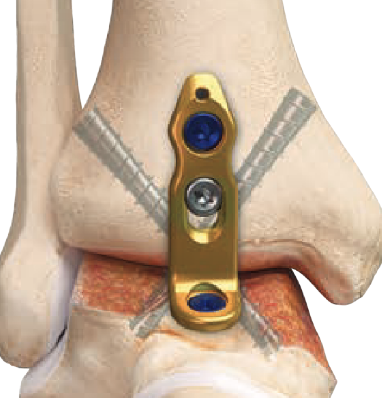
Technique
Acumed anterior ankle fusion video
Arthrex surgical technique PDF
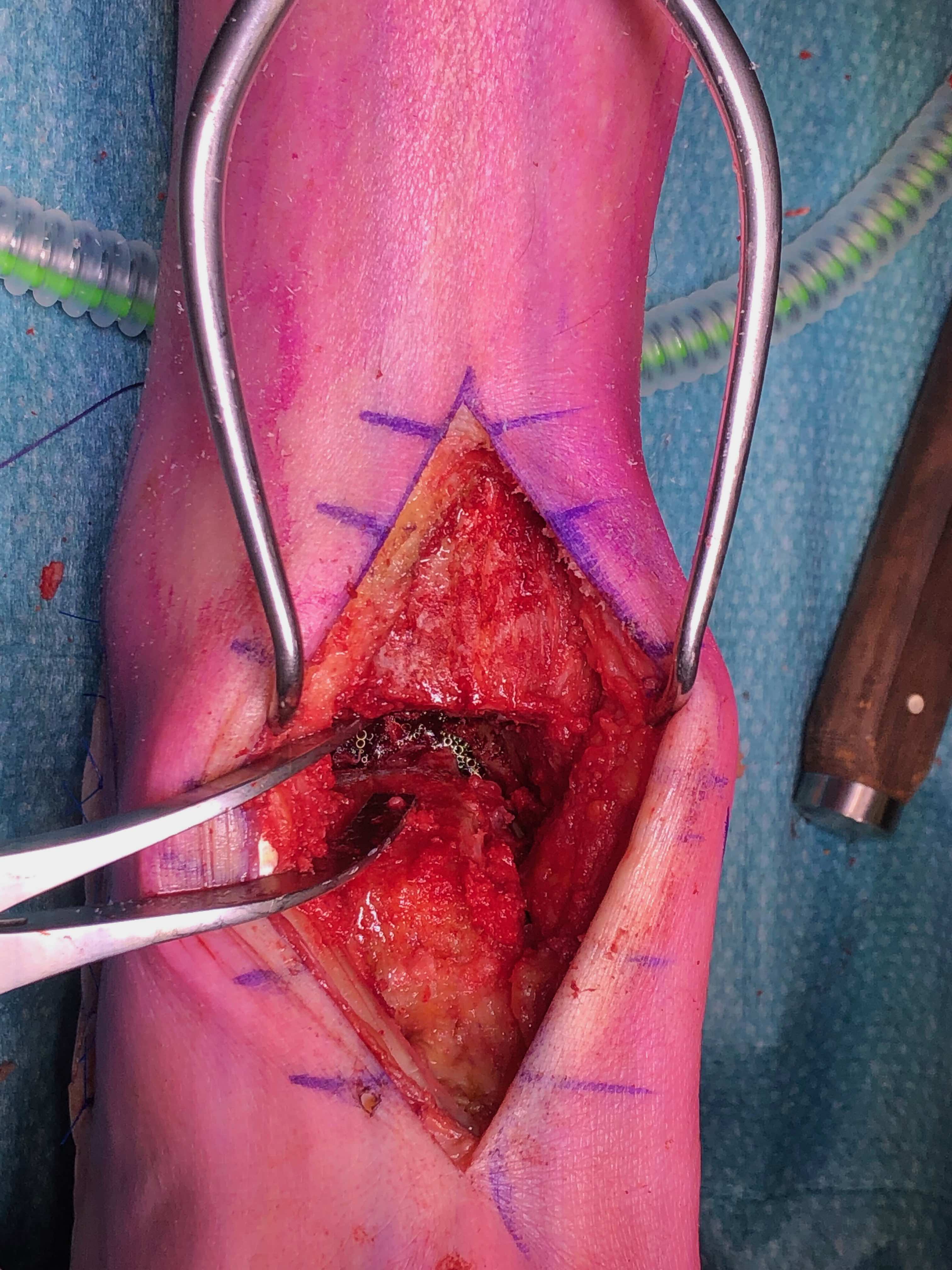
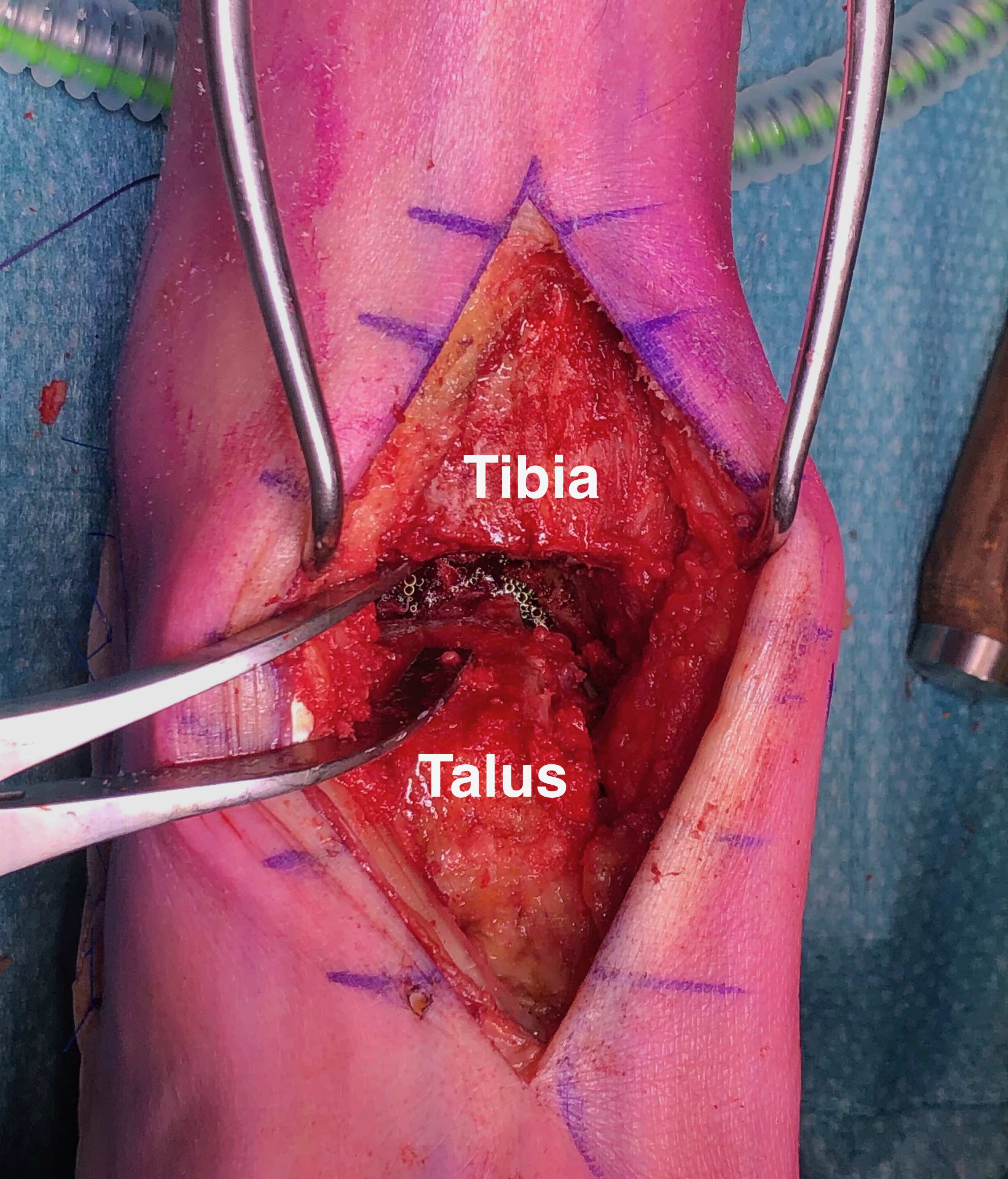
Anterior midline approach
- between tibialis anterior and EHL
- tibia and talar pins and ankle distractor
- debride joint surfaces
- fix with anatomically contoured anterior plate + screws
Arthroscopic ankle fusion
Contra-indications
Varus / valgus malalignment > 15 degrees
Technique
Arthrex arthroscopic fusion video
Ankle distractor
- anteromedial and anterolateral portals
- +/- posterolateral portal for flow
- debride cartilage surfaces with burr
- +/- bone graft
- neutral dorsiflexion, slight eversion / slight external rotation
- fix with 3 x 6.5 mm cannulated screws
- 2 medial and one lateral
Complications
Infection
Wound breakdown
Nerve damage
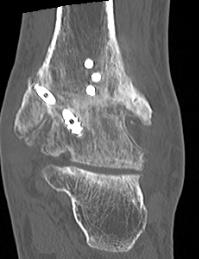
Nonunion
Incidence
Heifner et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review of ankle fusion
- 95% union rate
Leslie et al Foot Ankle Int 2023
- systematic review of CT confirmed union rate after ankle fusion in 237 ankles
- union rate 86%
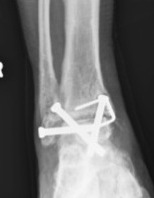
Risk factors
Patel et al Foot Ankle Spec 2023
- systematic review of risk factors for nonunion
- male / smoking / previous operative infection / AVN
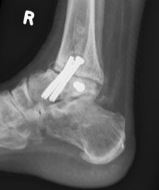
Adjacent joint arthritis / Subtalar arthritis
- database of 4700 ankle fusions
- subtalar arthrodesis rate of 3% at 5 years
