results
Galeazzi fractures
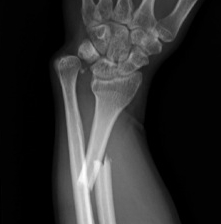
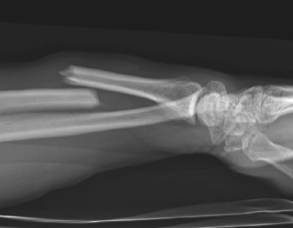
Definition
Fracture of the radial shaft with disruption to the distal radio-ulna joint (DRUJ)
External fixation
Indications
Snapping scapula
Definition
Disruption of the normal smooth motion of the scapulothoracic joint
- posterior scapula pain with overhead motion
Etiology
1. Bony abnormalities
- osteochondromas
- prominence of the superior medial border of the scapula / Luschka tubercle
2. Soft tissue abnormalities
- bursitis / scar tissue
- muscular weakness
3. Masses
Management
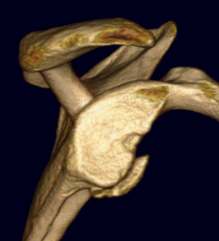
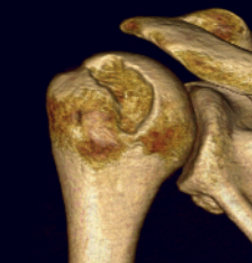
Operative management
Options
Arthroscopic labral repair +/- Remplissage
