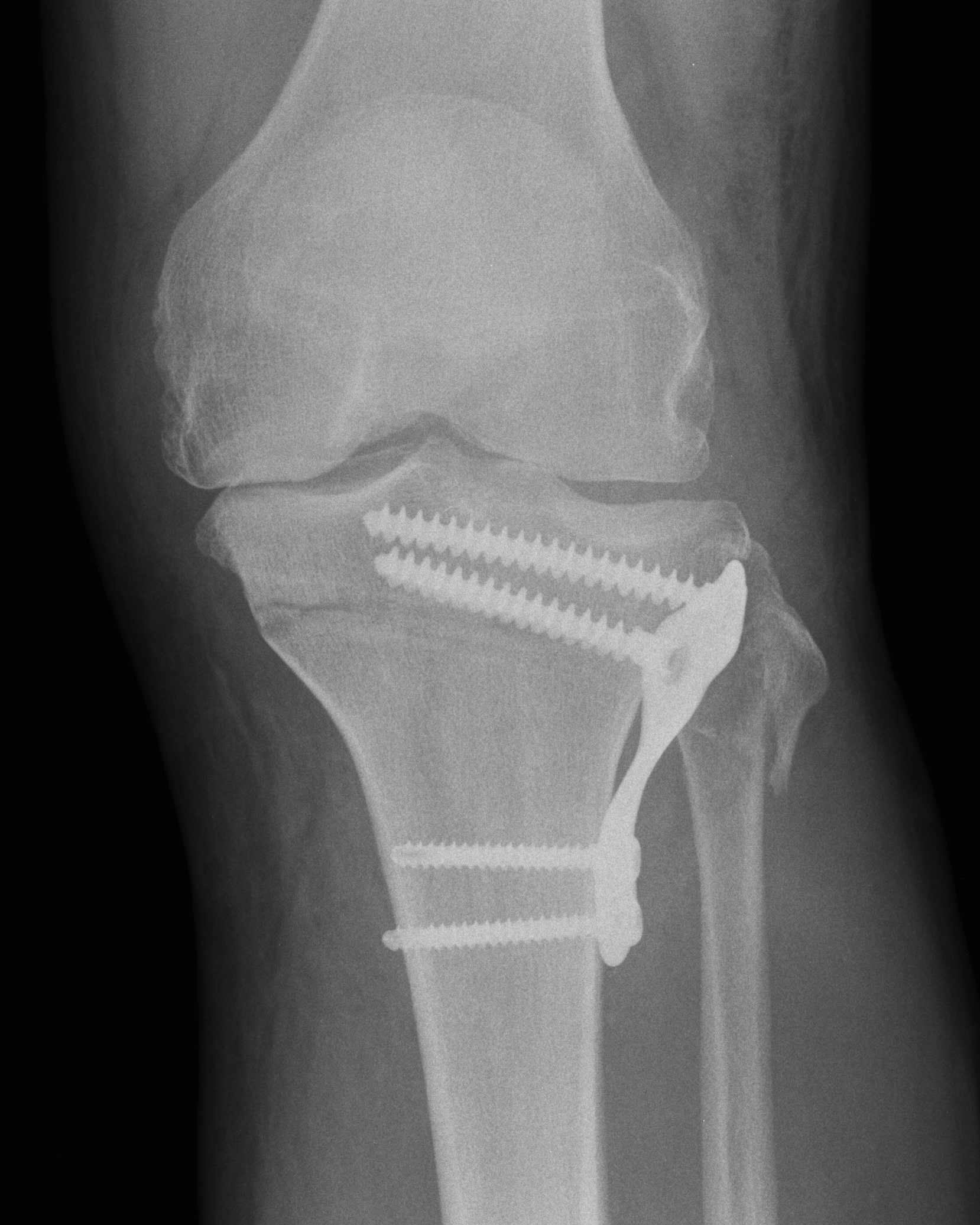
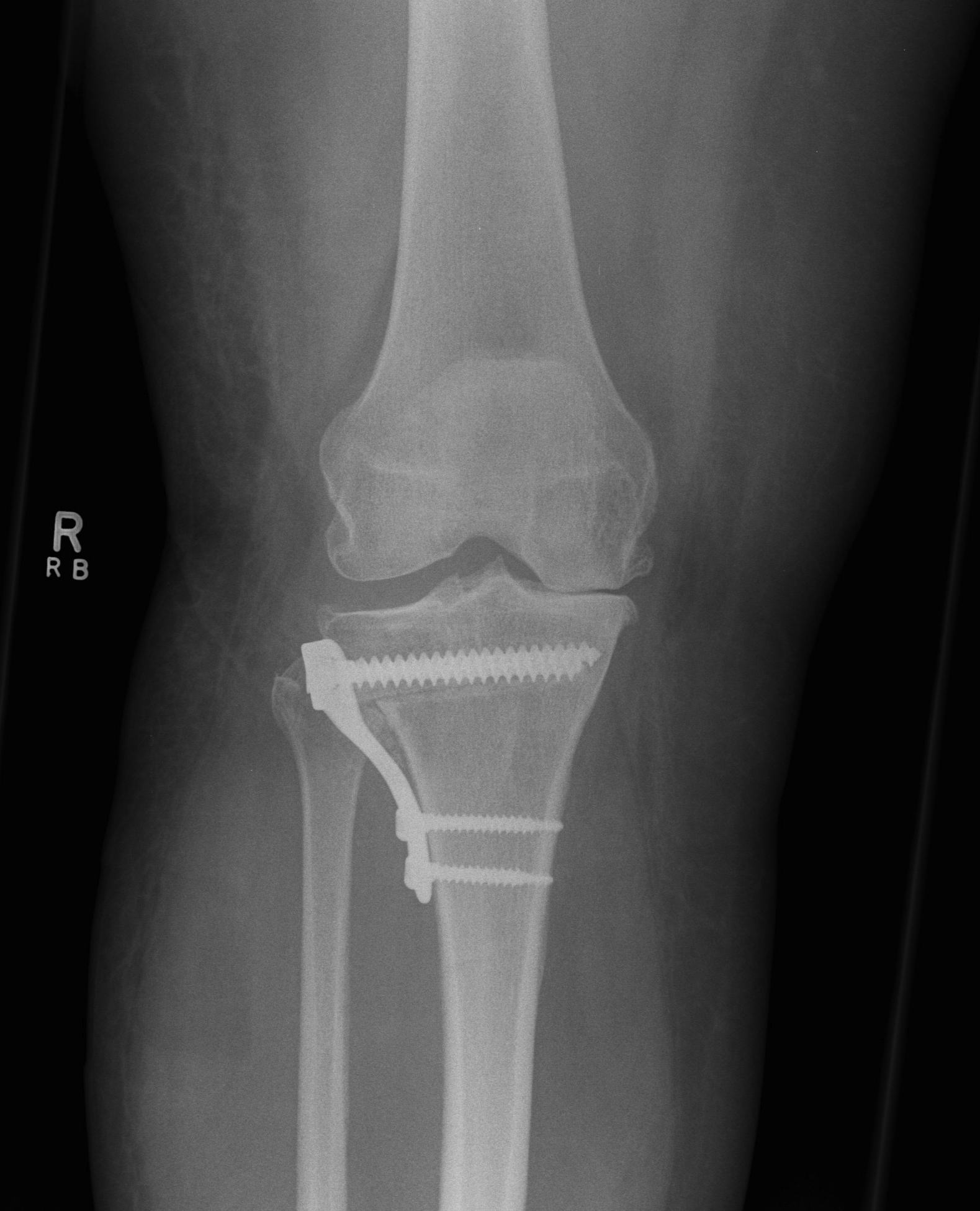
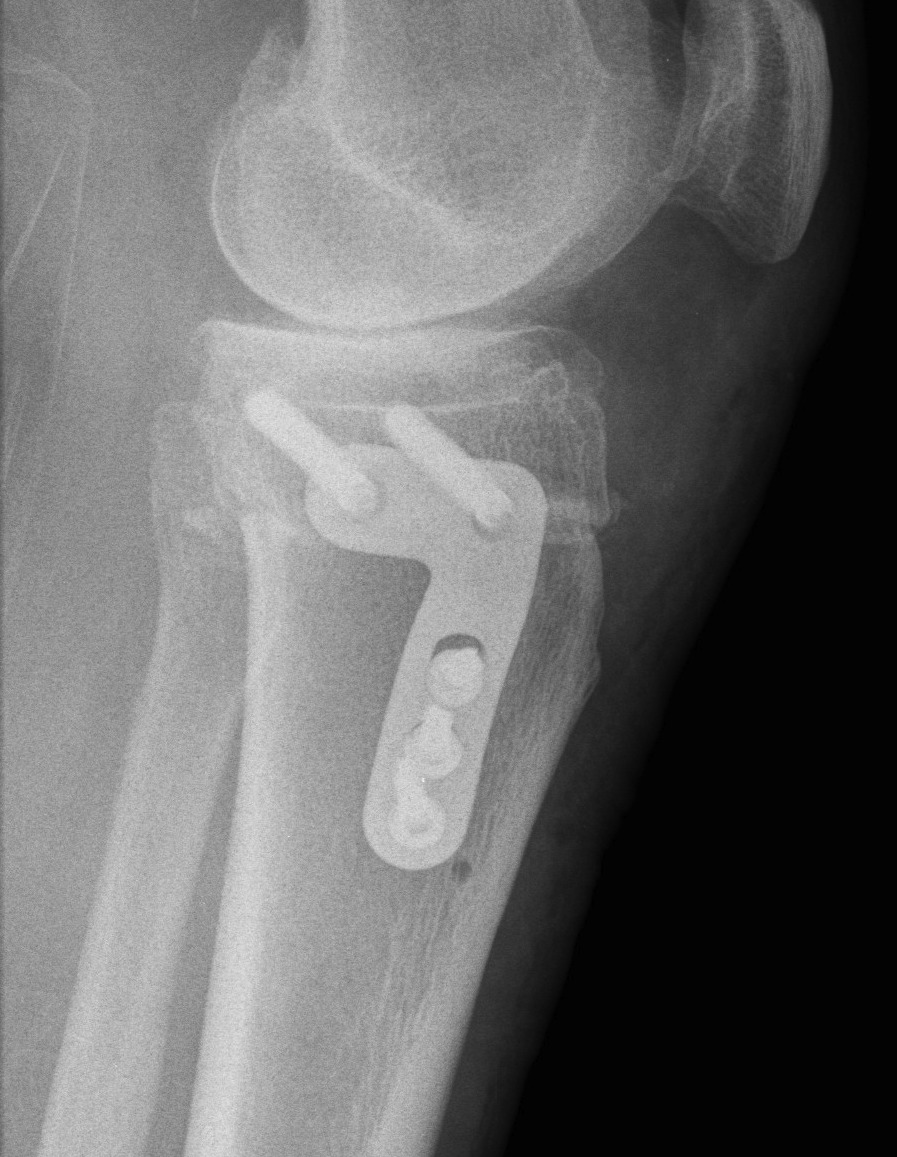
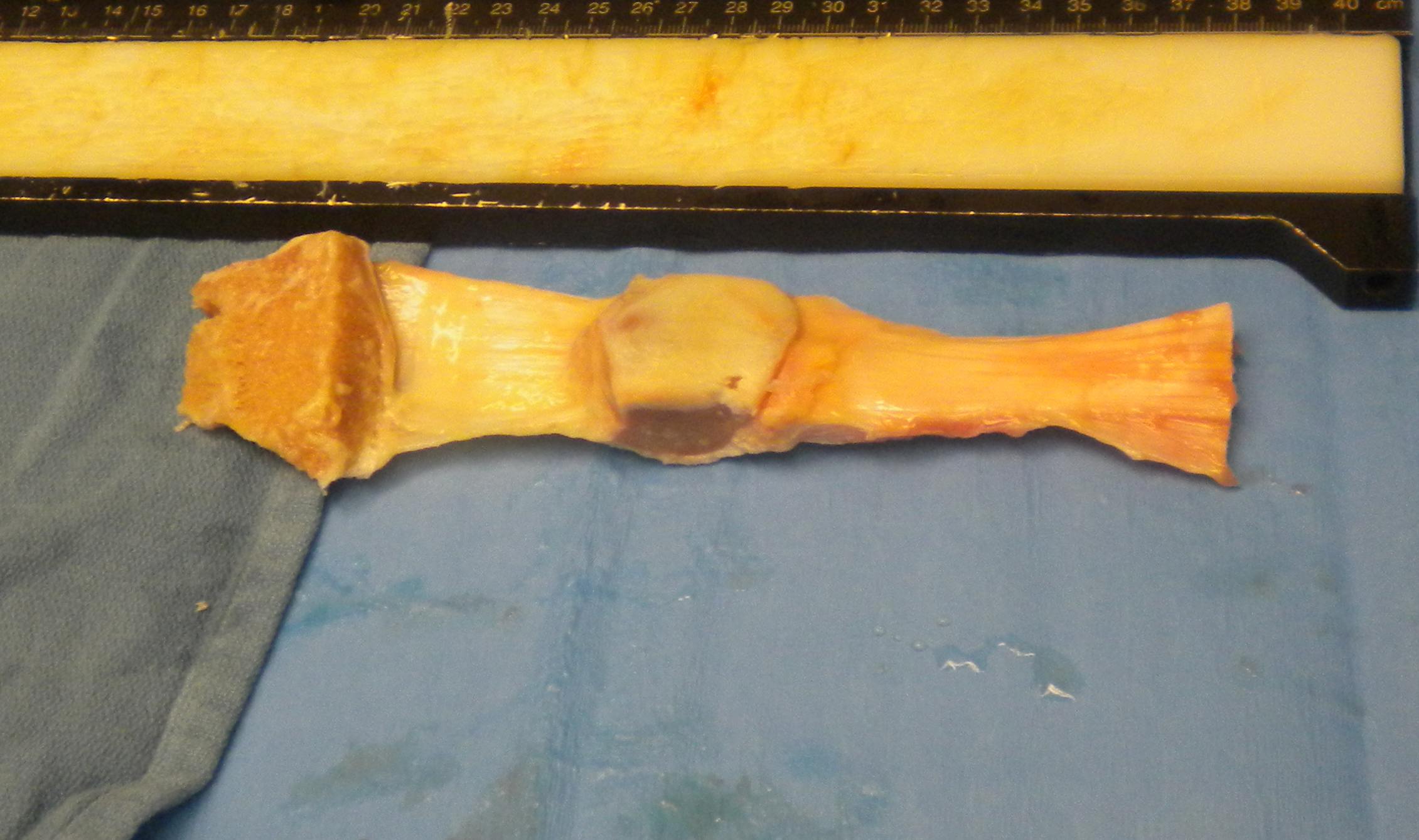
Conversion HTO to TKR
Approach
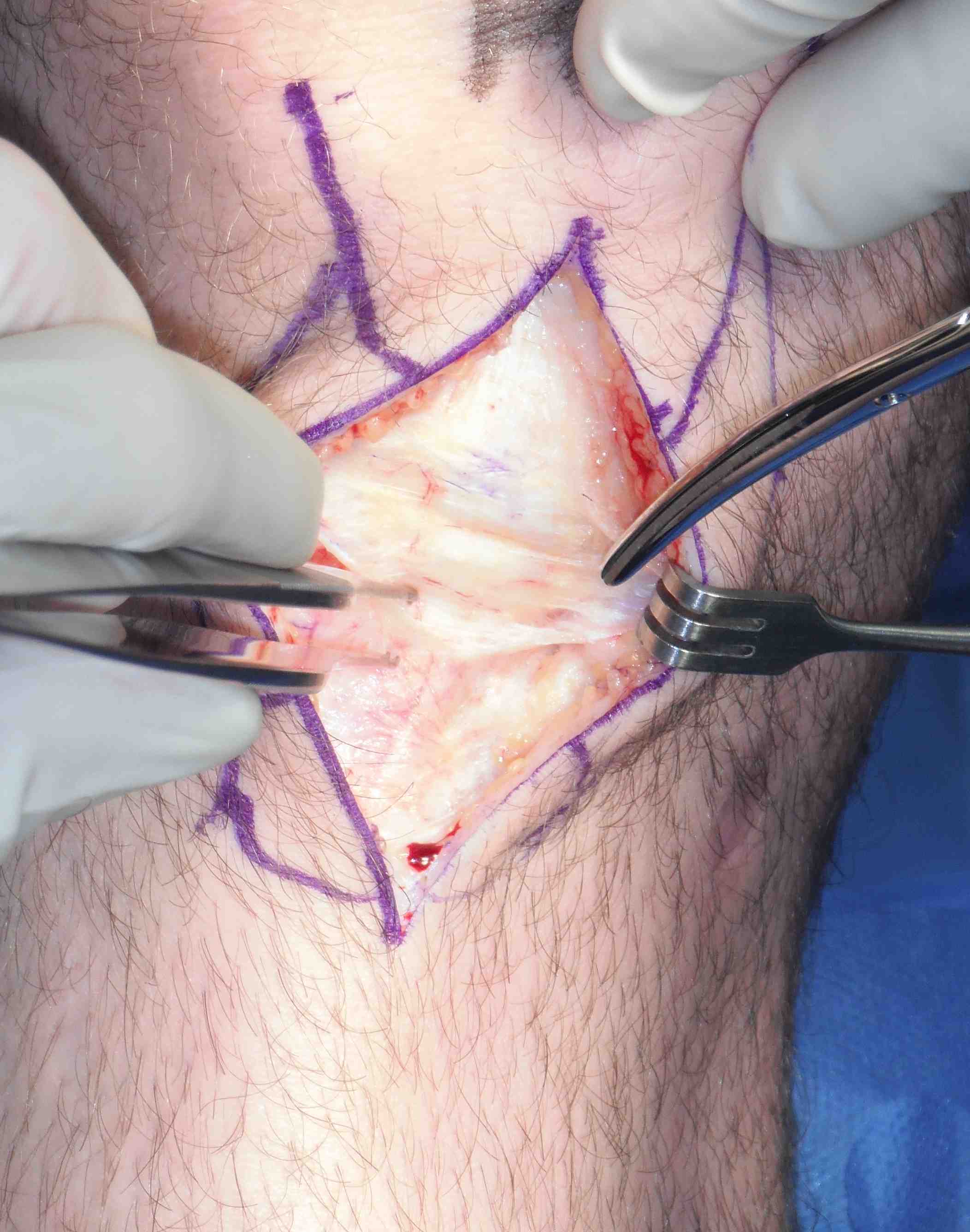
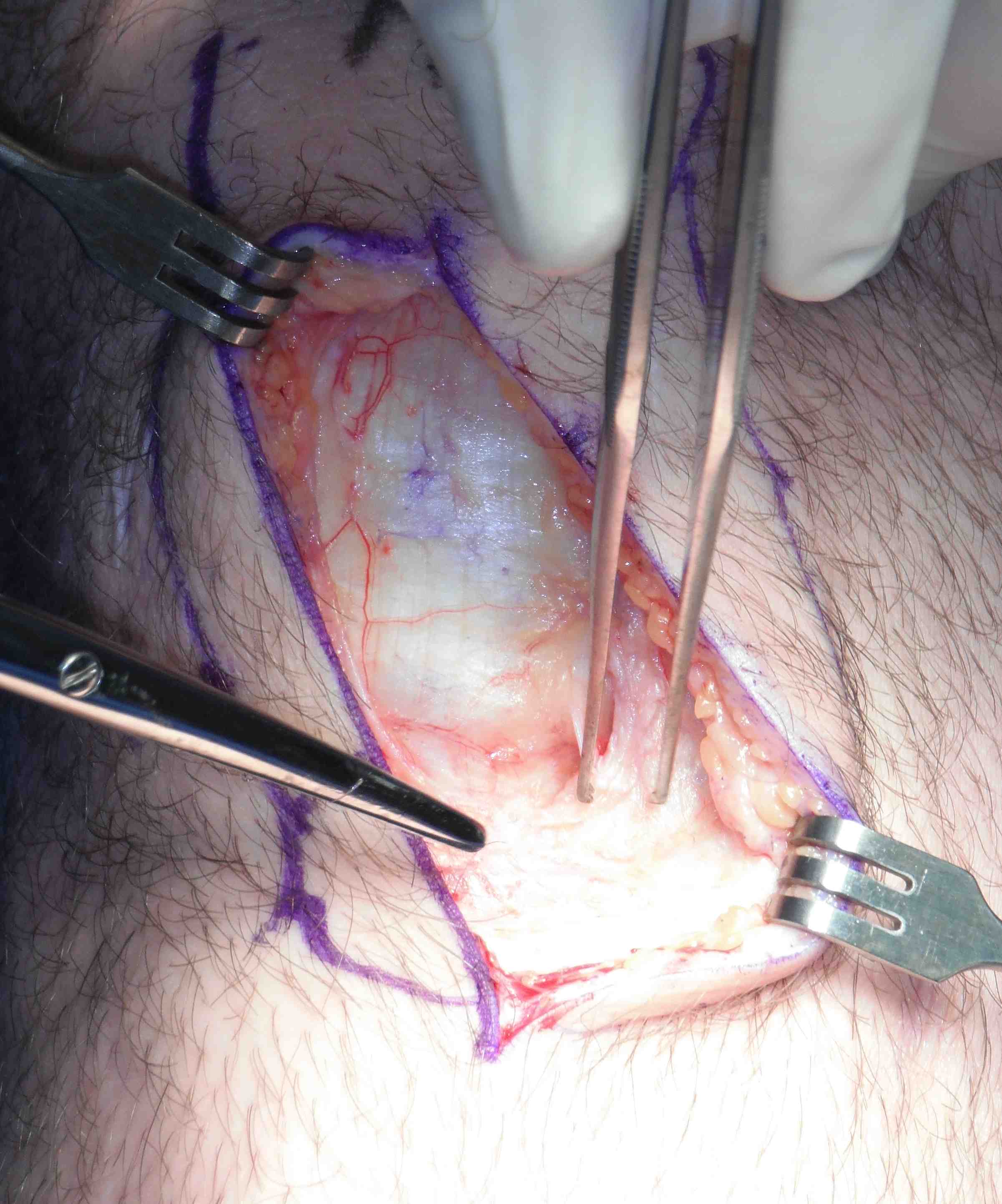
1. Incision and skin flaps
- previous incision may be L shaped
- may be good to use a vertical midline incision initially in HTO
- can usually incorporate incision
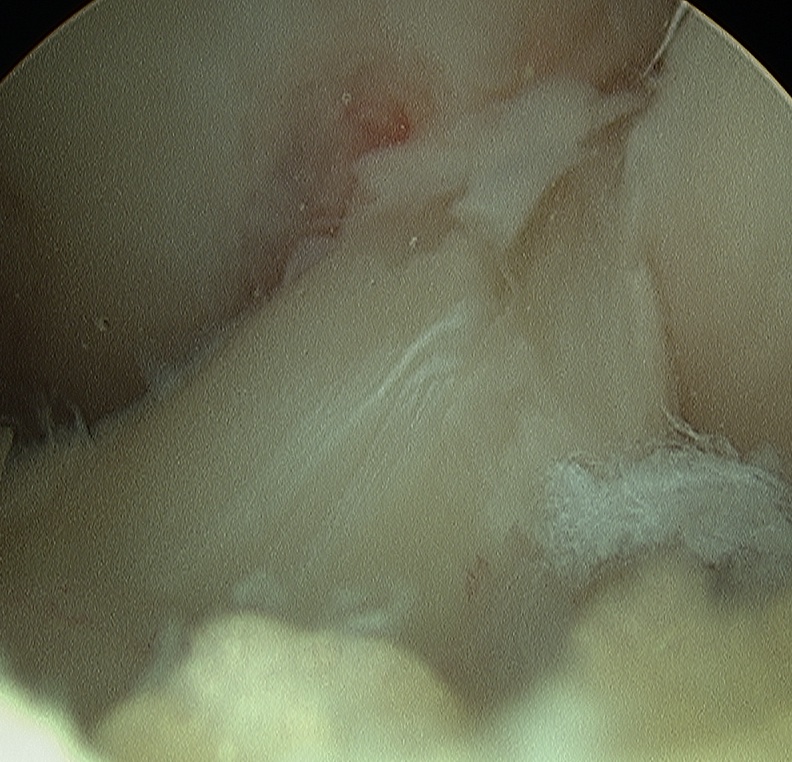
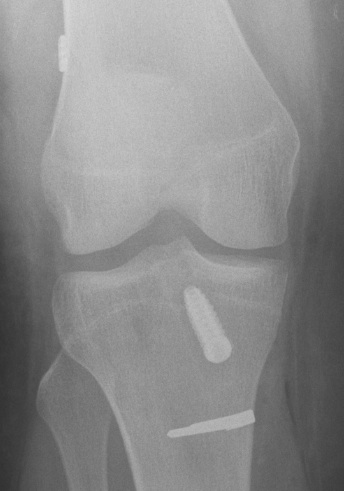
2. Removal of hardware
- may wish to consider staged procedure
- staples not usually a problem (can ignore)