Background
Definition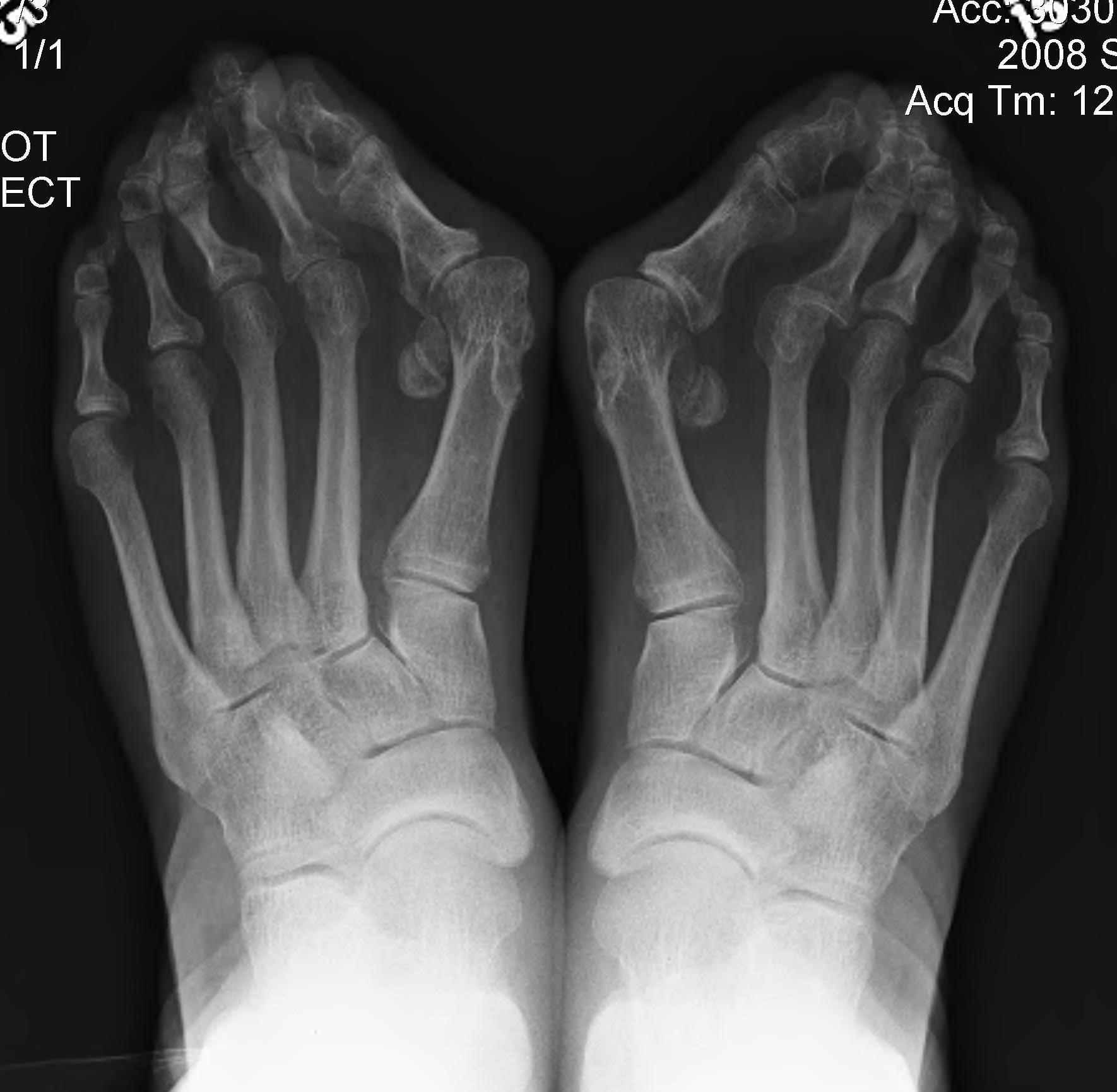
Bunion
- medial prominence of head of 1st MT
Hallux Valgus
- medial deviation 1st MT
- lateral deviation of great toe
Anatomy
Metatarsal head
- has 2 grooves separating ridge (cristae)

Bunion
- medial prominence of head of 1st MT
Hallux Valgus
- medial deviation 1st MT
- lateral deviation of great toe
Metatarsal head
- has 2 grooves separating ridge (cristae)
3 facets
1. Posterior facet (STJ)
2. Middle facet (sustenaculum tali)
3. Anterior facet (on distal medial aspect)
Anterior process
- forms calcaneocuboid (CCJ) articulation
Thalamic portion
- under lateral process talus
Tuberosities
Posterior tuberosity
- posterior process / T Achilles attachment
Incidence isolated deltoid ligament injury 2.5%
Strong fan-shaped structure
- composed of a deep and superficial layer
Superficial layer
- inserts as one continuous structure
- navicular anteriorly, spring ligament (calcaneonavicular), sustentaculum, and calcaneum
- measures 10 mm wide at its origin and 2 to 3 mm thick
1 - 2 %
Medial Aspect of foot
- proximal to navicular
- part of T posterior tendon
Usually will fuse with navicular (50%)
1. Probably not a cause of flat foot
- excising accessory navicular / rerouting / reattaching tibialis posterior
- will not help pes planus
2. Pain
- may fracture
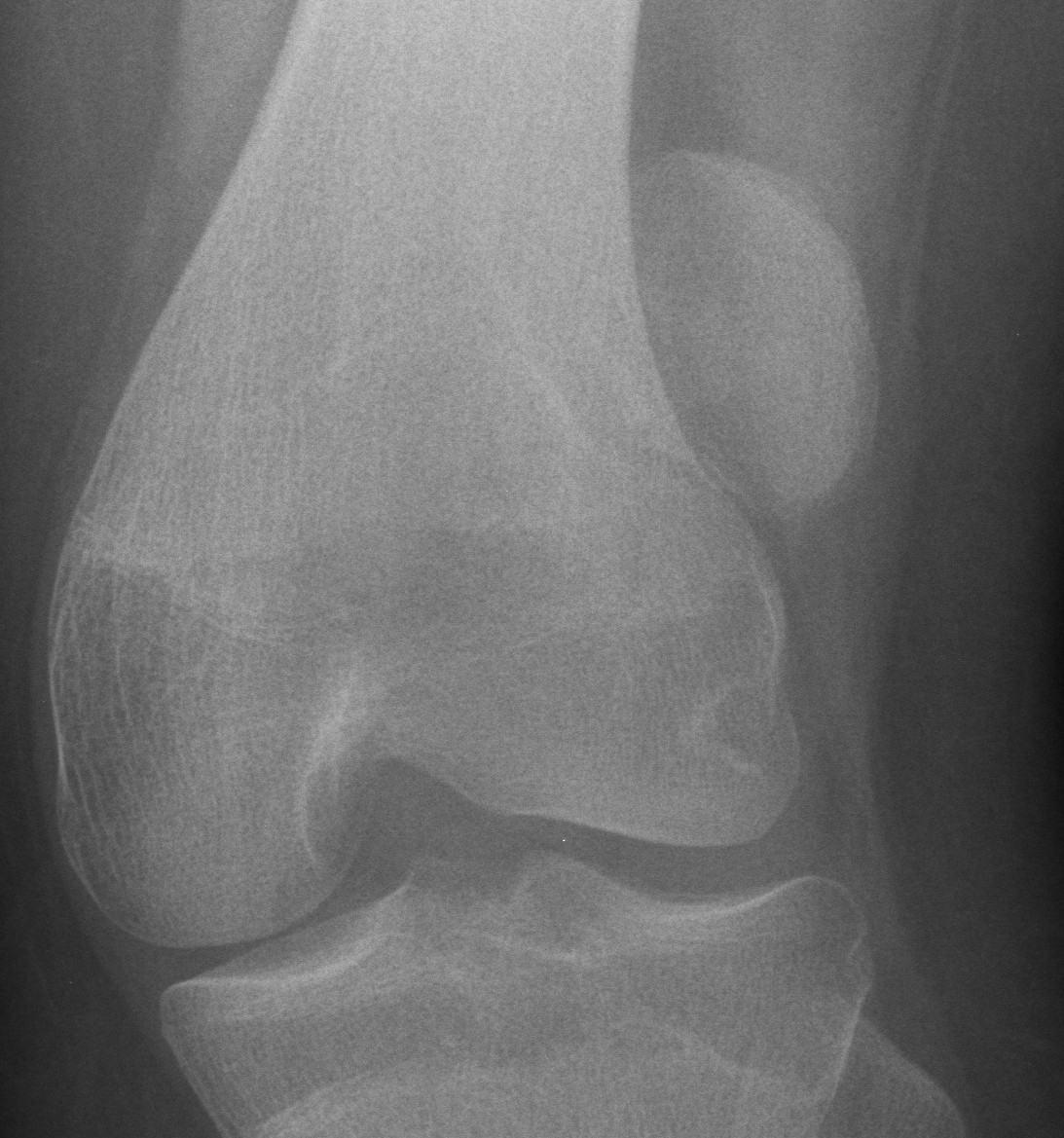
Repeated dislocation of patella with minimal trauma
- 15-20% of paediatric acute patella dislocations
- more common girls
- often bilateral
Dislocation occurs unexpectedly when quadriceps contracted with knee in flexion
Unusual anatomic convergence of ilium, pubis and ischium
- covered entirely by hyaline cartilage
- except at acetabular fossa, which is the site of attachment of the ligamentum teres
- deepened by peripheral fibrocartilage labrum
2 column theory (Letournel and Judet)
Anterior Column
- superior pubic ramus
- anterior acetabular wall, anterior dome
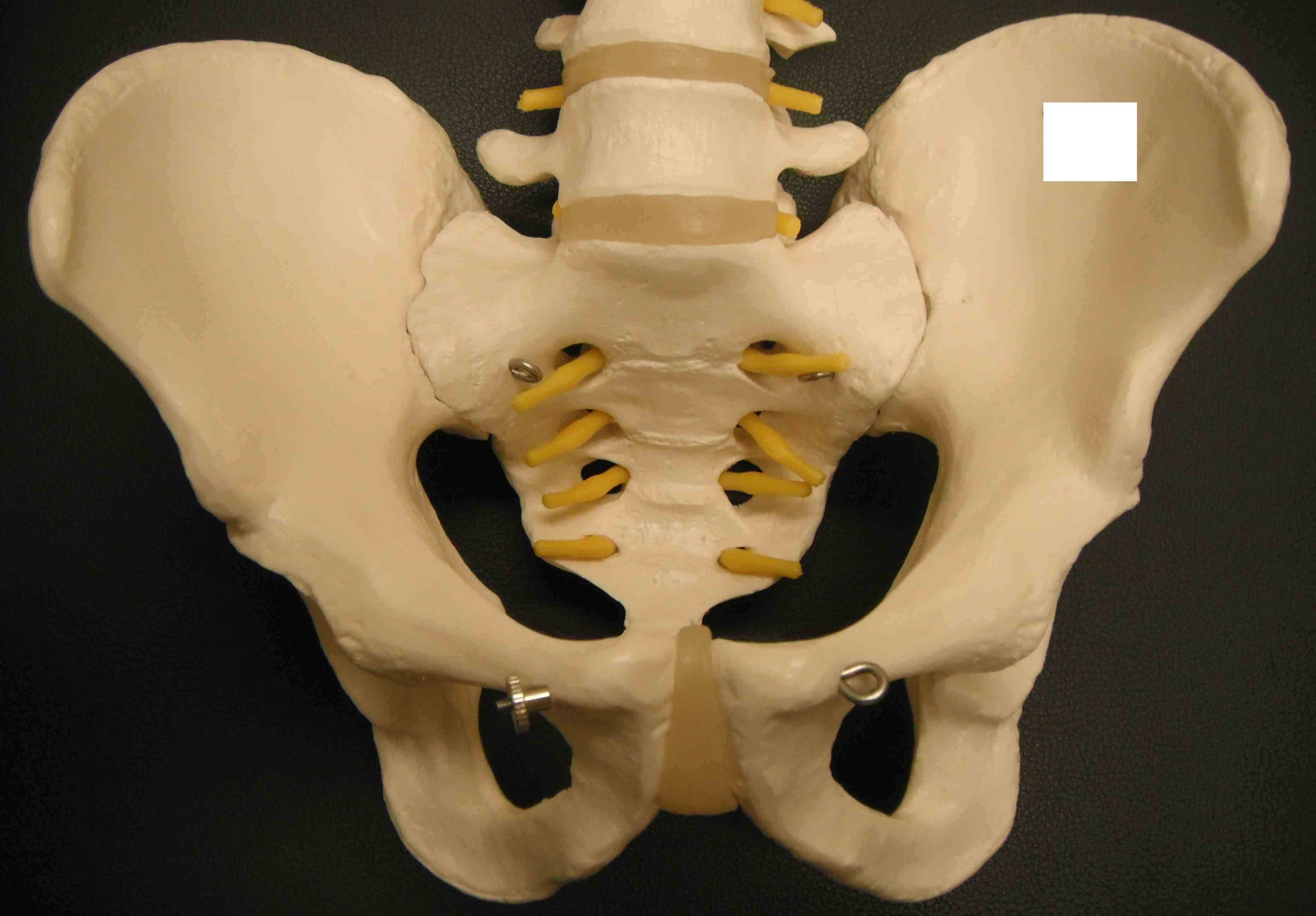
Pelvis is a true ring
- any anterior fracture must have a posterior injury as well
- integrity of the posterior sacroiliac complex is key
2 innominate bones + sacrum
Symphysis pubis < 5mm
SI joint 2-4 mm
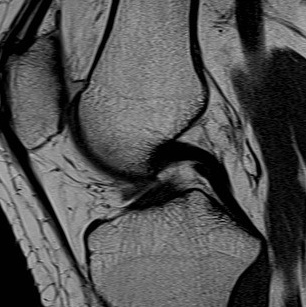
Size
2 x as strong as ACL
About the same length as ACL 38 mm
Cross sectional area 150% of ACL
13 mm diameter (thicker)
2 Bundles
1. Anterolateral
- most important
- double the size of the posteromedial
- tight in flexion
- try to reconstruct this bundle
LHB primary function is humeral head depressor
Also accelerate / decelerate arm in overhead sports
Biceps problems usually occur with other pathology
- rotator cuff / instability
3 main problems
1. Degeneration
Second most common hindfoot after calcaneal fractures
Aviators Astragalus
Fall from height
- hyper-dorsiflexion injury
- neck of talus strikes the anterior tibia
More than half surface covered by articular cartilage
- medial articular wall straight
- lateral articular wall curves posteriorly