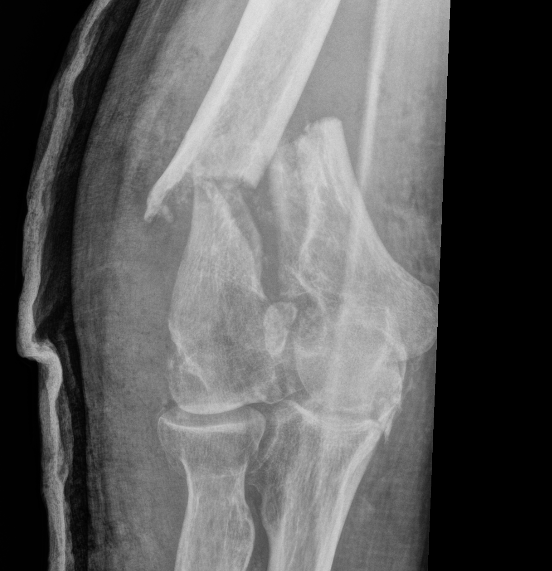
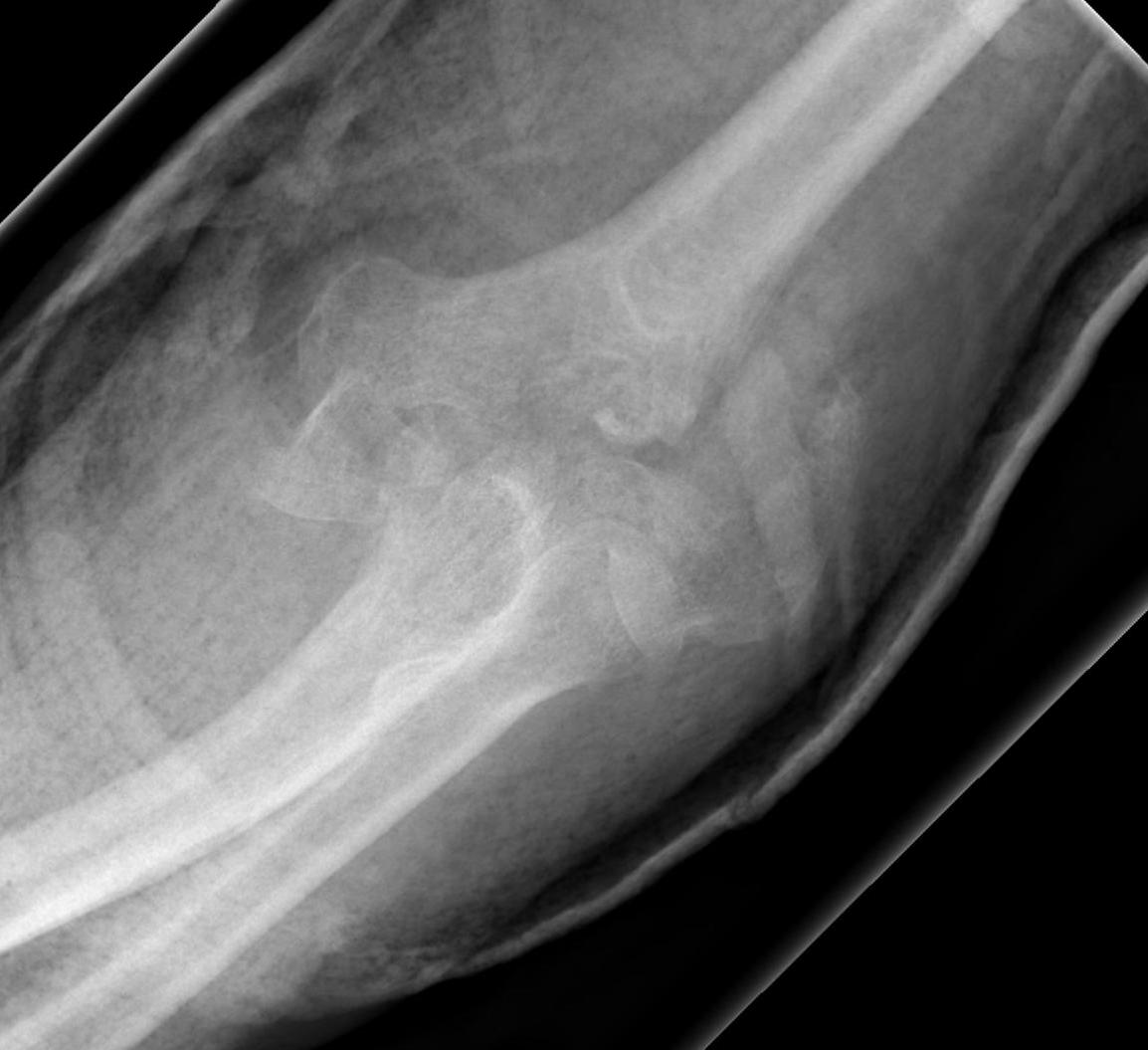

Epidemiology
2 groups
- young patient with high velocity injury
- older patient with low velocity injuries, and comminuted, osteoporotic fractures
Anatomy
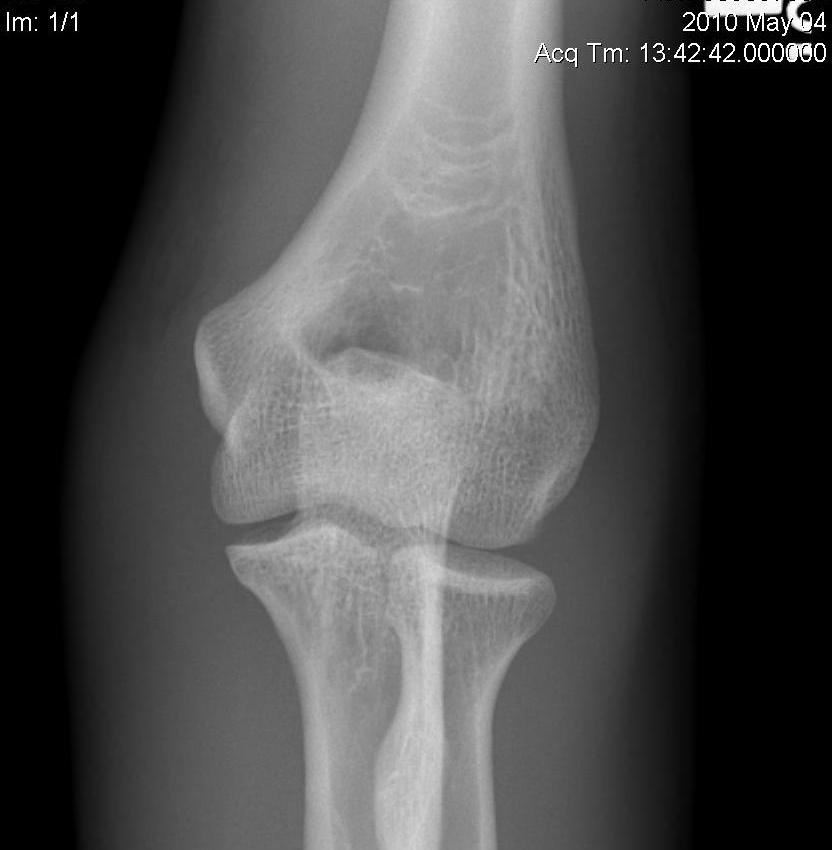
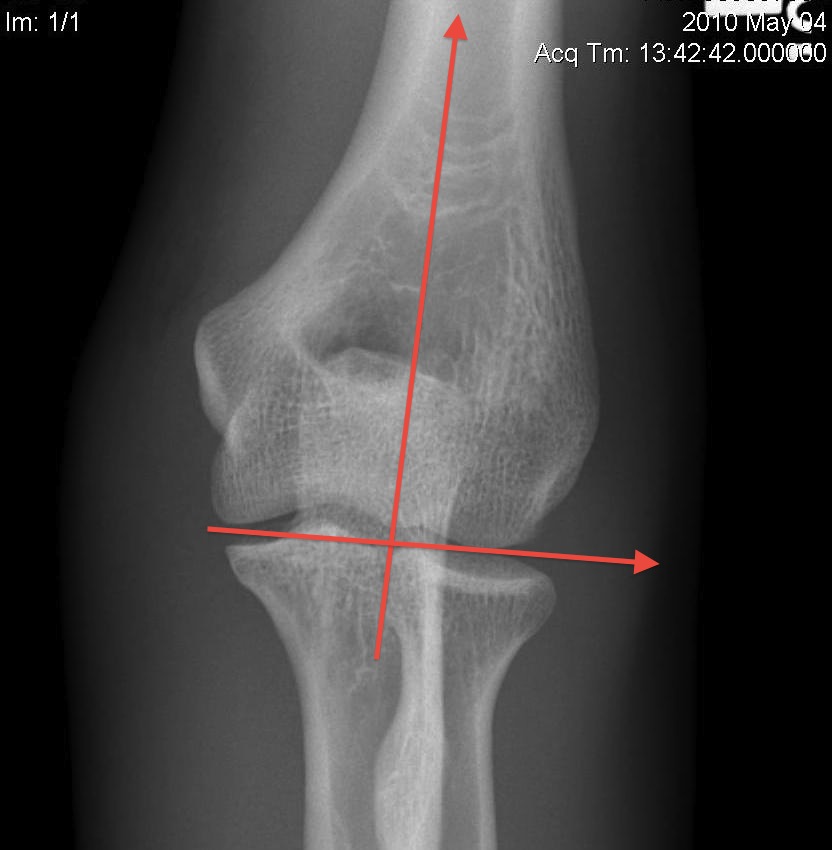
Humeroulnar joint
- hinged joint
- trochlea axis is centre of rotation
- 40o anterior angulation in sagittal plane
- trochlea 3-8o externally rotated
- 4 - 8o valgus
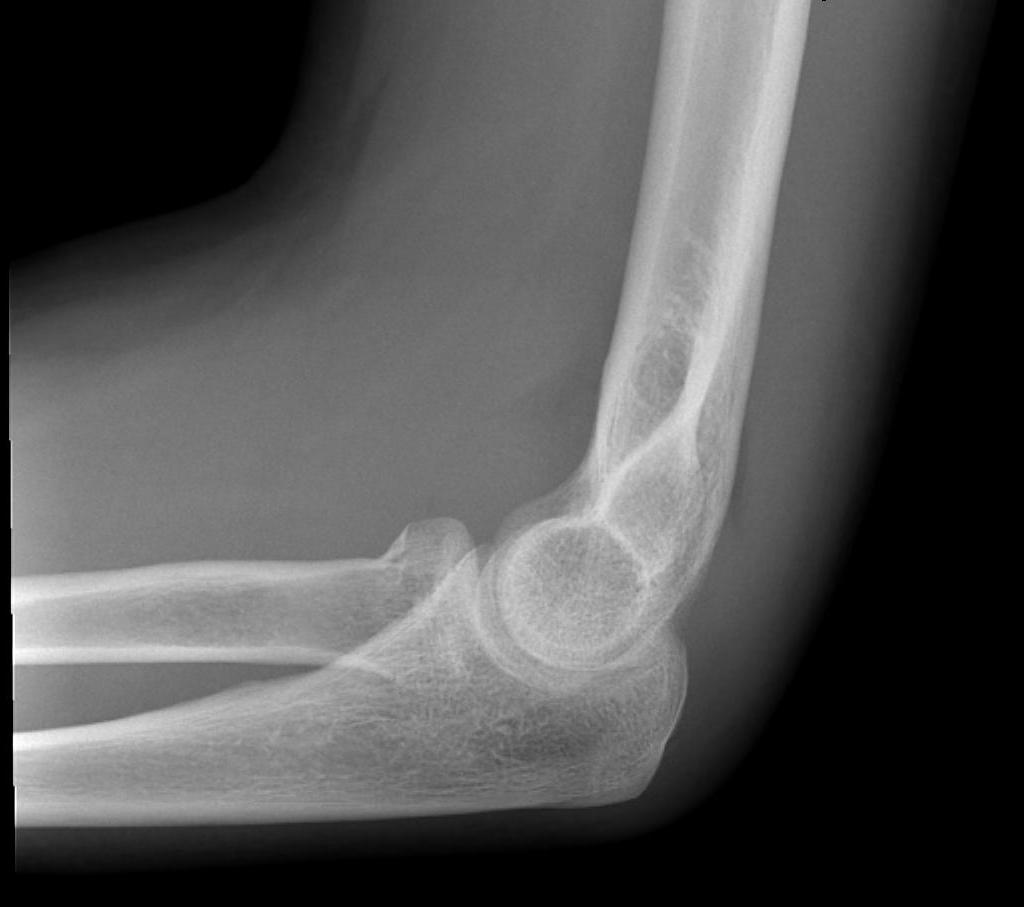
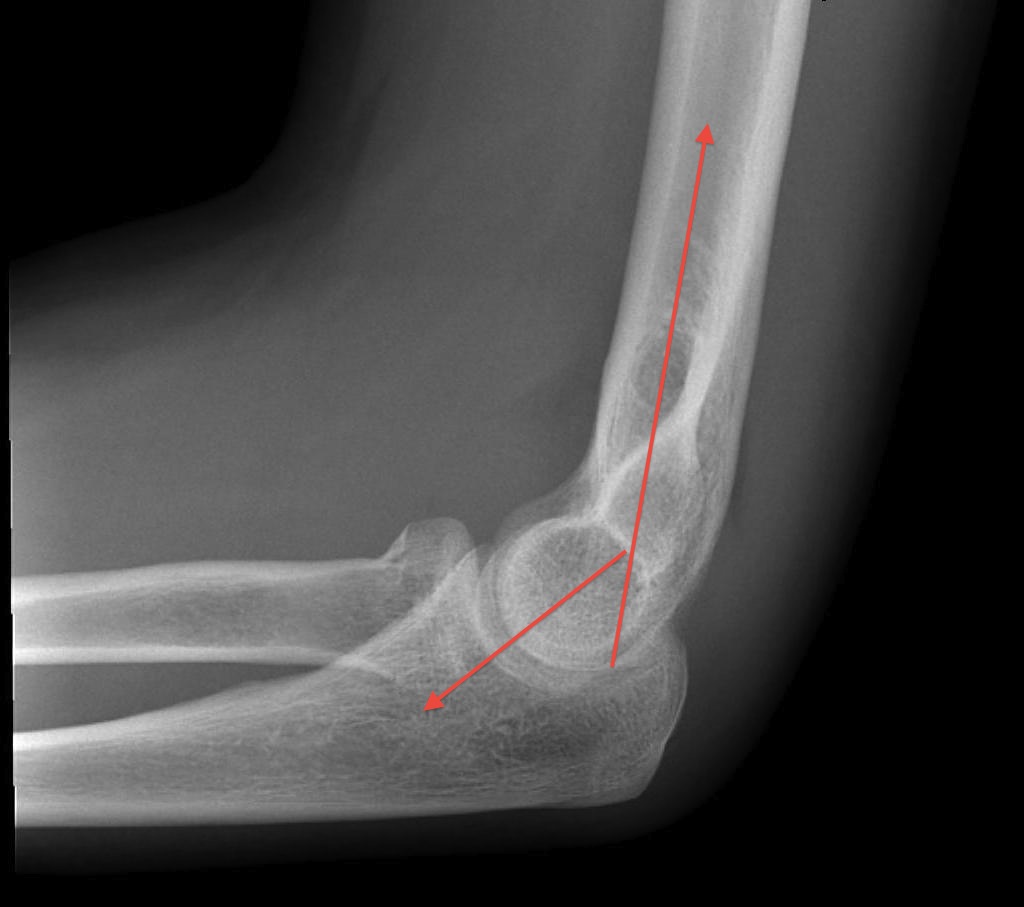
OTA / AO Classification
Type A: Extra-articular fracture
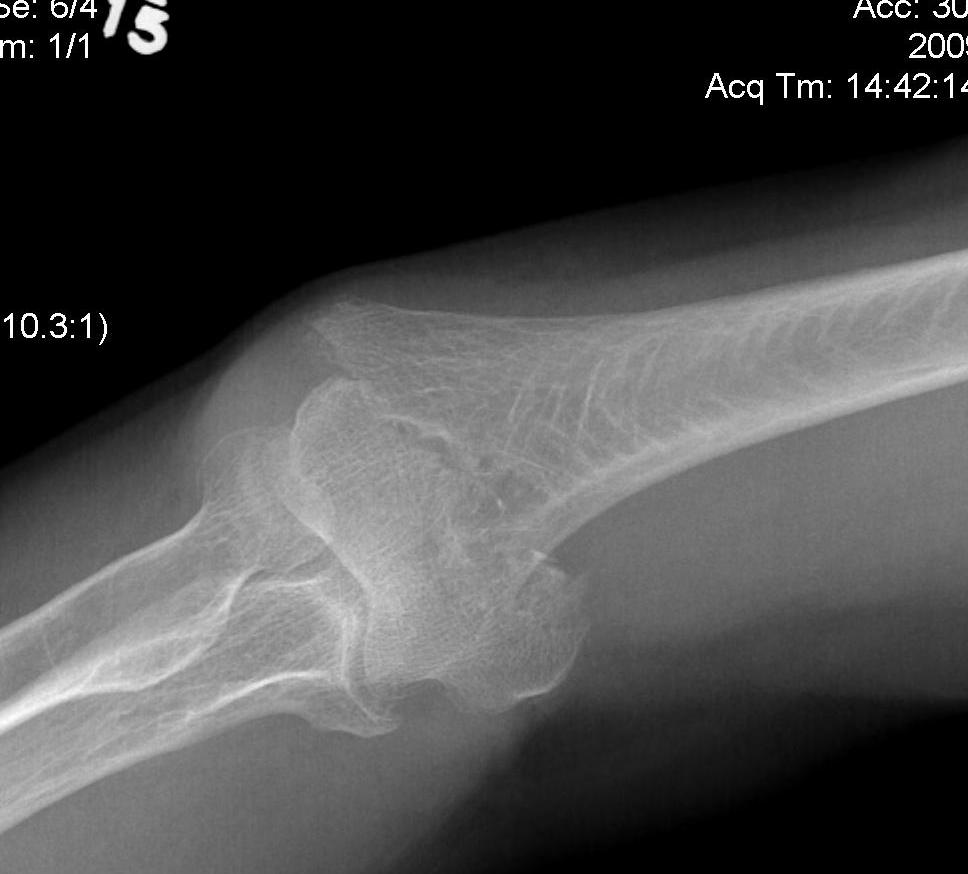
Type B: Partial articular fractures
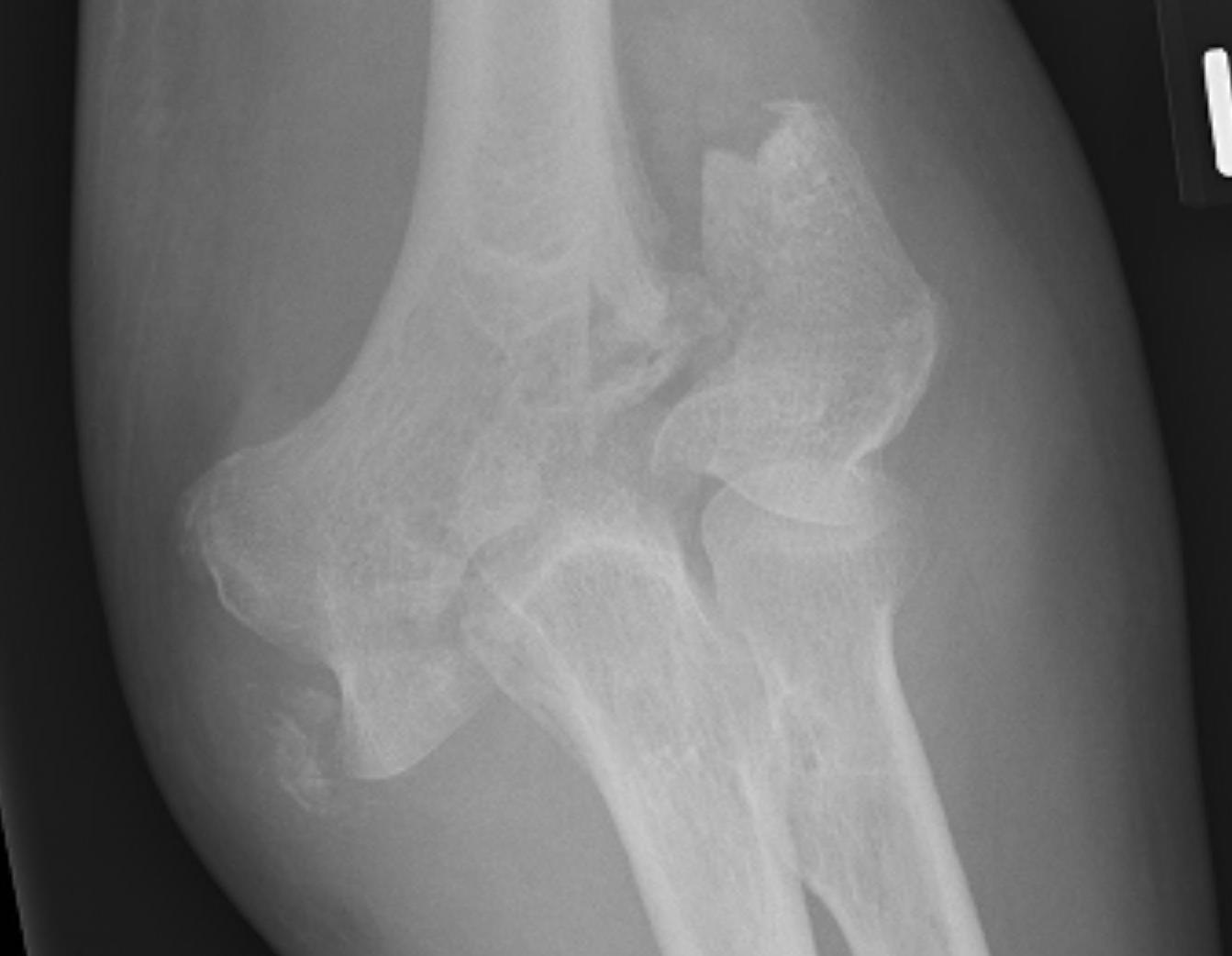
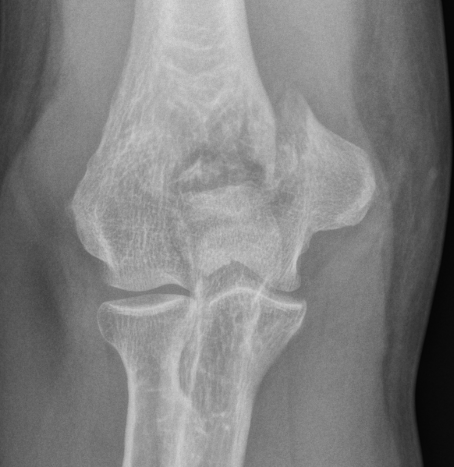
Lateral condyle Medial condyle
Type C: Complete articular fractures
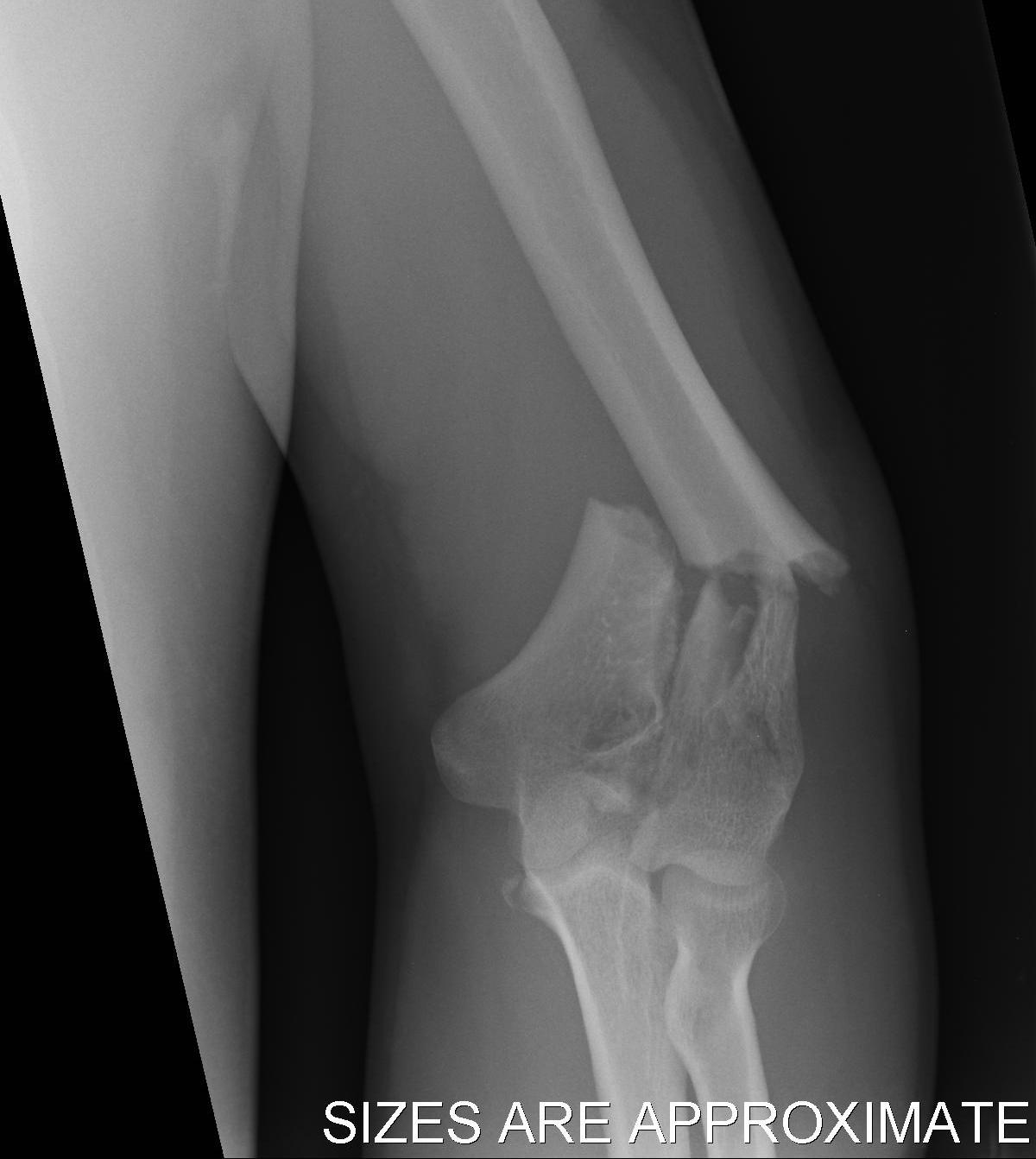
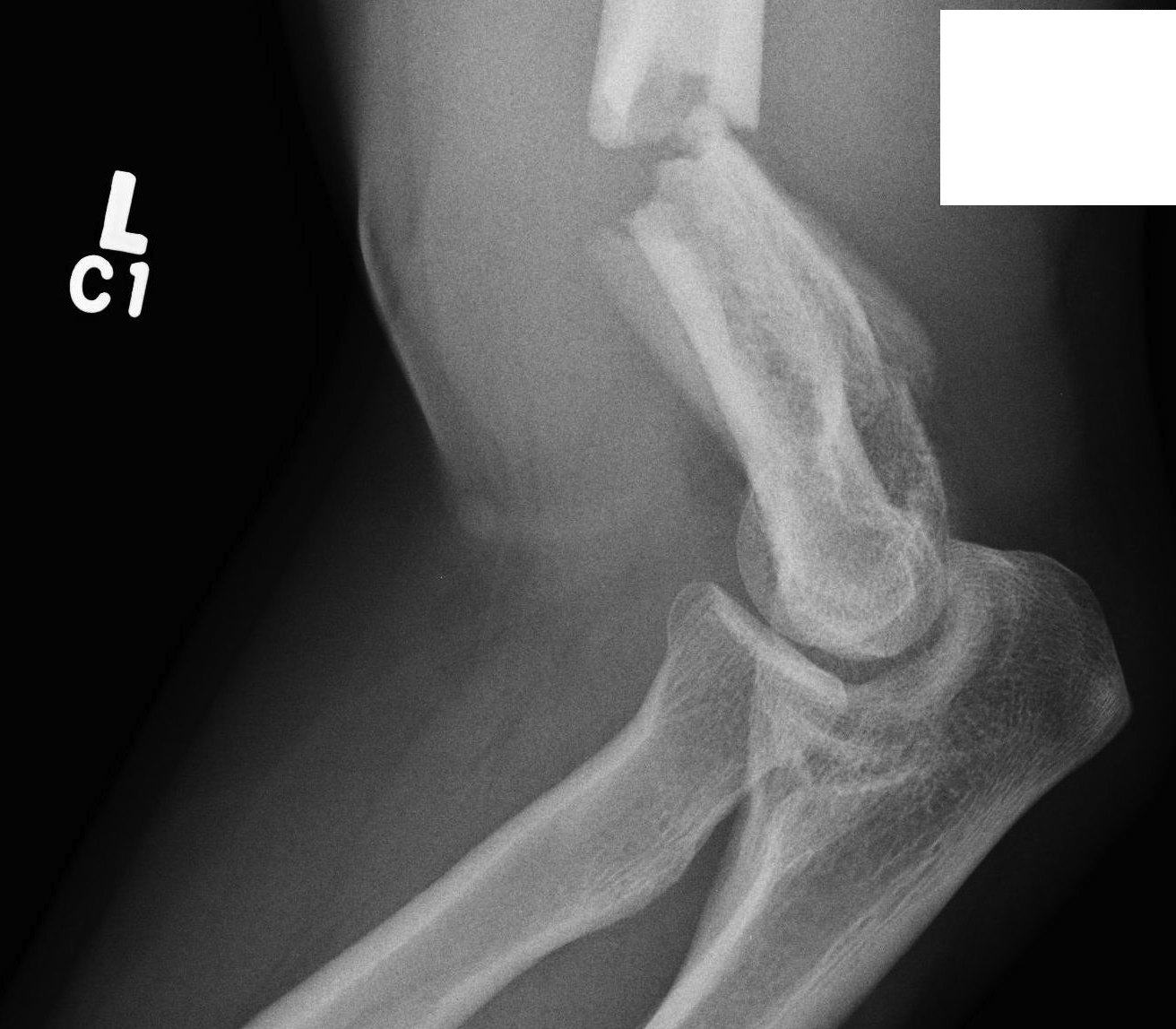
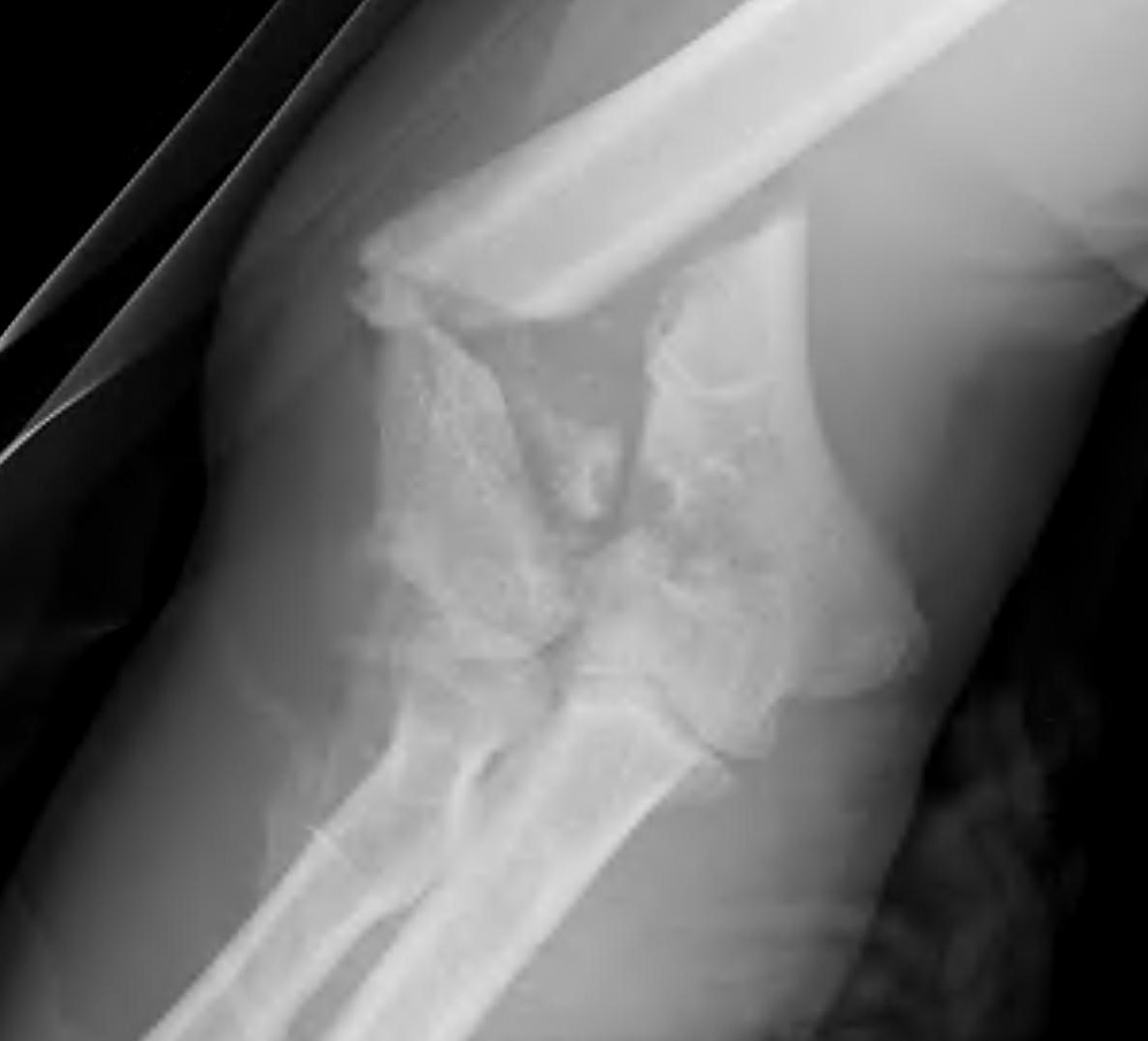
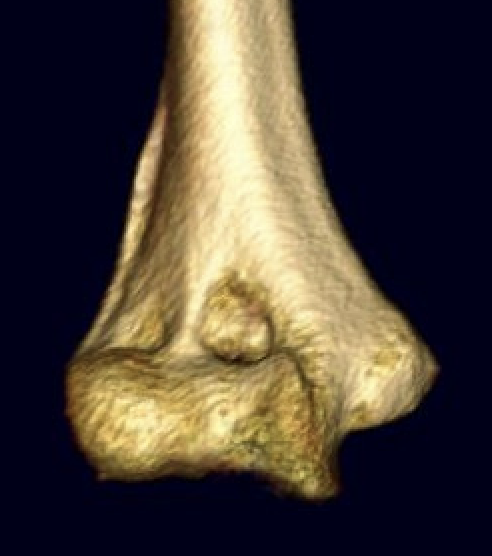
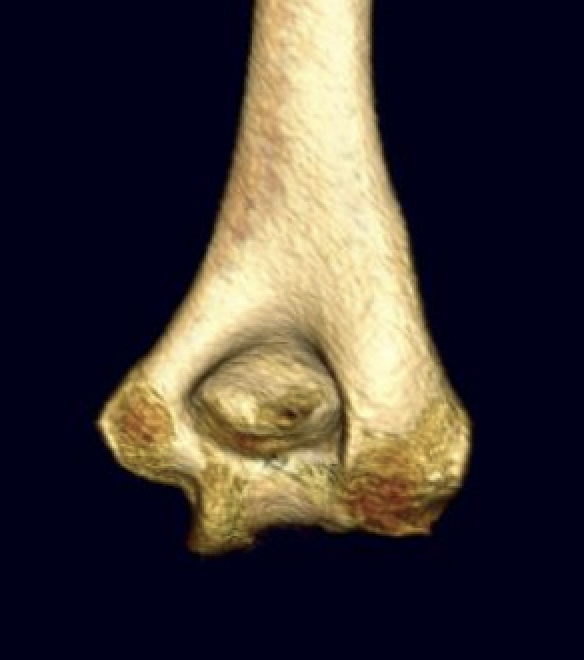
CT scan
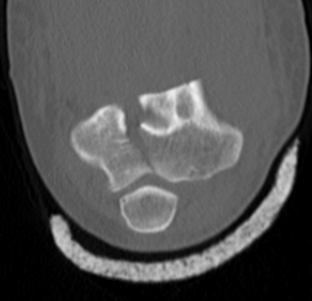
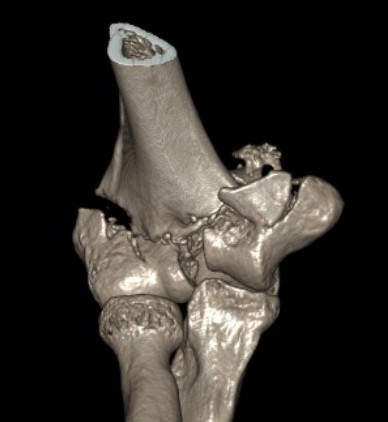
Operative Management
Options
1. ORIF
2. Distal humeral replacement
3. "Bag of bones" treatment
Bag of bones / nonoperative management
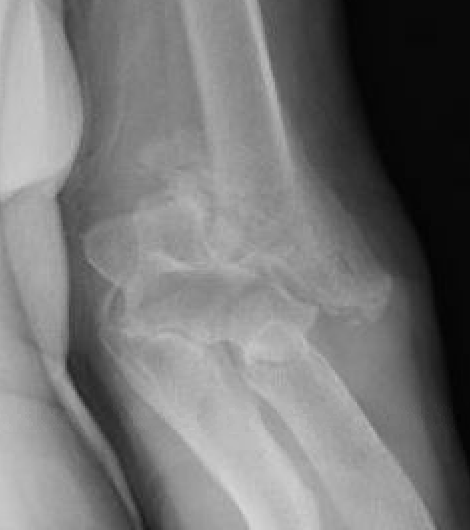
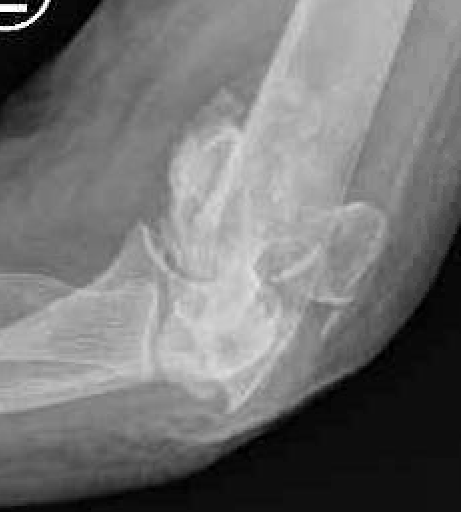
Initial injury in elderly patient
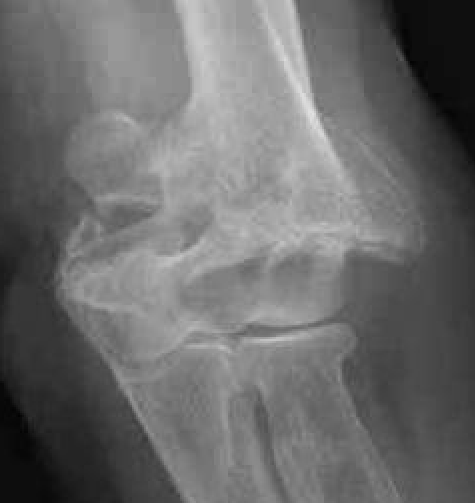
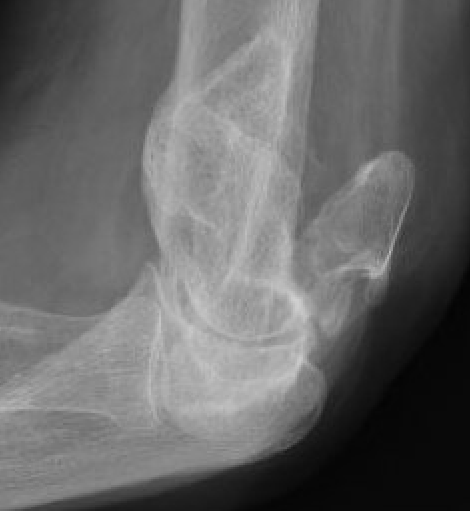
Elbow post treatment in cast
Indication
Patient elderly and not operative candidate
Technique
Initial rest in plaster then mobilisation
Results
- 40 "elderly and low demand" patients treated non-op
- 5 year mortality 40%
- 50% non union
- DASH score 38/100
- modest function, but avoids risks
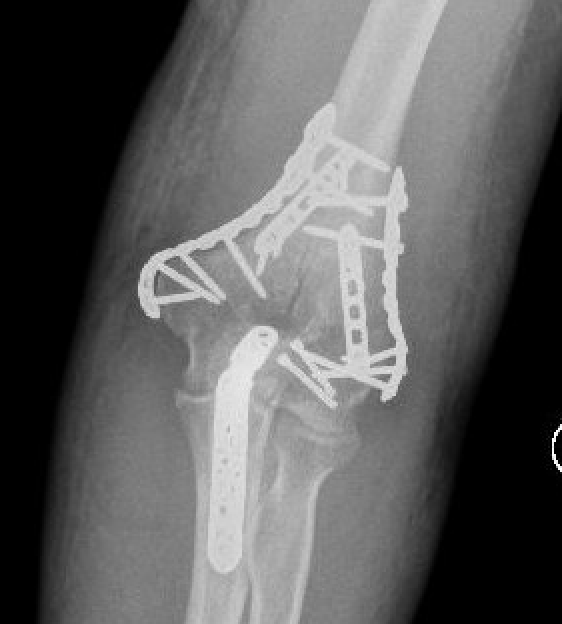
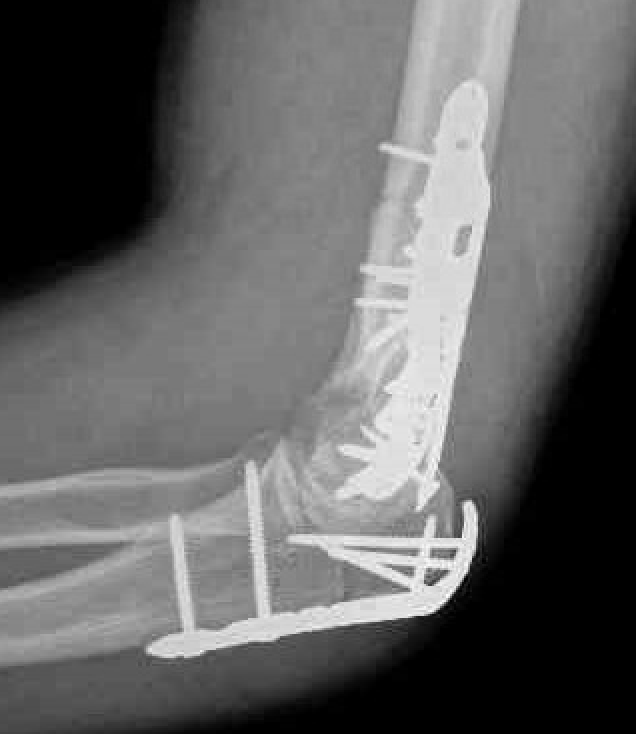
ORIF with plates
Approaches
1. Paratricipital
- mobilise triceps either side of humerus
2. Triceps reflecting / Bryan-Morrey
- elevate triceps aponeurosis medial to lateral off ulna
3. Triceps splitting
4. Olecranon osteotomy
Paratricipital Approach
Technique
AO foundation paratricipital approach
Posterior incision
- medially identify and protect ulna nerve
- laterally mobilize triceps from lateral intermuscular septum
- identify and protect radial nerve proximally

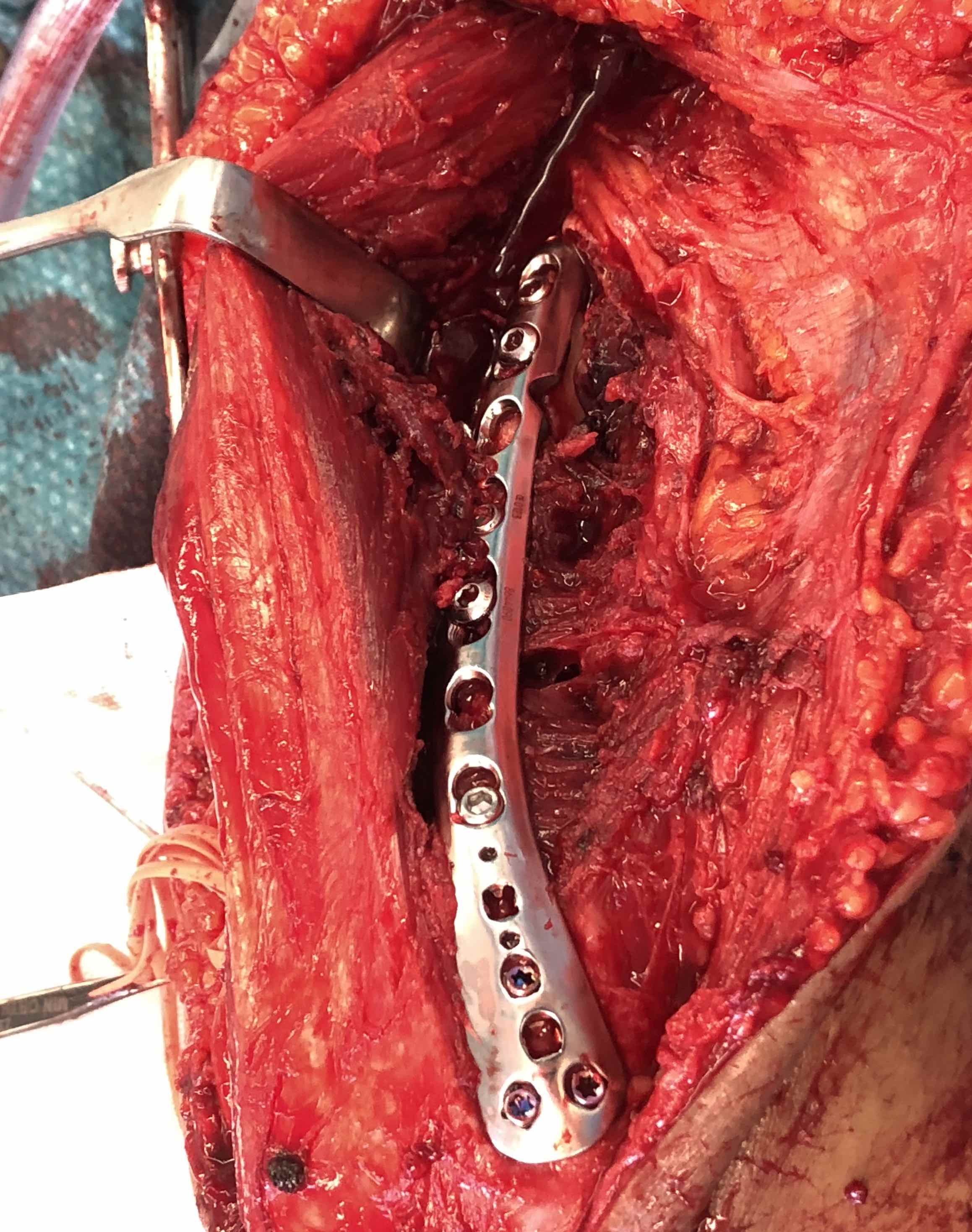
Posteromedial approach with ulna nerve protected Posterolateral approach with radial nerve protected
Olecranon Osteotomy
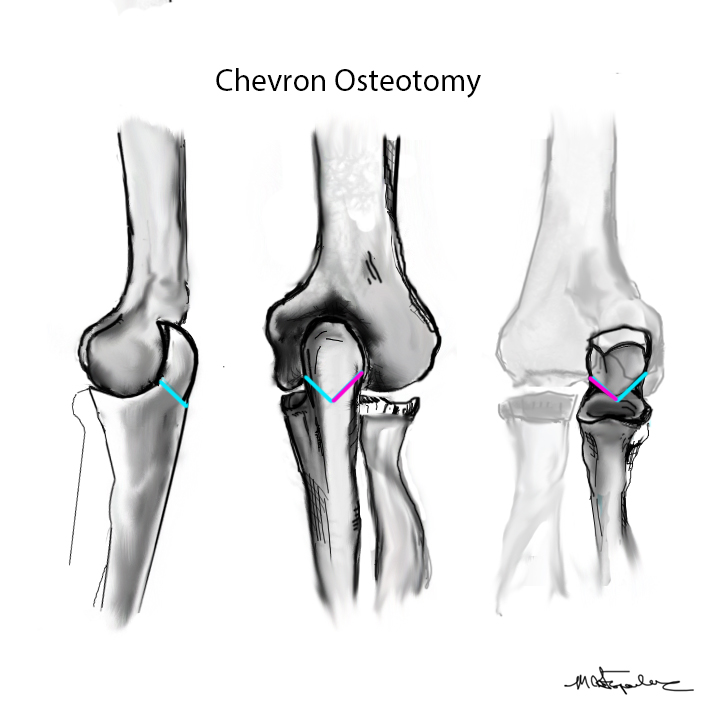
Indication
Complex intra-articular fractures
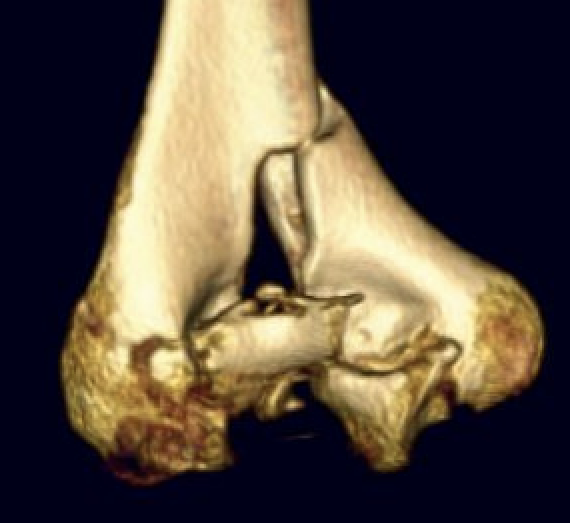
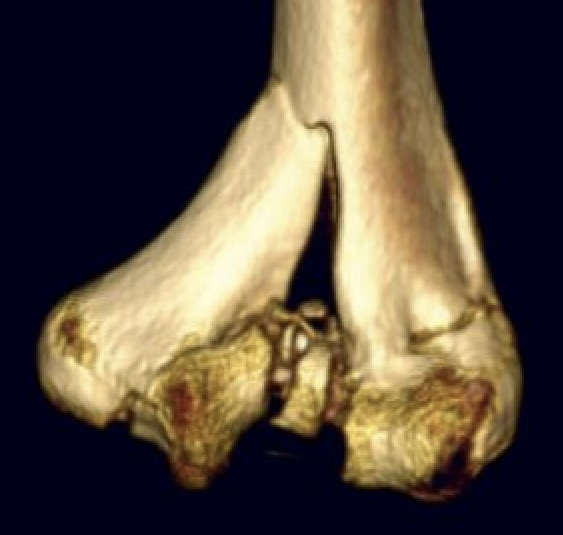
Technique
AO foundation surgery reference Chevron osteotomy
Chevron
- distally based V shaped
- through bare area of olecranon / smallest width of greater sigmoid notch
- 3 cm from tip
Fixation
- TBW v plate v intramedullary screw
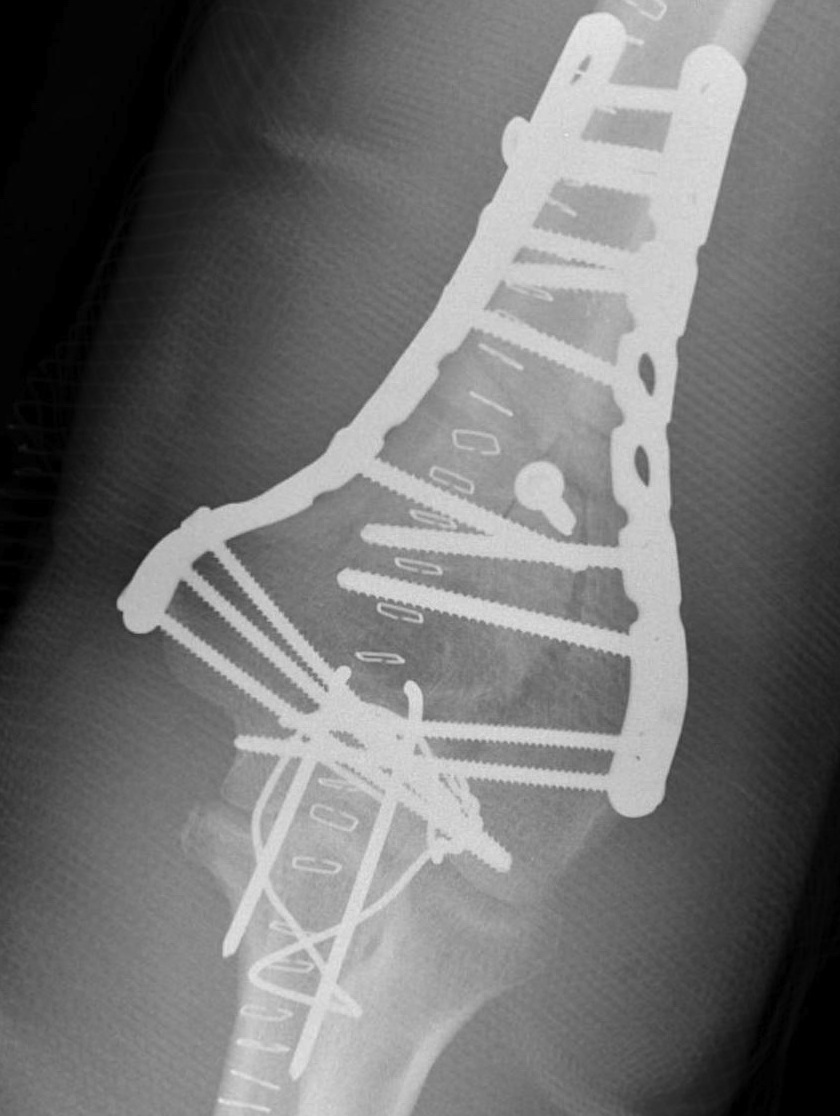
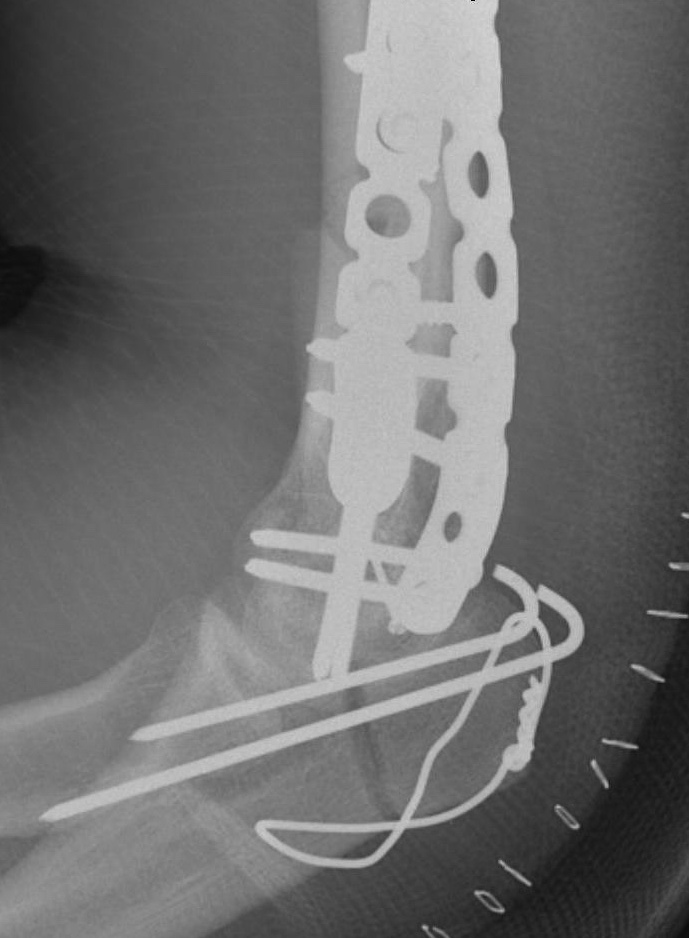
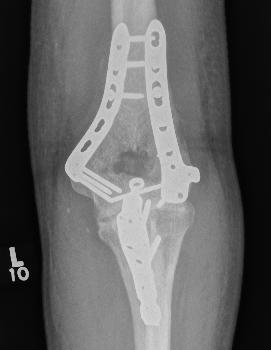
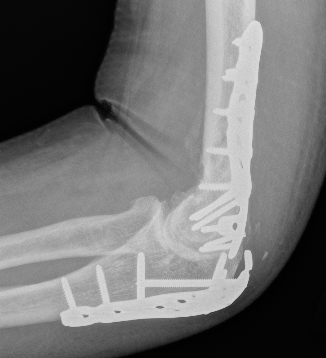
Results
- systematic review of olecranon osteotomy and paratricipital approach
- longer operative time and higher incidence of infection with osteotomy
- no difference in outcome / ROM / hetertopic ossification / ulnar nerve injury
Coles et al J Orthop Trauma 2006
- 67 intra-articular fractures treated with olecranon osteotomy
- no nonunions
Somerson et al Should Elbow 2022
- 63 patients
- 14% wound dehiscence or infection
- 10% symptomatic hardware
- olecranon osteotomy increased re-operation rate
Fixation techniques
Vumedi surgical fixation distal humerus fracture
Options
Precontoured anatomical plates
Parallel plates v perpendicular plates
Locking v non locking screws
Precontoured anatomical plates
Synthes distal humerus plates surgical technique PDF
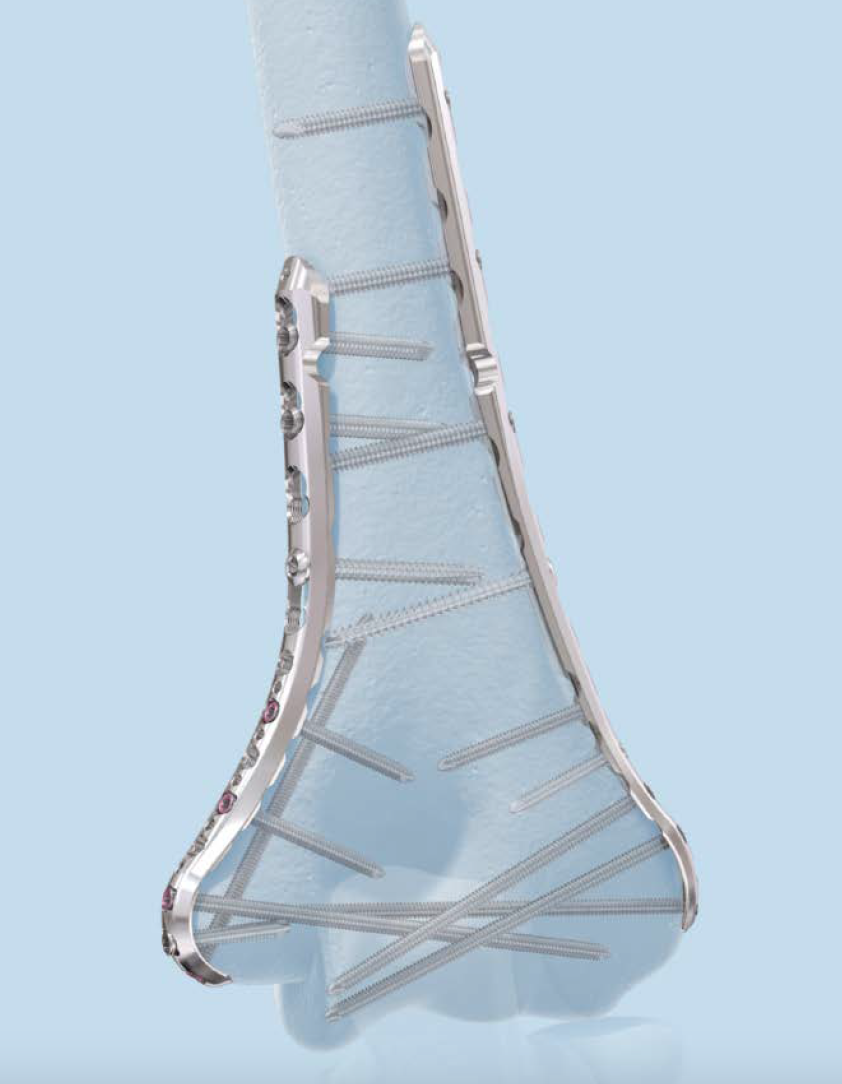

Parallel v perpendicular plates

Parallel plates - medial plate on medial column and lateral plate on lateral column
Perpendicular plates - plates at 90 degrees, with lateral plate posterior
- cadaveric model
- biomechanical superiority of parallel plates versus perpendicular plates
- systematic review of 83 studies and 2362 patients
- parallel plating lower incidence of revision for fixation failure (1% v 6%)
- perpendicular plating reduced overall complication (45% v 54%)
- these complications included lower incidence neuropathy, wound dehiscence, and implant prominence
Results ORIF
- 30 patients at a mean follow up of 19 years
- 87% good or excellent result
- mean flexion / extension arc 106 degrees
- 80% had evidence of OA on xrays
- mostly mild or moderate and not clinically significant
Complications ORIF
Han et al J Orthop Surg Res 2022
- multicentered retrospective study of 349 elbows
- postoperative ulna nerve symptoms 15%
- postoperative radial nerve symptoms 2.4%
- nonunion 4%
- deep infection 2%
- heterotrophic ossification 22%
- significant elbow stiffness 46%
- osteoarthritis 24%
Heterotopic Ossification
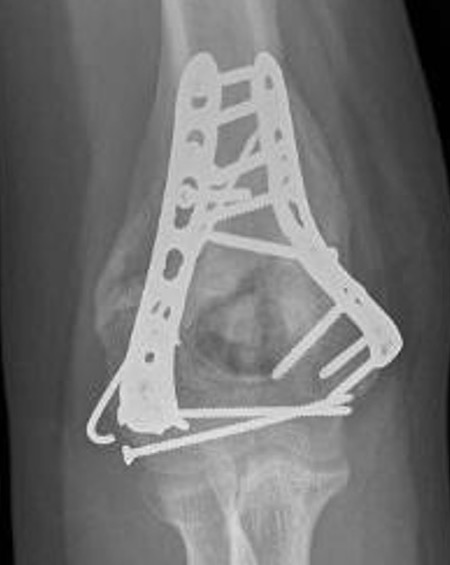
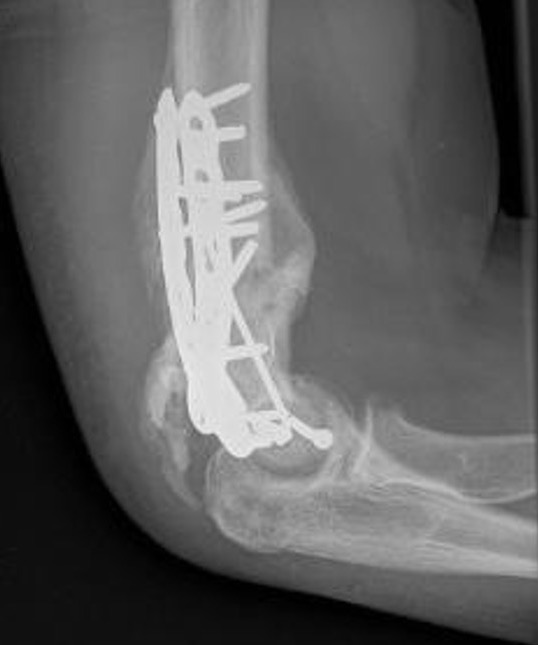
Ulna nerve injury
Chen et al J Orthop Trauma 2010
- patients undergoing ORIF distal humerus
- 48 patients who underwent ulna nerve transposition versus 89 who did not
- 33% ulna neuritis with transposition
- 9% ulna neuritis without transposition
Dehghan et al J Orthop Trauma 2021
- RCT of 58 patients undergoing distal humerus ORIF
- ulnar nerve transposition vs no ulna nerve transposition
- no difference between groups
- significant improvement in both groups over 12 months
Infection
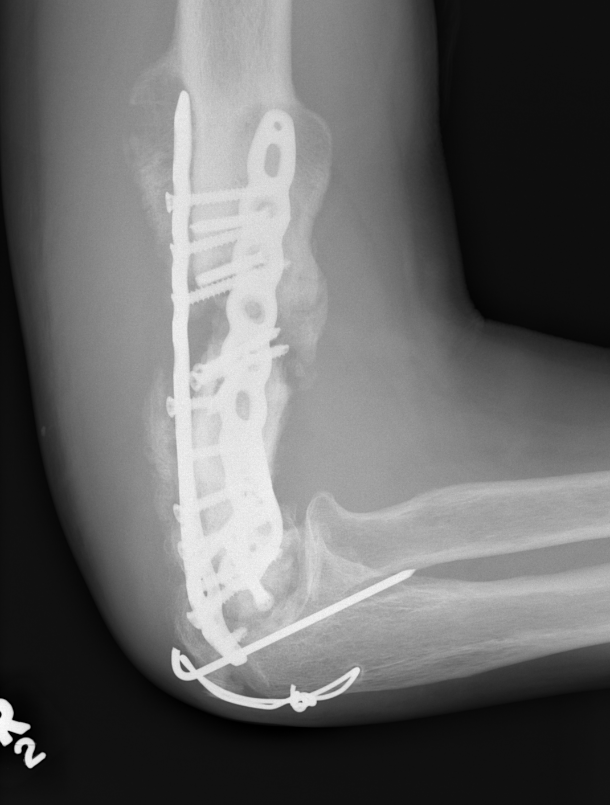
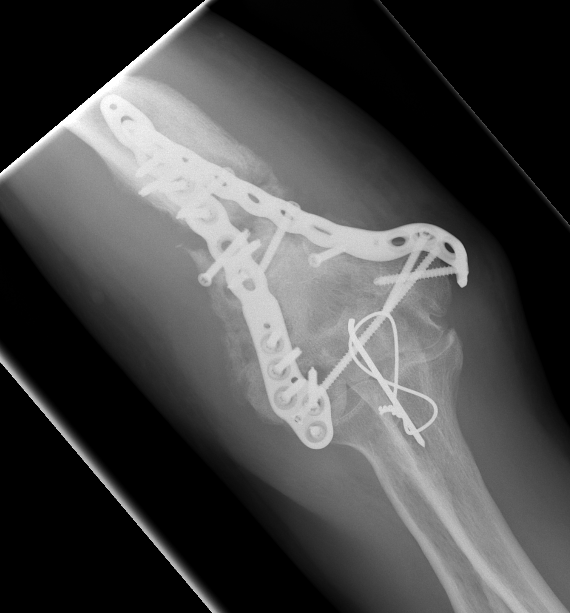
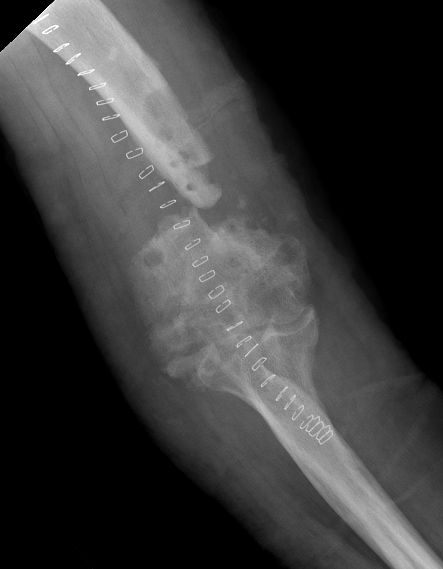
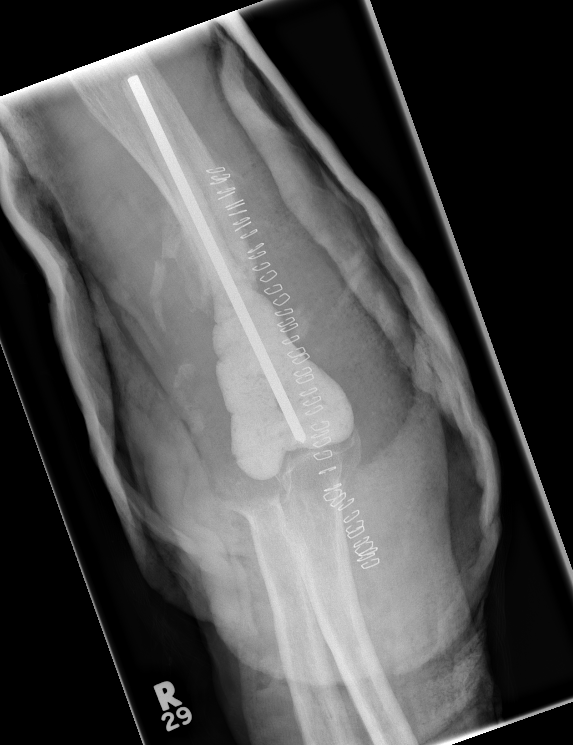
Arthroplasty
Indications
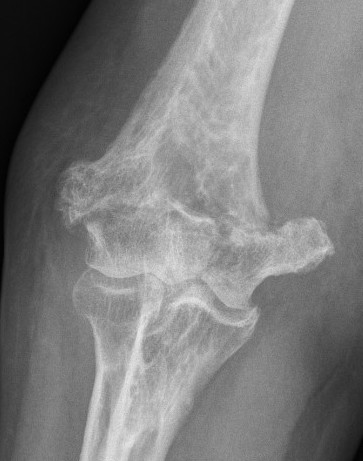
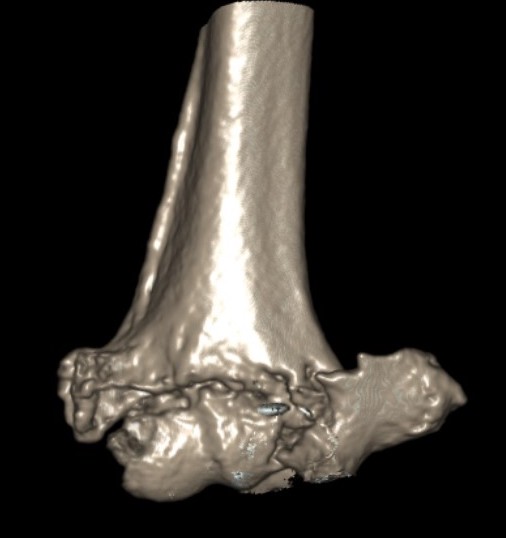
Elderly
Comminuted, osteoporotic distal humerus fracture
Results
Total Elbow Arthroplasty versus ORIF
- RCT 42 patients > 65 years of age
- ORIF verus semiconstrained TEA
- 5 ORIF patients converted to TEA intraoperatively
- better elbow score at 2 years
- no difference in DASH score at 2 years
- mean ROM 107 TEA and 95 ORIF
- systematic review of ORIF v TEA
- better flexion / extension arc and lower reoperation with TEA
- no difference outcome measures
Elbow Hemiarthroplasty versus ORIF
- systematic review of ORIF versus elbow hemiarthroplasty in patients > 50 years old
- no difference outcome measures
- high rate of complications in both
Total Elbow Arthroplasty versus Elbow Hemiarthroplasty
Indications hemiarthroplasty
- younger patient < 65 with unreconstructable fracture
- intact collaterals
Advantages
- able to lift heavier weight
Disadvantage
- instability
- late wear of olecranon cartilage
- RCT of 40 patients > 60 years of age
- hemiarthroplasty versus TEA
- no difference in outcome at 2 years
Technique
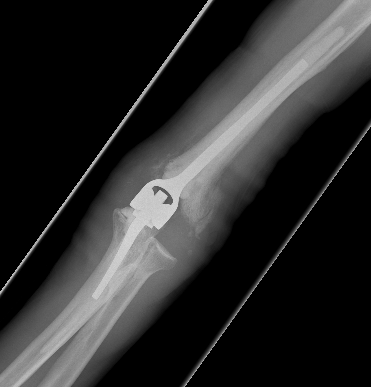
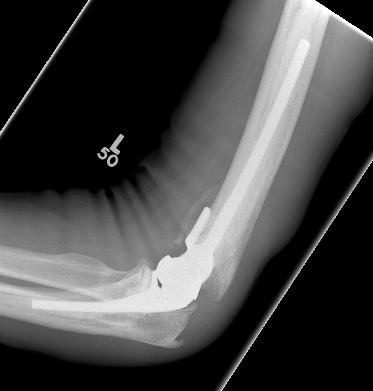
Vumedi Total Elbow Arthroplasty for distal humerus fracture
Vumedi Distal humerus replacement via triceps split
