Definition
A highly malignant tumor composed of small round cells
Second most common bone malignancy in childhood and adolescence
Genetics
Likely of neurogenic origin
Balanced translocation t11;22
Location
Central
- pelvis (12%)
- scapula / vertebrae / rib / sacrum
Peripheral
- femur (20%) / humerus (11%) / fibula
Epidemiology
Usually 2nd decade
- 5-30 years
- peak 10 years
Male:Female 3:2
History
Pain and swelling
± Systemic symptoms
- fever, weight loss, malaise
Examination
Usually large soft tissue mass
Bloods
Elevated WCC, ESR
Elevated LDH associated with poorer prognosis
Xray
Often diaphyseal
- diffuse permeative destruction
- can be subtle
Periosteal reaction
- Codman's triangle / onion skinning / sunburst appearance
Sunburst appearance
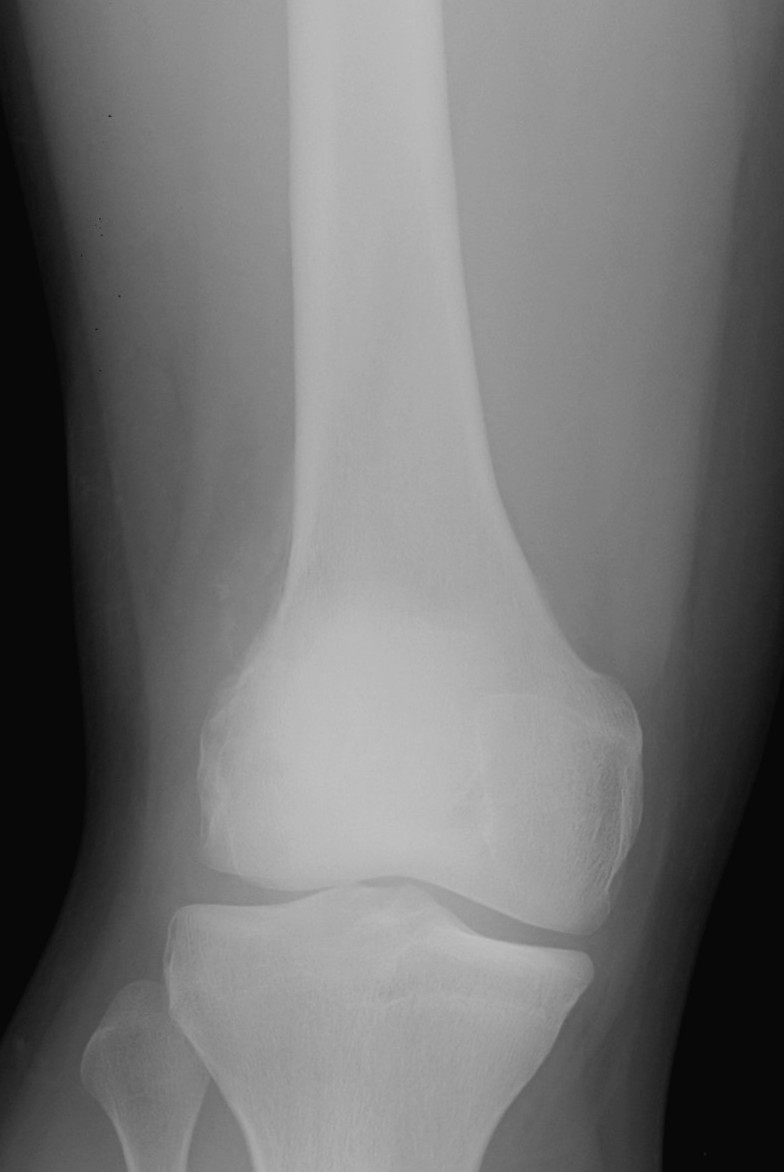
Onion skinning lateral distal femur

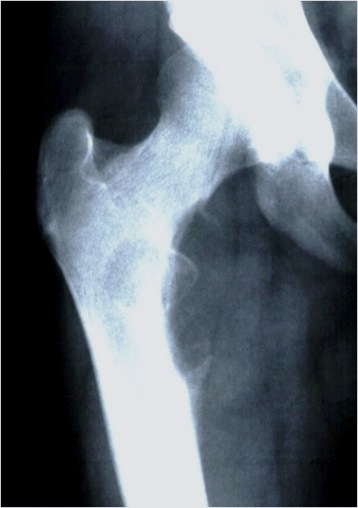
Ewing's acomion Ewings lesser trochanter
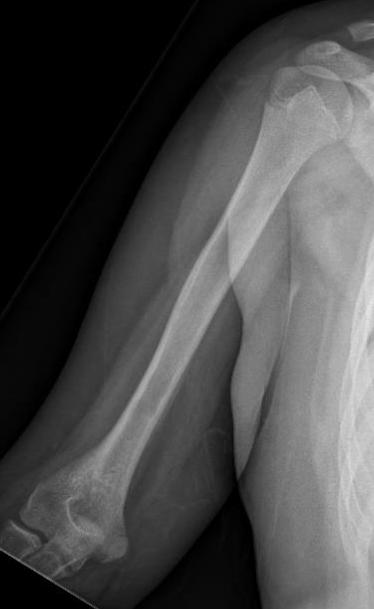
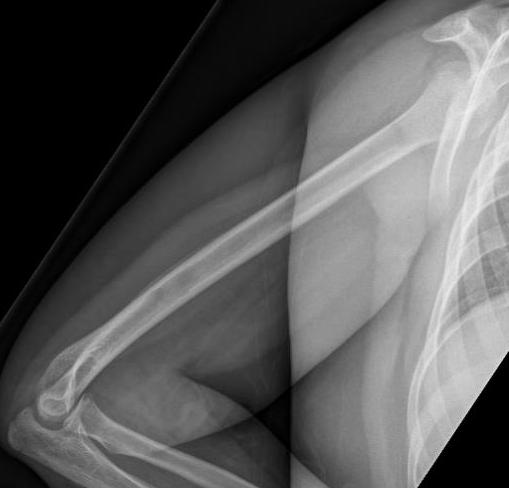
Subtle periosteal reaction humerus
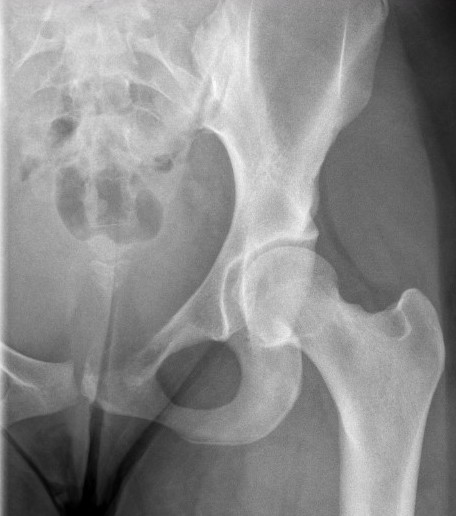
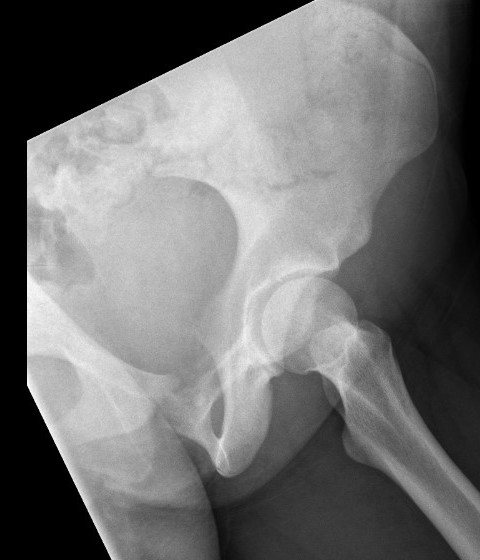
Ewings superior pubic rami
Differential diagnosis
Ewing's / lymphoma / osteomyelitis / eosinophilic granuloma
MRI
Low signal intensity of T1 / high signal intensity on T2
- intramedullary extent
- skip lesions
Significant soft tissue mass with significant edema
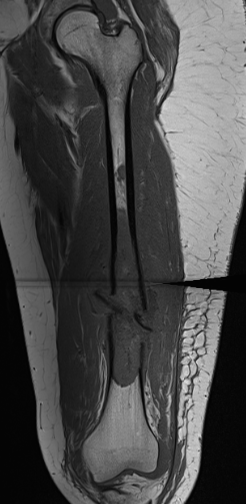
Pathological fracture with skip lesion
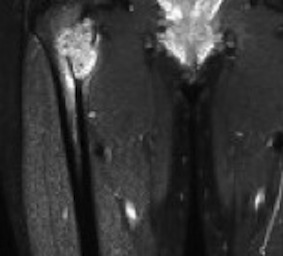
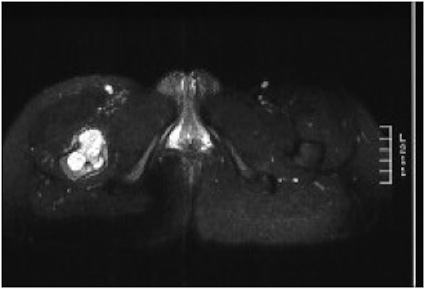
Ewing proximal femur

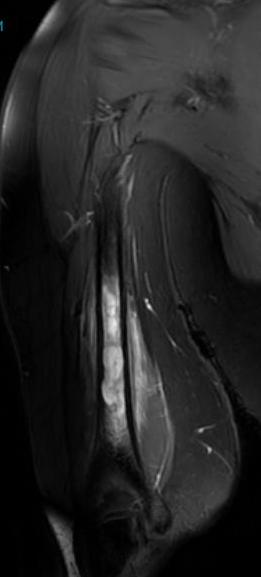
Ewing's humerus
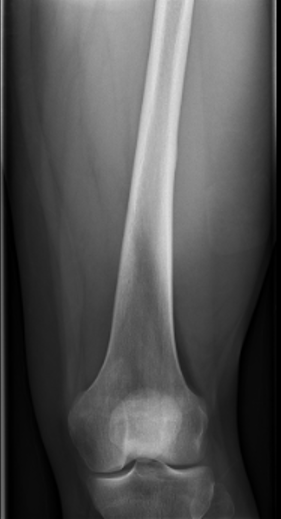
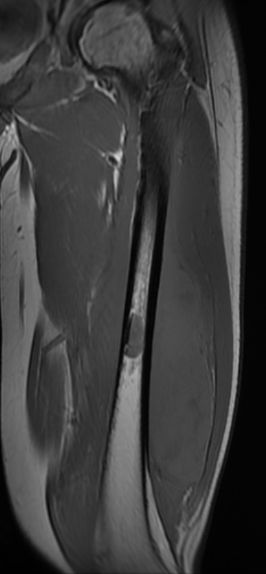
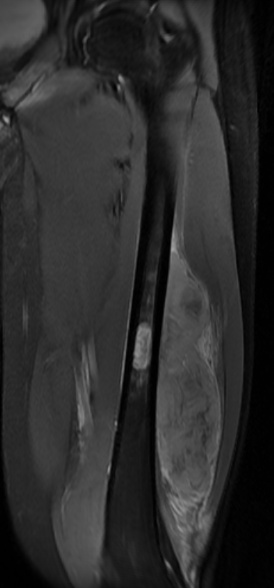
Ewing's femoral diaphysis, subtle on xray with large soft tissue component
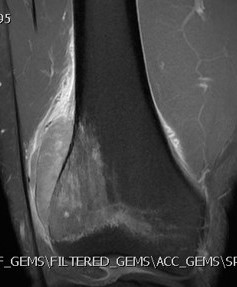

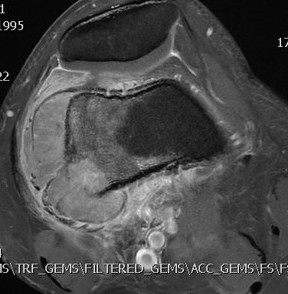
Ewing's distal femur
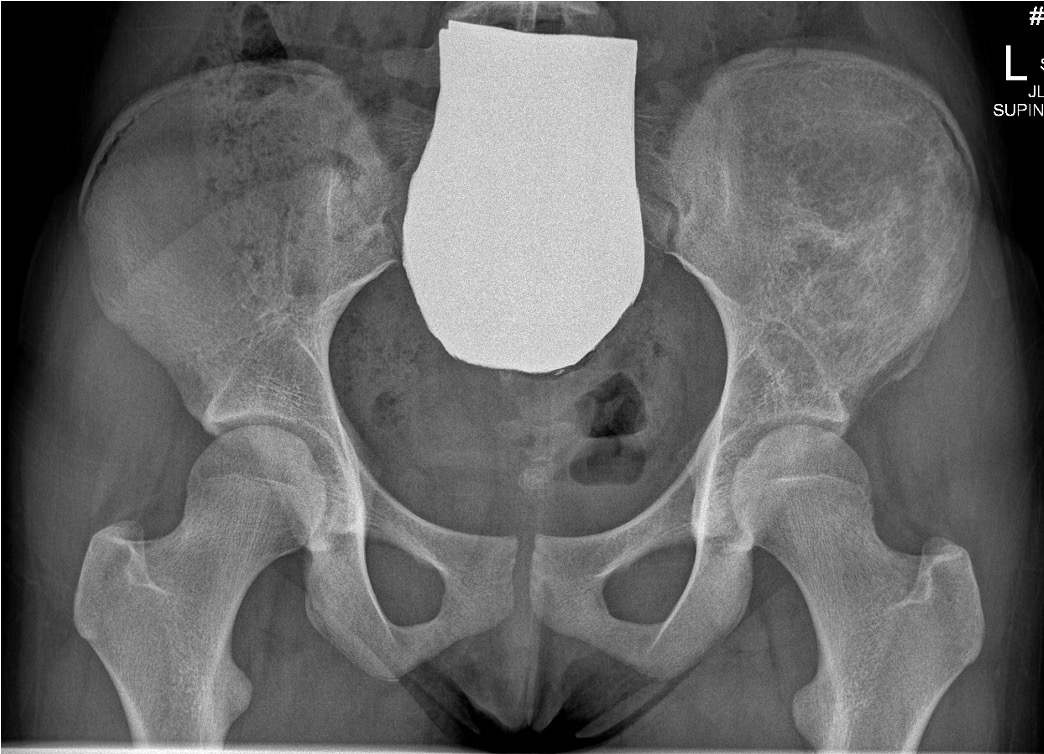
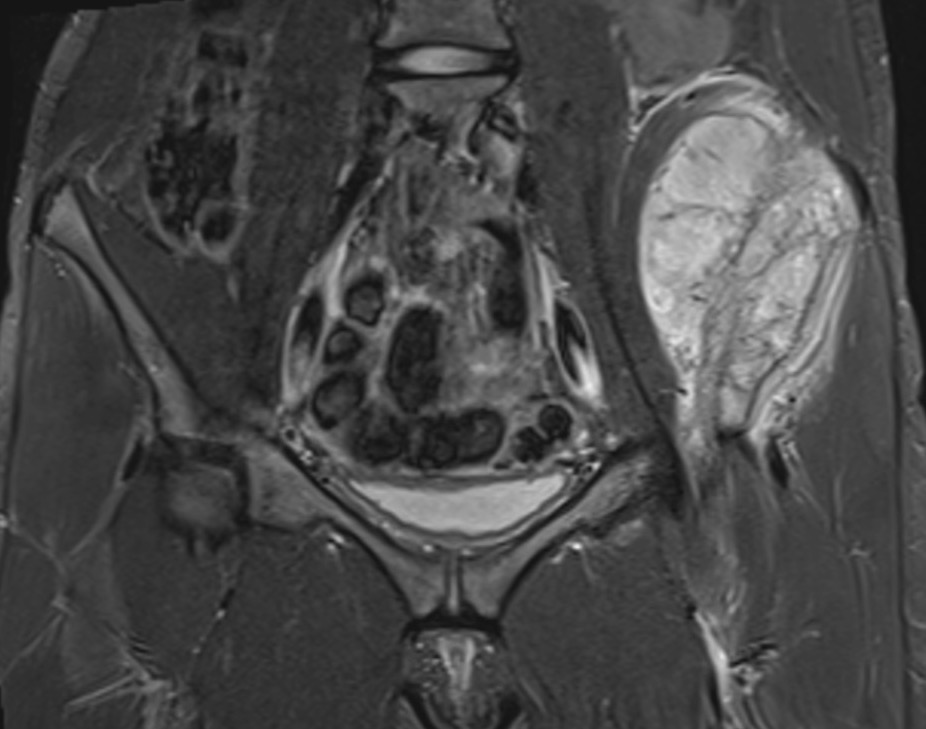
Ewings iliac crest
CT
Bone Scan
Look fo occult bone metastases
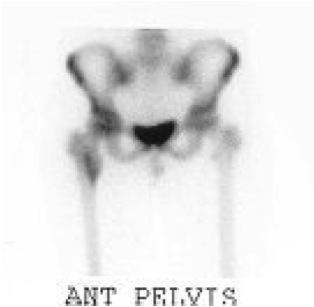
Ewings proximal femur involving femoral head
Chest Xray
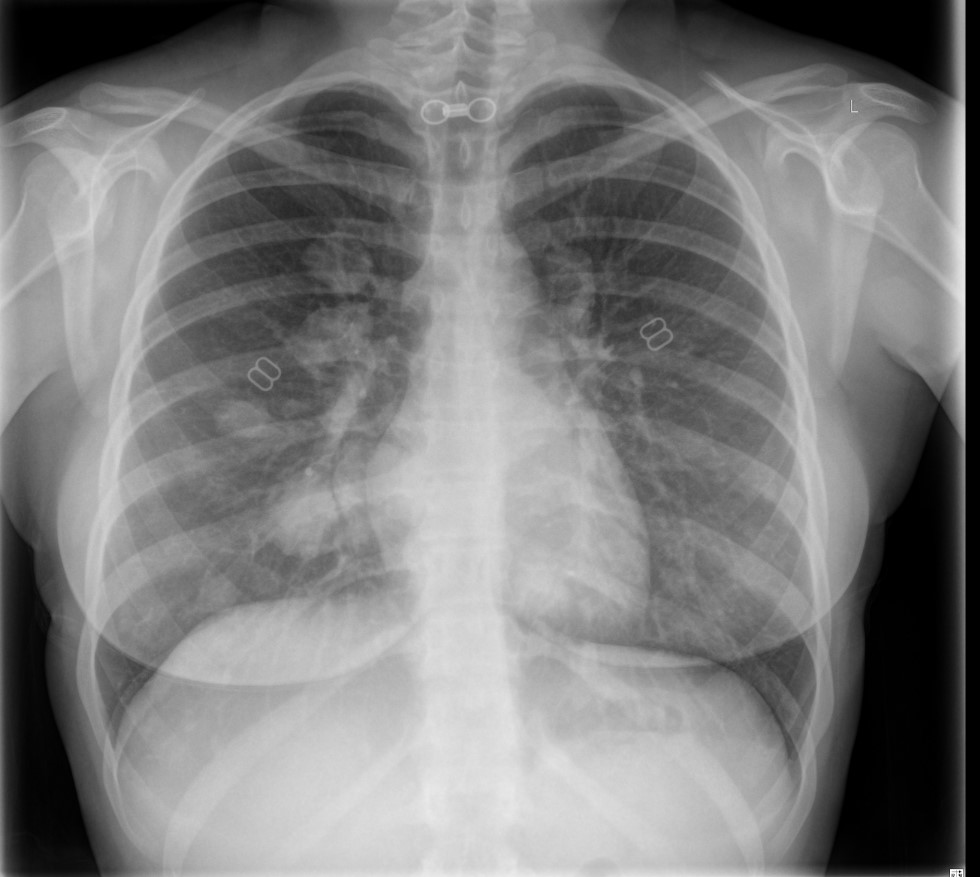
Chest metastasis
Histology
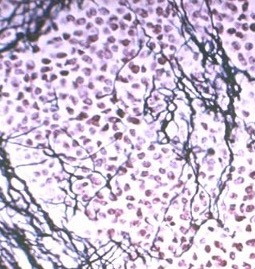
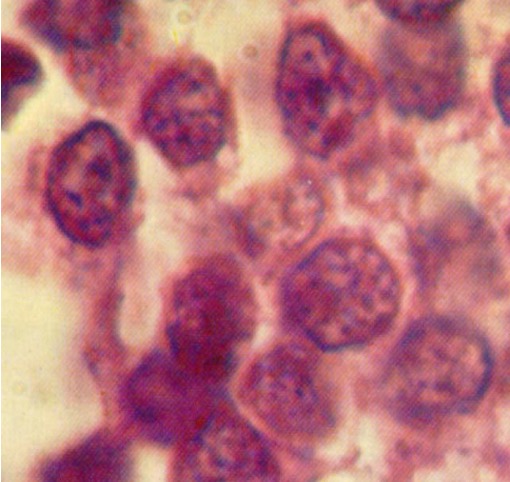
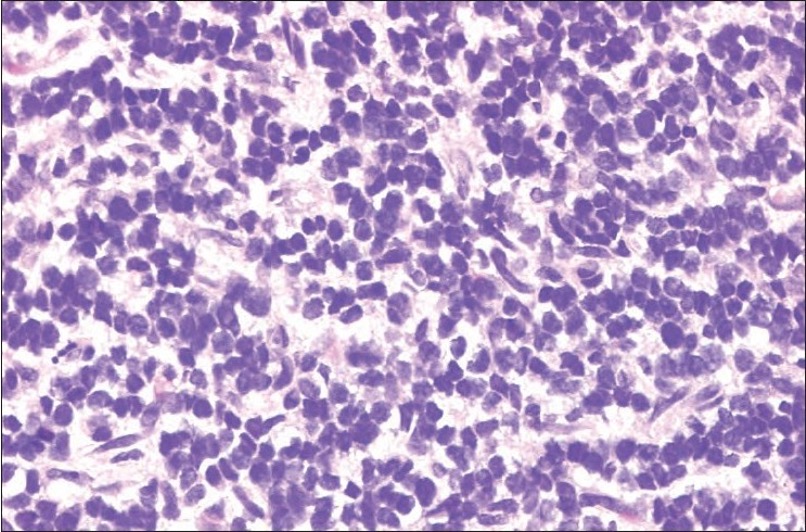
Sheets of uniform round cells
- distinct nuclei with minimal cytoplasm
- abundant glycogen
- positivity for neural markers such as S-100 protein / vimentin
Rosette formation
- indicative of neural differentiation
Differential diagnosis histology of small round cell tumors
- histology / immunohistochemistry / electron microscope / cytogenetics
| DIfferential Diagnosis | Immunohistochemisty | Electron microsope | Cytogenics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ewings |
PAS reaction positive 90% - stains glycogen and mucin |
Positive to vimentin / S100 / MIC 2 |
EWS-FLI1 fusion gene t(11;22) translocation |
||
| PNET (Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumour) |
Older population Worse prognosis |
Positive to vimentin / S100 / MIC 2 |
t11;22 translocation |
||
| Lymphoma | Common leukocyte antigen | ||||
| Rhabdomyosarcoma | Actin / desmin / myoglobin positive |
Cytoplasmic filaments Occasional Z bodies |
|||
| Metastatic neuroblastoma | PAS reaction positive | Negative to vimentin, MIC 2 |
Cytogenics
EWS-FLI1 fusion gene from t(11;22) translocation seen in 85% of Ewing's
Le Deley et al J Clin Oncol 2010
- European Ewing study group
- 565 patients
- studied different types of fusion genes
- no difference in prognosis or outcomes
Bone marrow biopsy
Cesari et al Paediatr Blood Cancer 2019
- 504 cases of Ewing's
- incidence of positive Ewing's on biopsy was 2%
- of these 11/12 had known metastasis on imaging
- suggest reconsidering bone marrow biopsy as part of staging for Ewing's
Management
Algorithm
1. Neoadjuvent chemotherapy
2. Restage
3. Surgical resection
4. Chemotherapy
5. Radiotherapy - if margins inadequate
Preoperative Chemotherapy
Aim
- eradicate micrometasis
- reduce tumor volume for resection
- guide postoperative chemotherapy
VACD Regime (Vincristine / Actinomycin / Cisplatin / Doxorubicin)
Alternate with Iphosphamide / Etoposide
Restage
See response following neoadjuvent chemotherapy
- MRI of affected region
- CT Chest
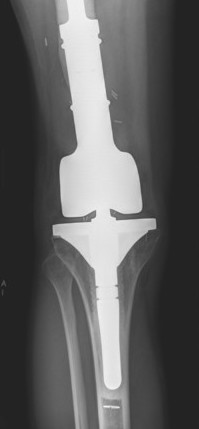
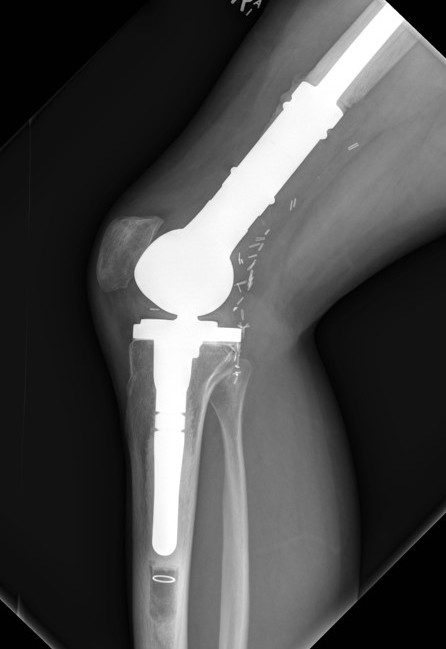
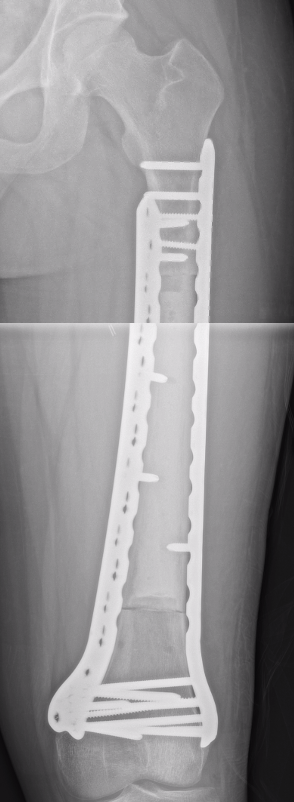
Wide Resection - limb salvage / amputation
2 cm margin of normal tissue if able
Assess histological response

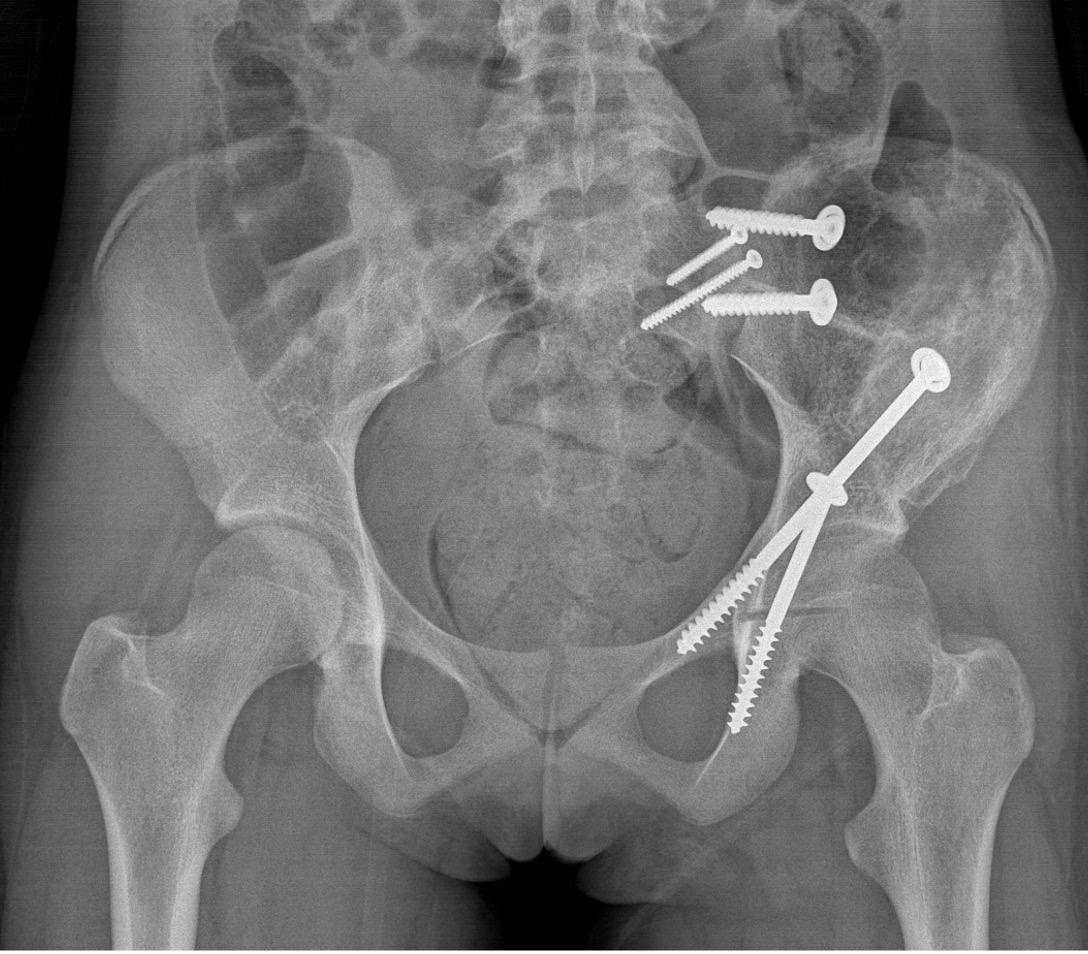
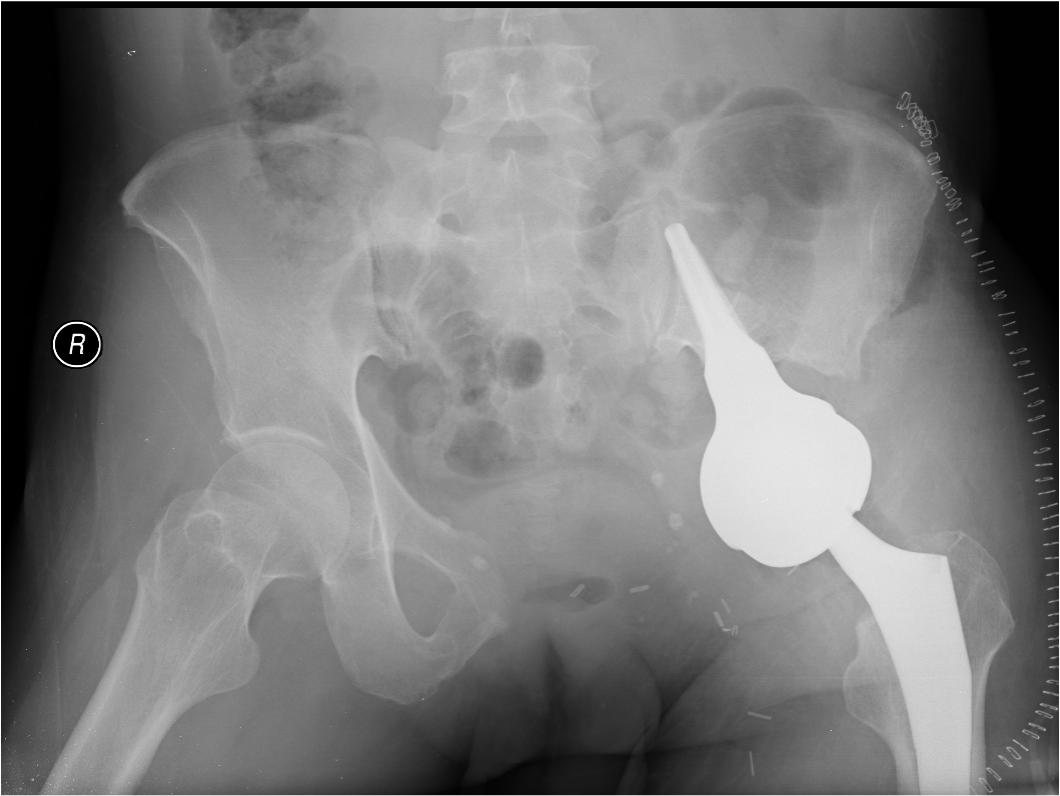





Radiotherapy
Indications
- inadequate margins
- non resectable
- poor response to chemotherapy
Prognosis
1. Location
Lower survival with central Ewing's
Brown et al Cancer Treat Res Comm 2022
- 296 / 1152 (26%) patients with Ewing sarcoma of the pelvic bones
- metastasis in 46% at time of diagnosis
- only 29% received surgical resection
- 5 year survival 40%
- 10 year 42%
- higher metastasis and lower survival compared to non pelvic Ewing's
- 339 pelvic Ewing's
- 47% had metastasis at time of diagnosis
- 180 patients localized disease evaluated
- sacral tumors 5 year survival 72%
- innominate bone tumors 5 year survival 56%
2. Disease volume
Paulussen et al J Clin Oncol 2008
- 647 patients randomized to chemotherapy based upon tumor volume
- < 100 mls versus > 100 mls
- < 100 mls 5 year survival 68%
- > 100 mls 5 year survival 52%
3. Metastasis
Ladenstein et al J Clin Oncol 2010
- 281 patients with disseminated Ewings
- treated with chemotherapy / surgery / chemotherapy / stem cell transplant
- 3 year disease free survival 27%
4. Response to chemotherapy
Albergo et al Bone Joint J 2016
- 293 patients without metastasis
- survival based on guide to chemotherapy
- 0 - 50% necrosis: 5 year survival 49%
- 51 - 99% necrosis: 5 year survival 72%
- 100% necrosis: 5 year survival 94%
5. Resectable disease
- 143 patients average age 10 with localized Ewing's
- 5 year survival 77%
- higher with resectable disease
