Definition
Patellar Tendinitis
Epidemiology
Most common in athletes
- especially if involved in running, jumping and kicking
- over use injury
Basketball players
Aetiology
Chronic overload v inferior patella impingement
Schmidt et al Am J Sports Med
- dynamic MRI in patients with jumper's knee v controls
- no evidence of impingemnt
- concluded that chronic overload main cause
Incidence of inferior patella spurs
- likely part of pathology
Clinical Features
Insidious onset of pain at inferior pole of patella
- initially after activity only, worse as cools down
- localised tenderness at inferior pole
- may progress to rupture
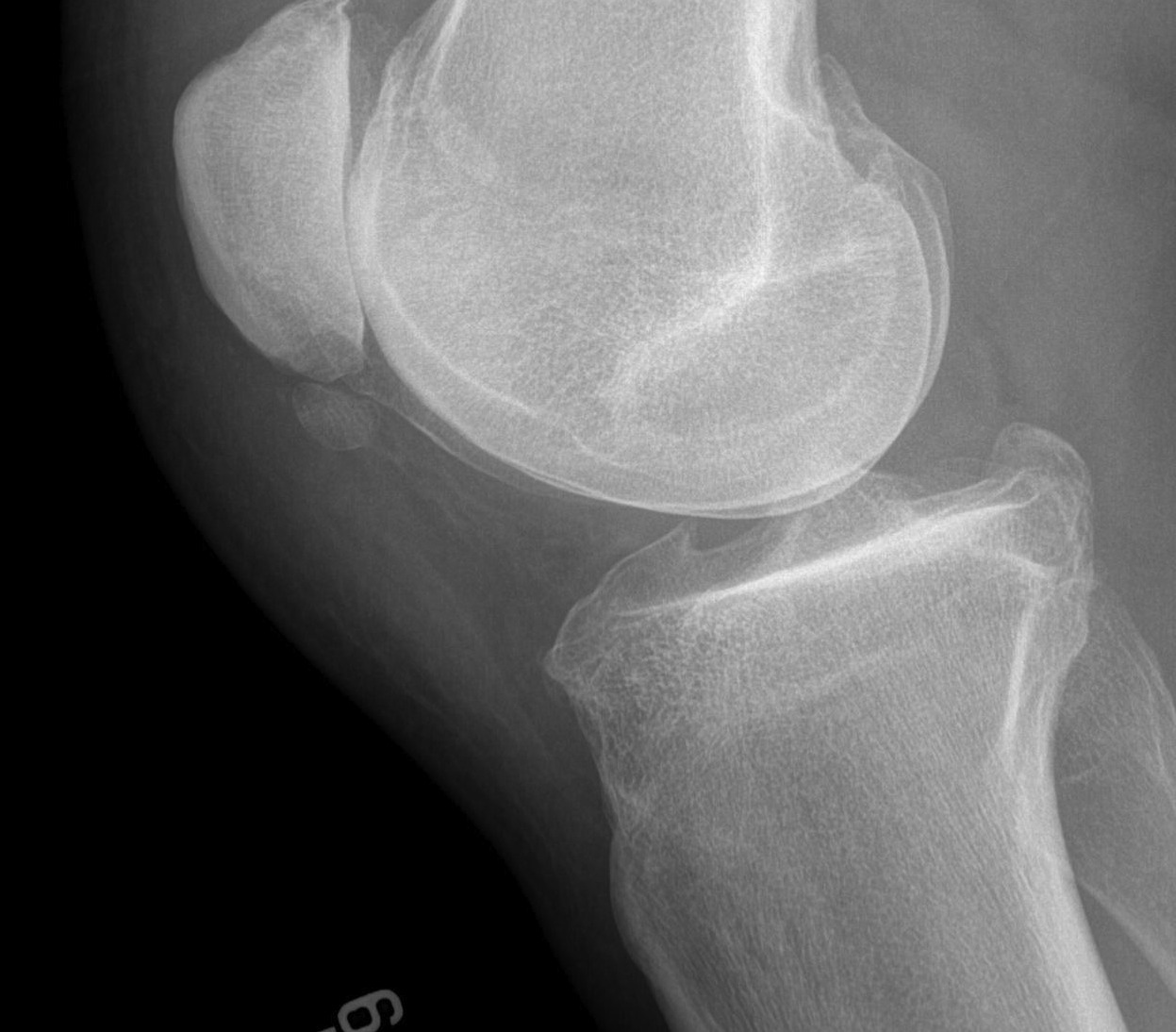
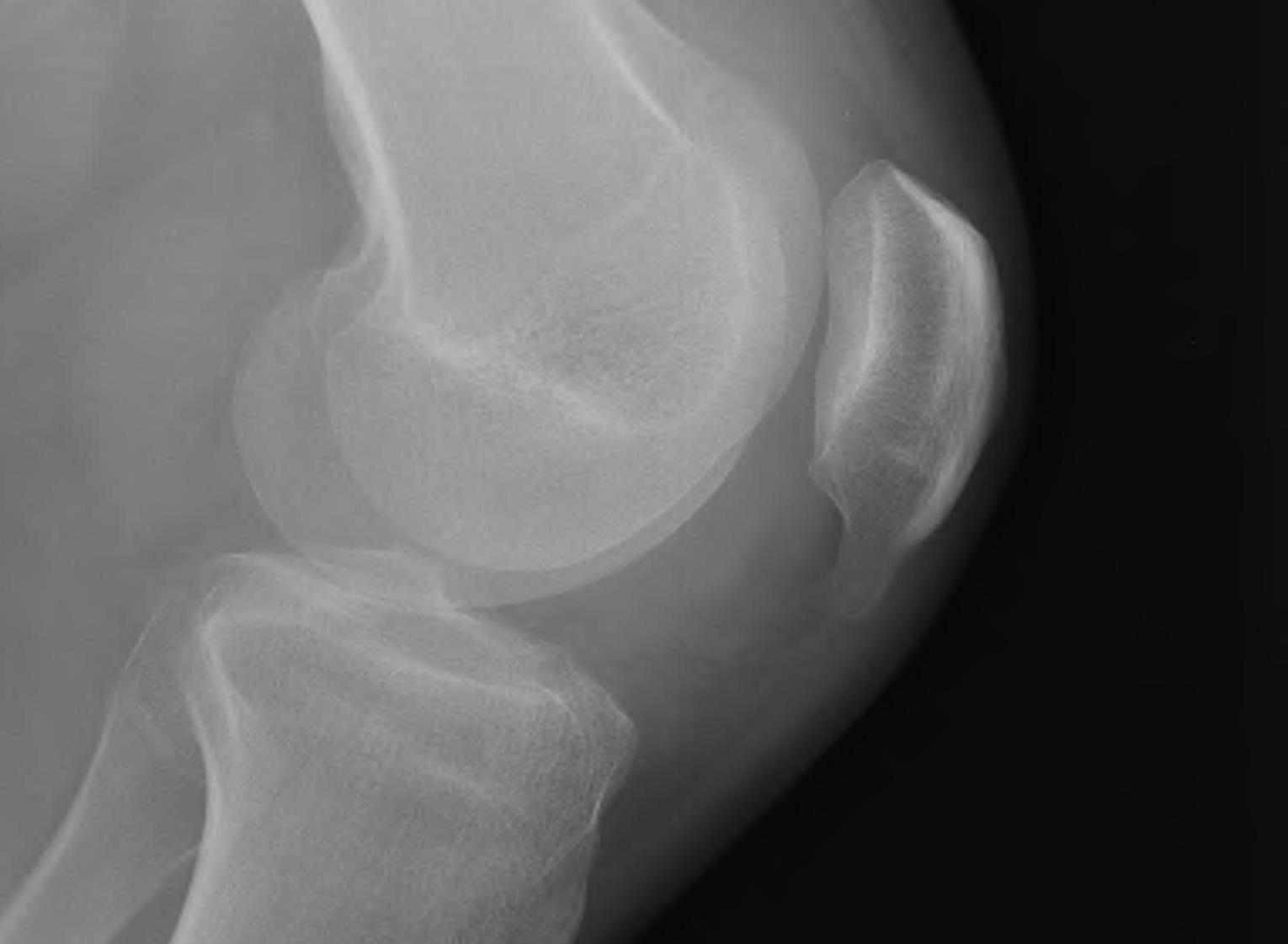
X-ray
Usually normal
May see
- traction spurs
- calcification of patella tendon
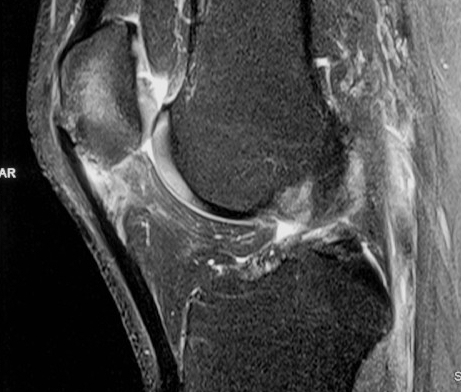
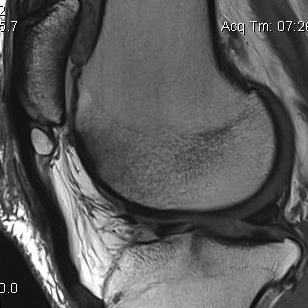
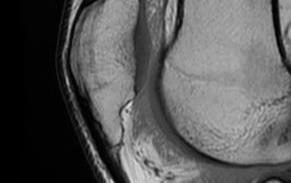
MRI
Cyst / Degeneration
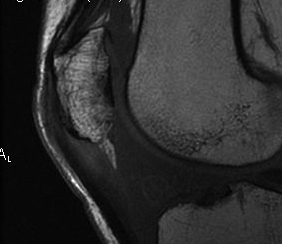
Traction spurs / calcification / ossicles
Non-operative
Activity modification
Rest 6/52
- warm up & stretching
- ice & NSAIDS
Sport rehabilitation protocol
Concentration on eccentric exercises
- decline squats on a 25o decline board
Jonsson et al B J Sports Med 2005
- RCT of concentric v eccentric quads exercises
- superior results with eccentric
Engebretsen et al JBJS Am 2206
- RCT of eccentric rehab v surgery
- no advantage surgery
- recommended minimum 12 weeks non operative treatment in all cases
HCLA
Contra-indicated
Platelet Rich Plasma
Fillardo et al Int Orthop 2010
- compared three injections PRP 2 weeks apart in 15 chronic patients
- compared wth 16 patients treated with physiotherapy alone
- significant improvements in PRP group
Charousset AJSM 2014
- 3 consecutive US guided PRP into tendon defect
- sucess in 21 / 28 athletes
ECSW
Vulpiani et al J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2007
- 4 sessions every 2 days
- 73% successful in all patients
- 87.5% successful in athletes with return to sport at 6 weeks
Operative
Indications
Fails to resolve & interferes with activity
Technique
Arthroscopy
1. Resection fat pad
2. Resection posterior inflammed portion of tendon
3. Careful burr resection of inferior pole patella
- 1 - 2 mm
- does't affect patella tendon insertion
- removes source of impingement
- likely stimulates healing process
Results
Lorbach et al Arthroscopy 2008
- arthroscopic debridement inferior pole patella in 20 patients
- 18/20 good or excellent results
Pascarella AJSM 2011
- arthroscopic debridement undersurface of tendon / tendinopathy
- excise distal pole
- success in 66 / 73 knees
- RTS by 3 months
