Definition
Complex sprain
- pain after ankle sprain
- suggests another injury
- sytematic review of 31 studies following acute lateral ligament injury
- up to 33% patients still have pain 1 year after acute ankle sprain
Differential diagnosis
1. Soft tissue
- anterolateral impingement
- Bassett's ligament
2. Bony Injury
- osteochondral lesion / loose body
- fracture anterior calcaneum / lateral process talus / sustenaculum tali
3. Tendon / ligament
- high ankle sprain / syndesmotic injury
- peroneal dislocation / tears
- sinus tarsi syndrome
- Achilles tendonitis
Soft Tissue
Anterolateral impingement
Causes
- synovitis around torn or injured ATFL
- scarring in lateral gutter
Symptoms
- pain and swelling lateral gutter
Molloy test
- pain with dorsiflexion and pressure to anterolateral groove
Treatment
- ankle arthroscopy
- anterolateral tibio-talar synovectomy
Bassett's ligament
Thickened accessory (AITFL)
Bony Injury
Osteochondral lesion
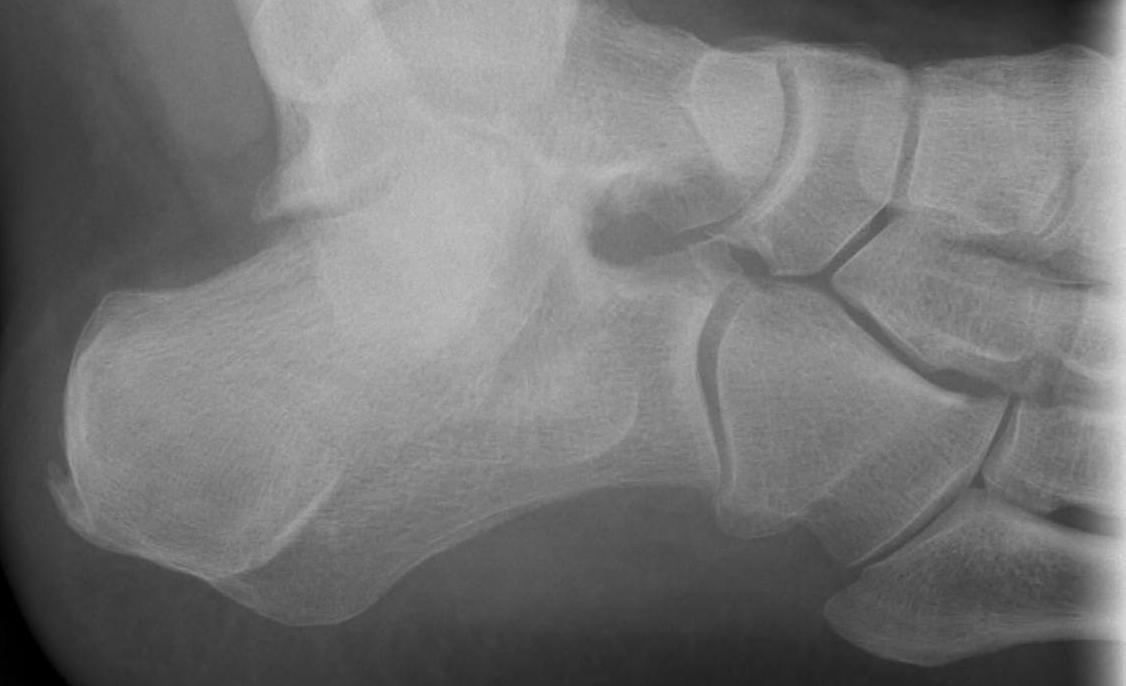
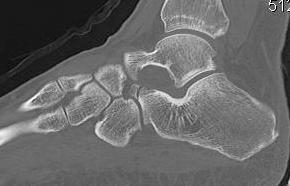
Fracture anterior process of calcaneum
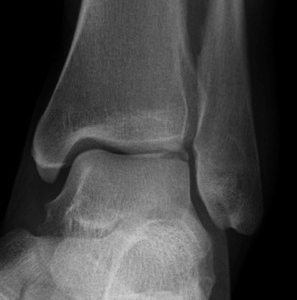
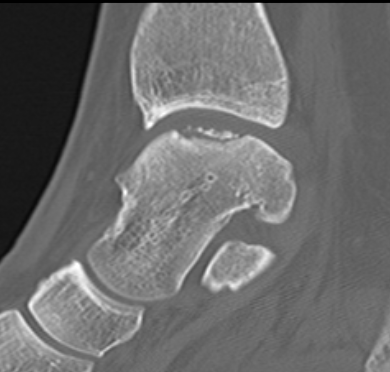
Fracture lateral process of talus
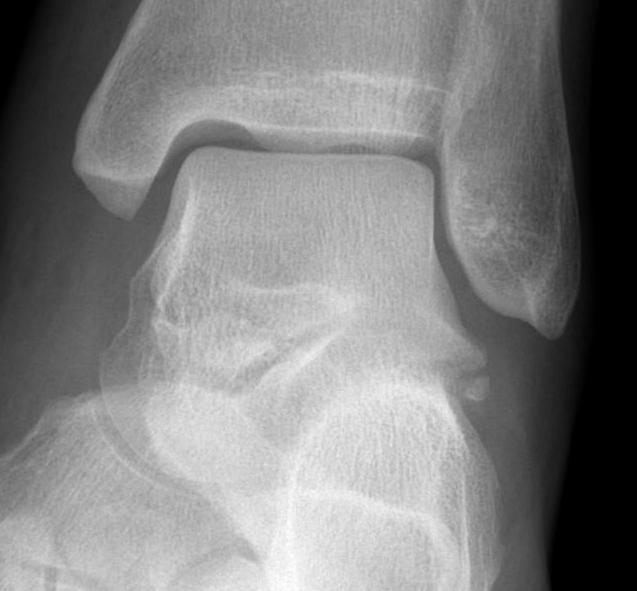
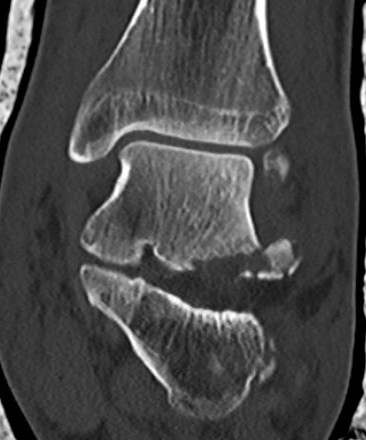
Fracture Sustenaculum Tali
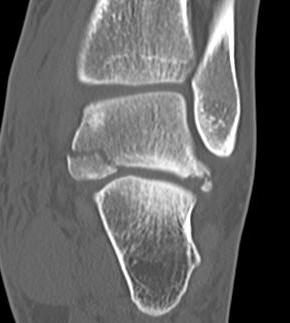
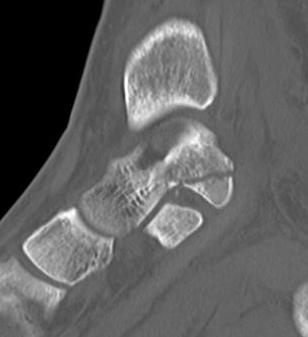
Tendon / Ligament
High ankle sprain / syndesmotic injury
Peroneal dislocation / tendonitis / tears
Sinus Tarsi Syndrome
Injury to interosseous ligament between talus and calcaneum
Achilles tendonitis
