Adamantinoma & Osteofibrous Dysplasia
Definition
Rare low-grade malignant tumour
- cell of origin unknown
Epidemiology
Usually second or third decade of life
Site
90% diaphysis of tibia
Mandible
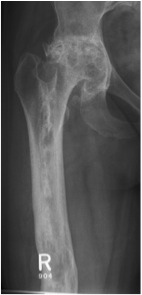
X-ray
Most common anterior cortex of tibia
Rare low-grade malignant tumour
- cell of origin unknown
Usually second or third decade of life
90% diaphysis of tibia
Mandible
Most common anterior cortex of tibia
Systemic Connective Tissue Disease
Chronic inflammatory disease resulting from abnormal immunoregulation
Unknown
Thought similar to RA
1. Genetic factors
2. Environmental factors
Young females
F:M 9:1
Peak 35 years old
Acute disease
- characterised by generalized rigidity & convulsions
- caused by exotoxins/neurotoxins produced in Clostridia Tetani infections
Annual world mortality is 1 million
West 15-100/year
Clostridium Tetani
- anaerobic
- spore-bearing Gram positive Bacillus
Clostridial Myonecrosis
- necrotizing, gas producing infection of skeletal muscle 2° Clostridia
- life threatening & rapidly progressive
There are 3 types of bacterial gas-forming infections
1. Classical clostridial gas gangrene
- rapid onset of sepsis / couple of days
- muscle nearly always involved
- critically ill immediately following an open injury
Very rare
- Mainly affects children
Characterised by multiple osteomyelitic changes
- predominantly in metaphyseal region of long bones
All cultures negative
Antibiotics do not affect course of disease
Pain is most common symptom
Stage the infection, the host & the management
1. Stage host / maximise healing potential
2. Stage infection / MCS / sensitivities
3. Debride all infected bone and ST
4. Stabilise skeleton
5. Eliminate dead space
6. Soft tissue coverage
Definition
Infection of bone 2° blood-borne bacteria
Most common children
- peak 10 years
True haematogenous OM rare in adults
- usually involves spine
M: F 2:1
Most common femur & tibia
Joint inflammation secondary pyogenic organism
All age groups
Usually children
- 50% < age 3
M= F
Any joint
- Infants = Hip
- Children = Knee
- Adults = Large Joints
IVDU - SCJ & SIJ
Two Routes
Dystrophic or Metastatic
1. Metastatic
- hypercalcaemia / hyperphosphatemia
2. Dystrophic
- more common
- onto damaged connective tissue
- tendon / ligament / cartilage
- calcific tendonitis shoulder
- Pellegrini-Steida lesion MCL
Deposited around chondrocytes & into avascular portion of CT