Hip arthroscopy
Indications
Labral tear
Cam / pincer impingement
Loose bodies / trauma / synovial proliferation
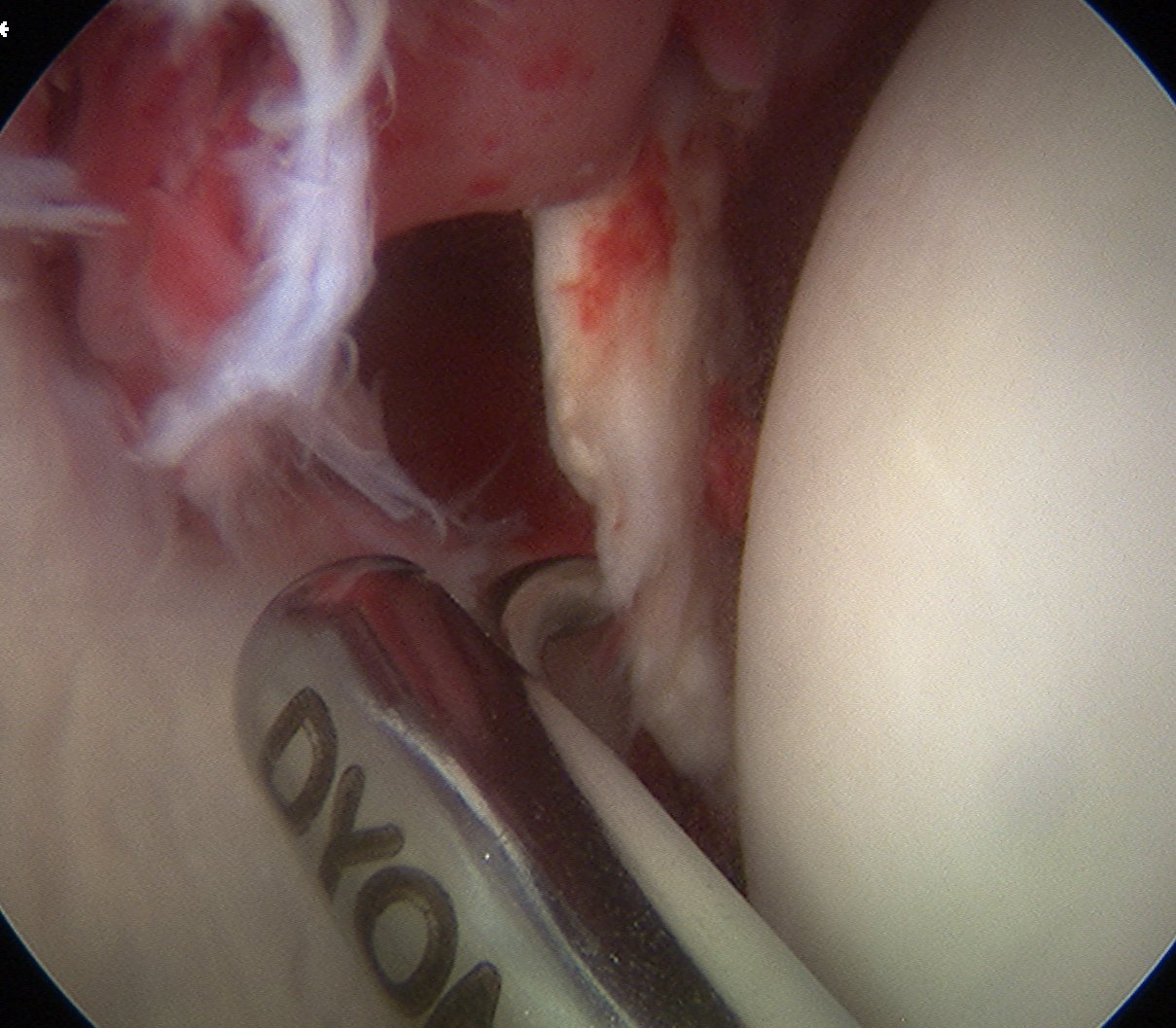
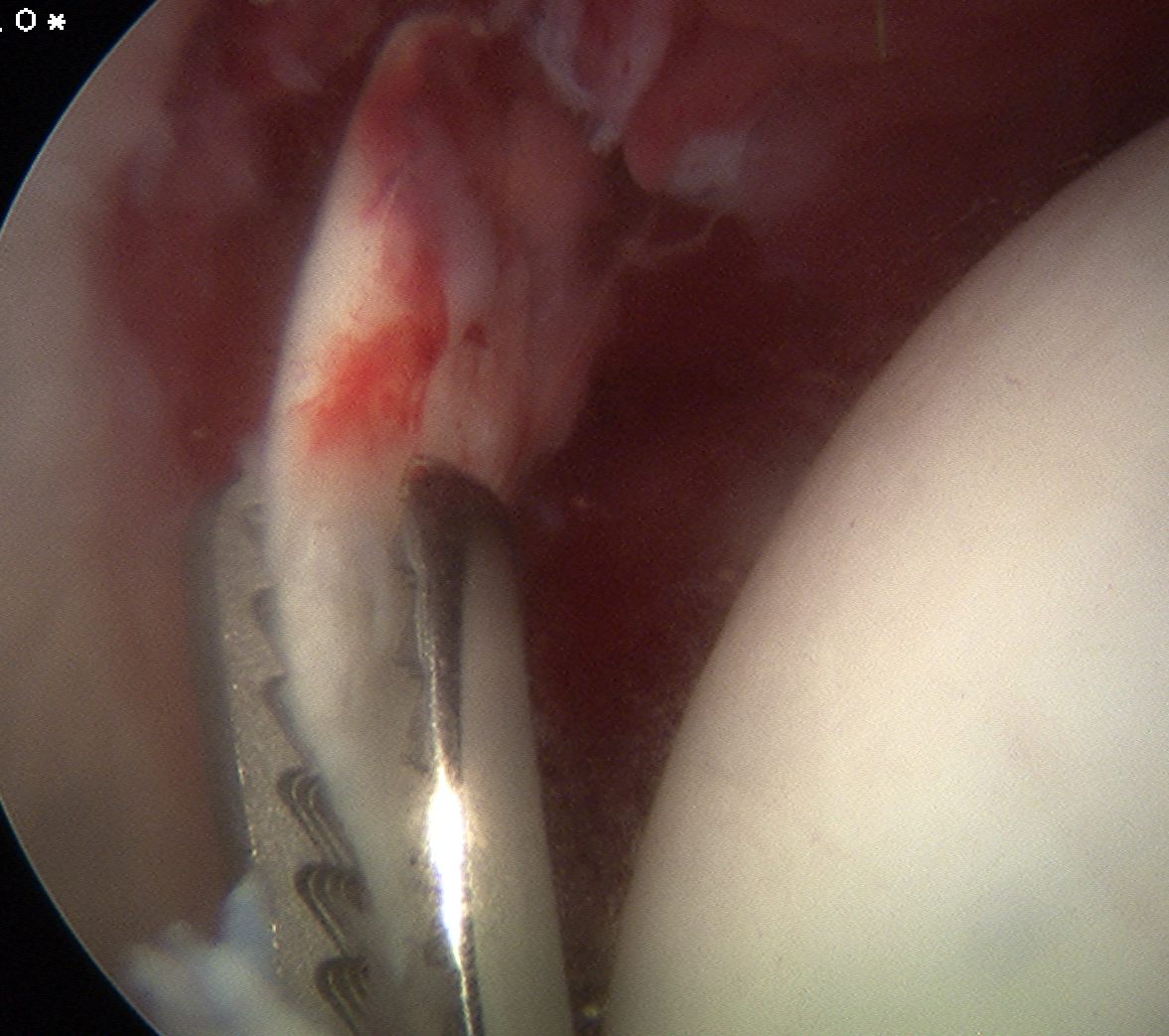
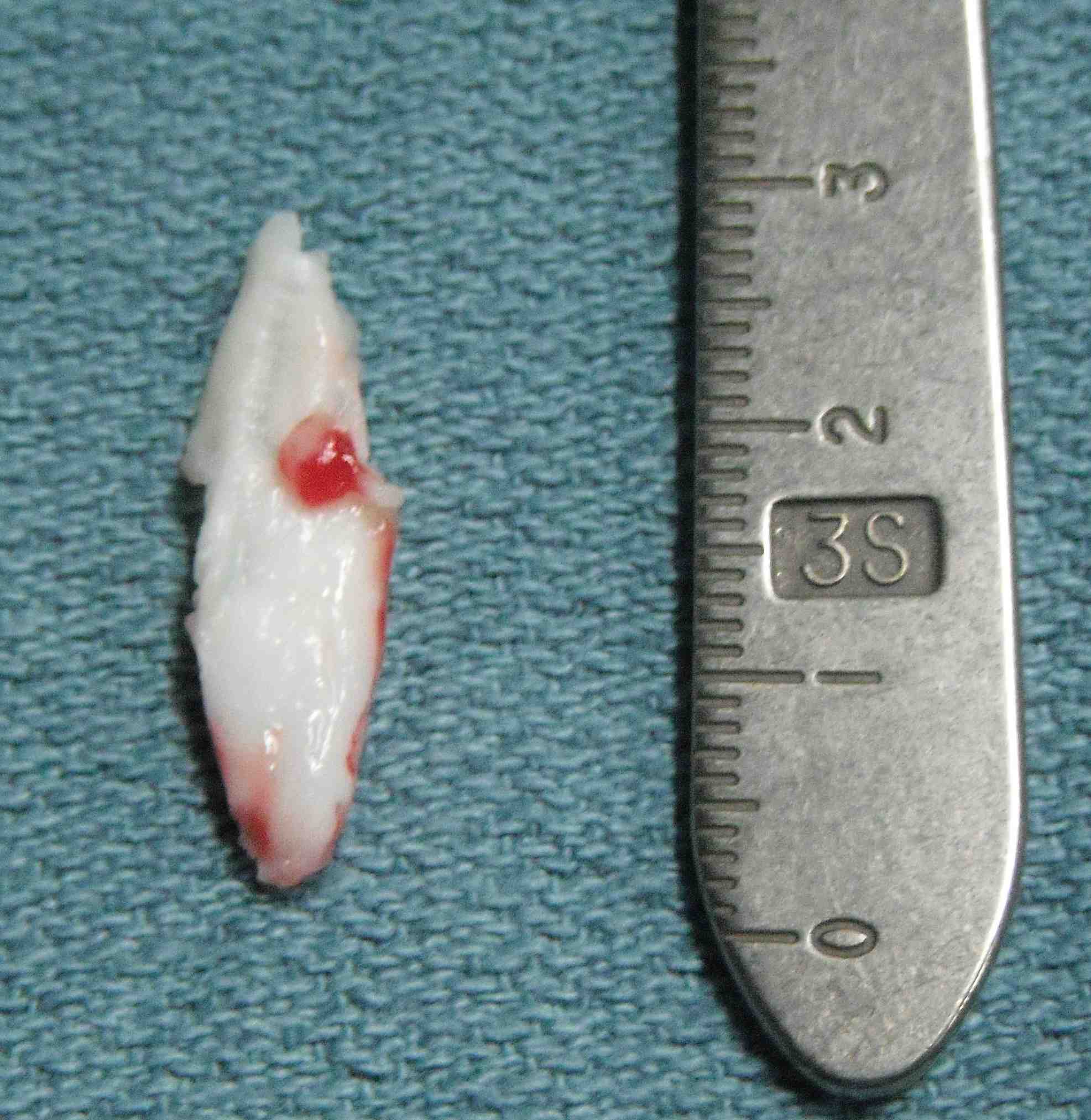
Removal loose body post trauma
Hip arthroscopy technique
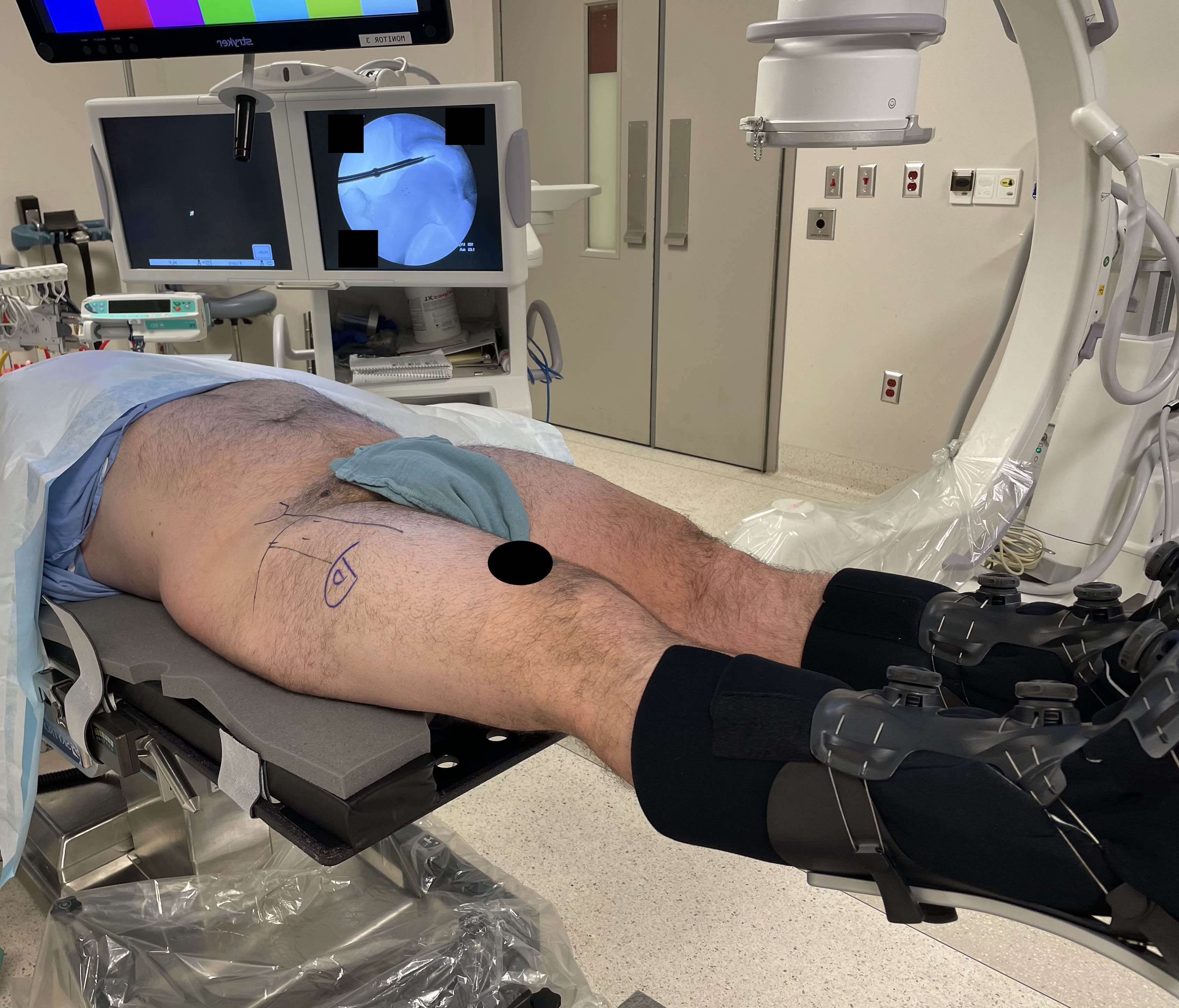
Position
Supine
Lateral
Traction
Need 10 mm of distraction to enter joint and avoid chondro-labral damage
- full muscle relaxation
- traction table
- post versus postless
- occasionally need venting with needle to break vacuum suction
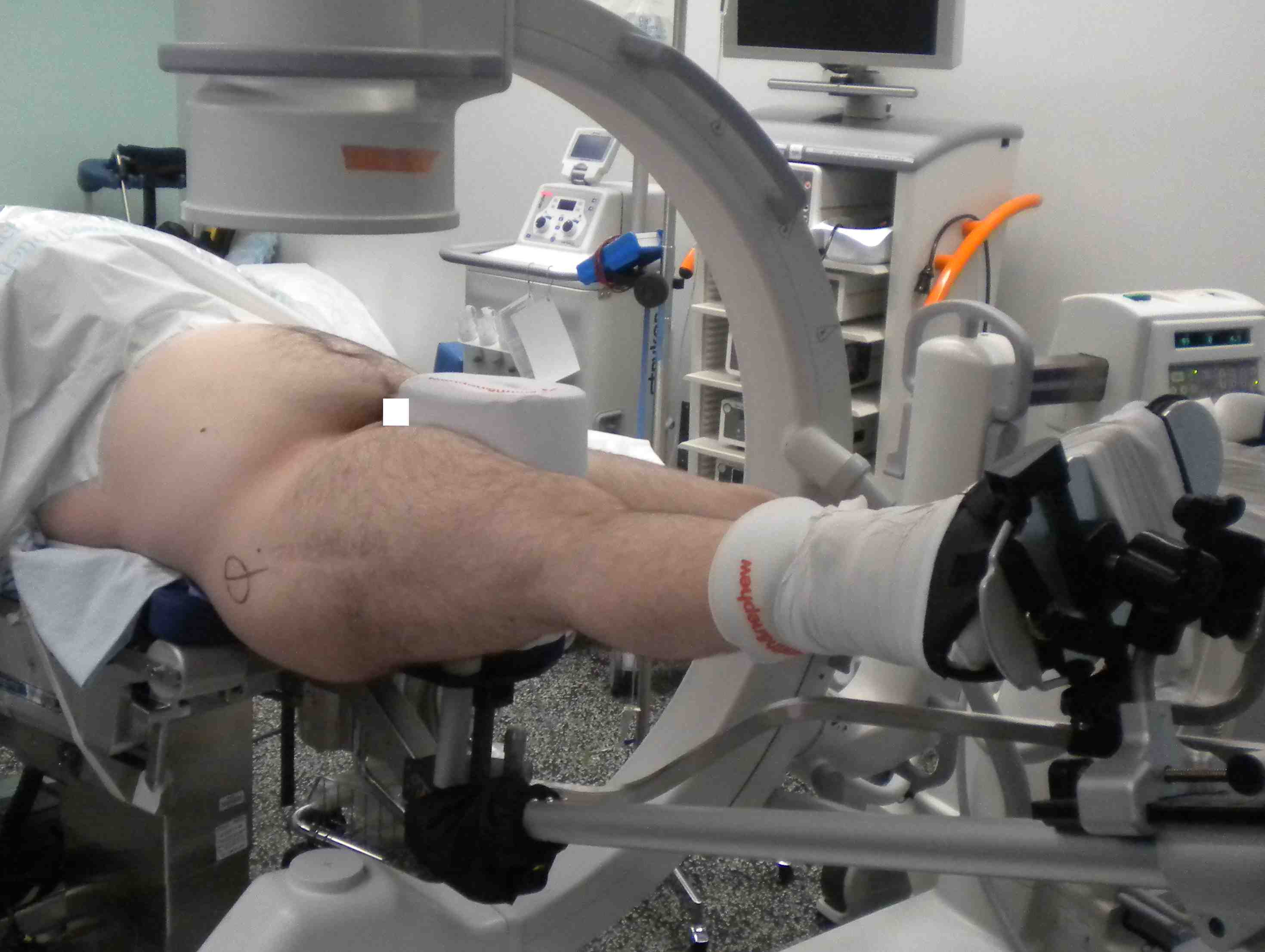
Traction bed with post Post less traction bed using friction pad under patient
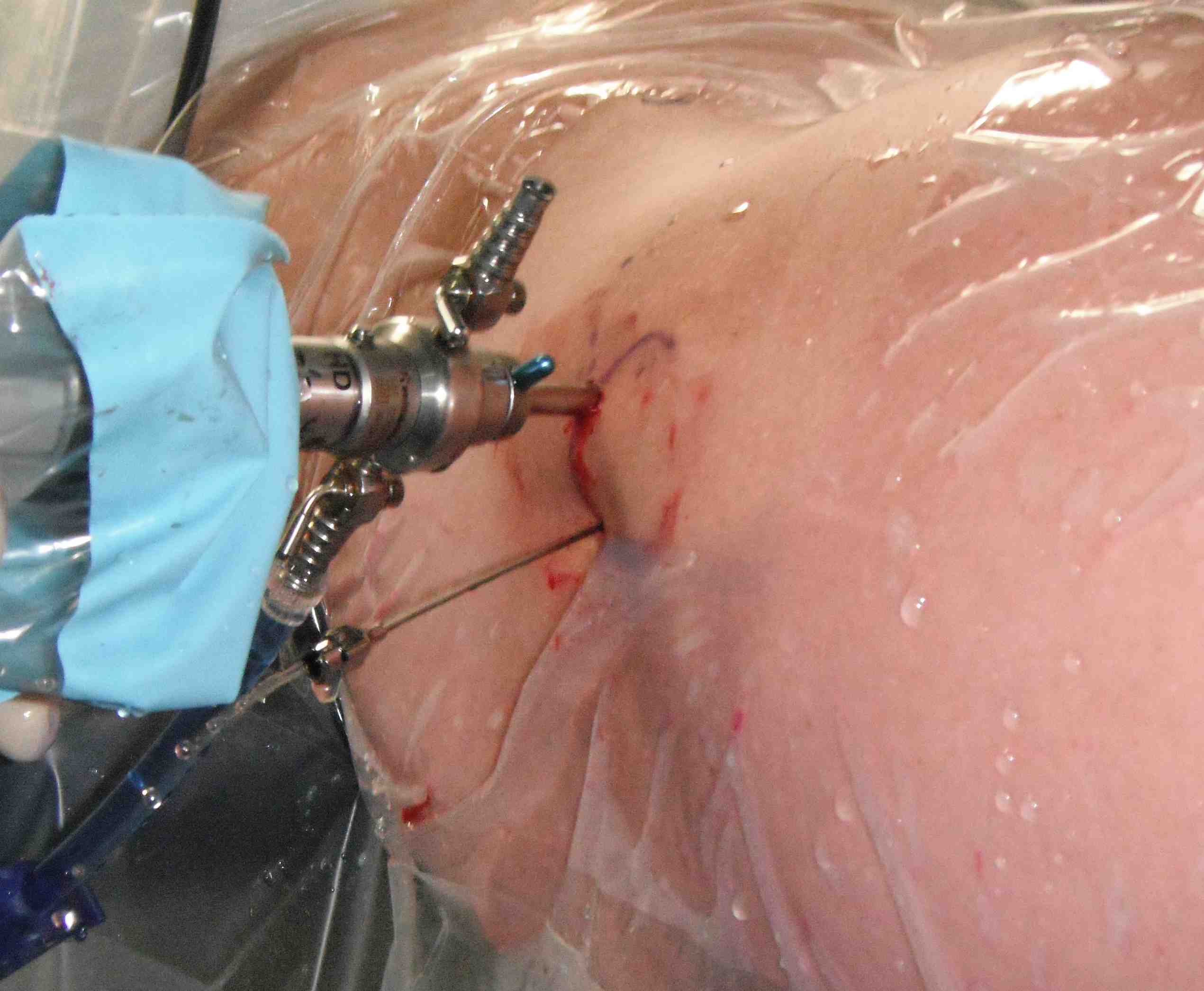
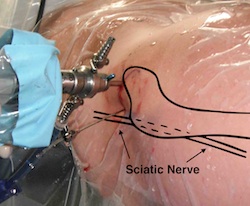
Portals
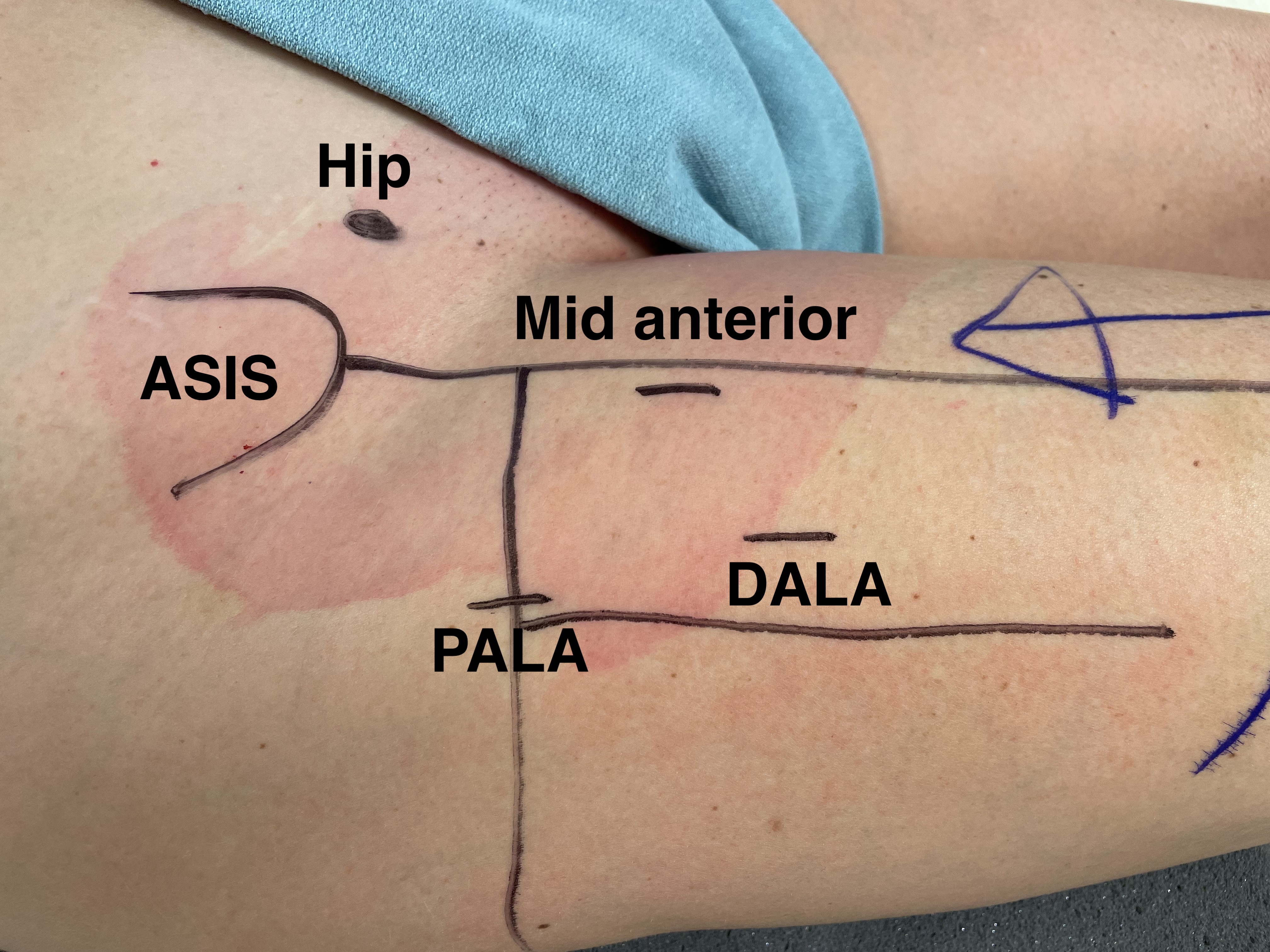
PALA - Proximal anterolateral viewing portal
- entry point anterolateral aspect greater trochanter
- image intensifer
- insert just above head to avoid translabral penetration (between acetabulum and labrum)
- typically 20 degrees posterior depending on patient size
- guide wire / dilators / cannula
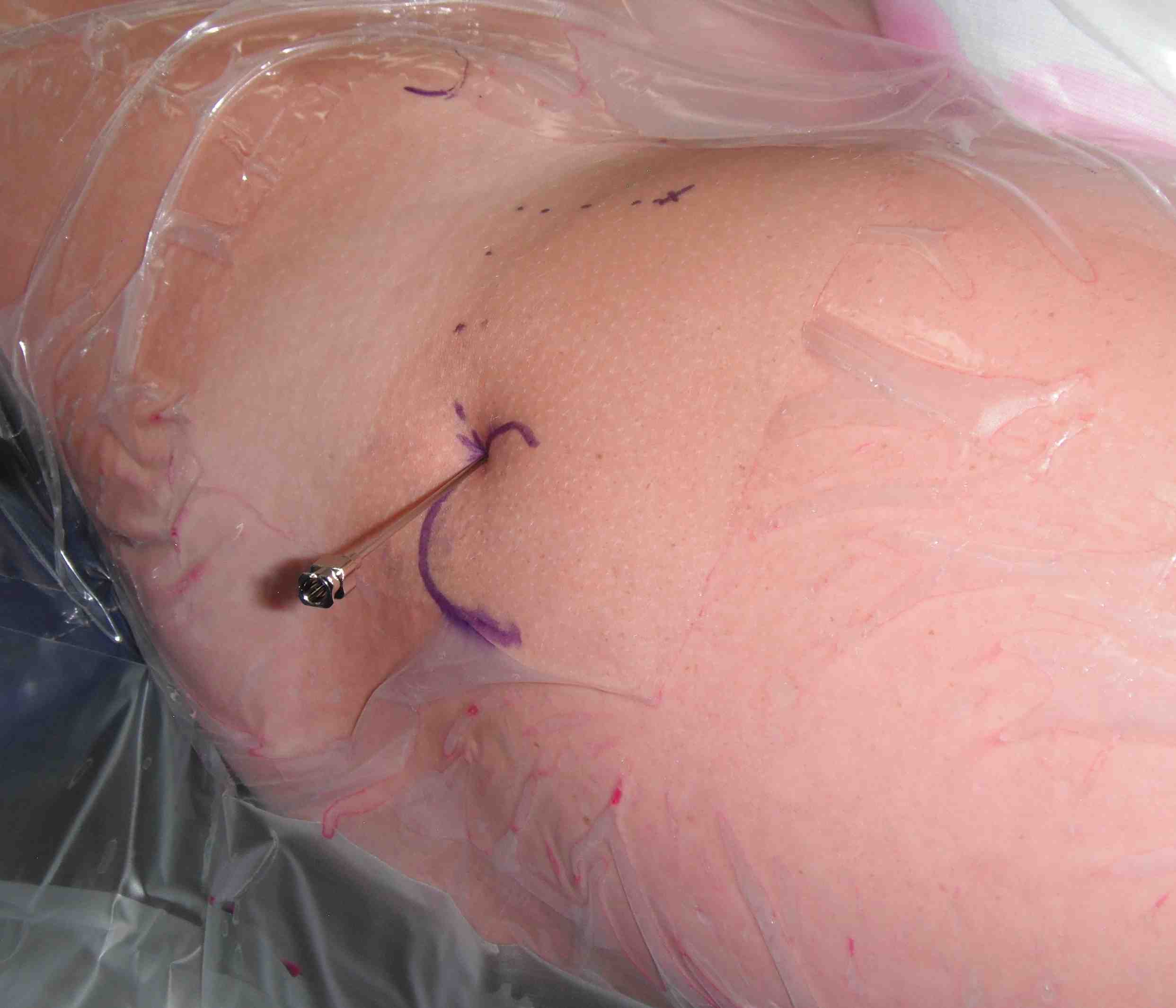
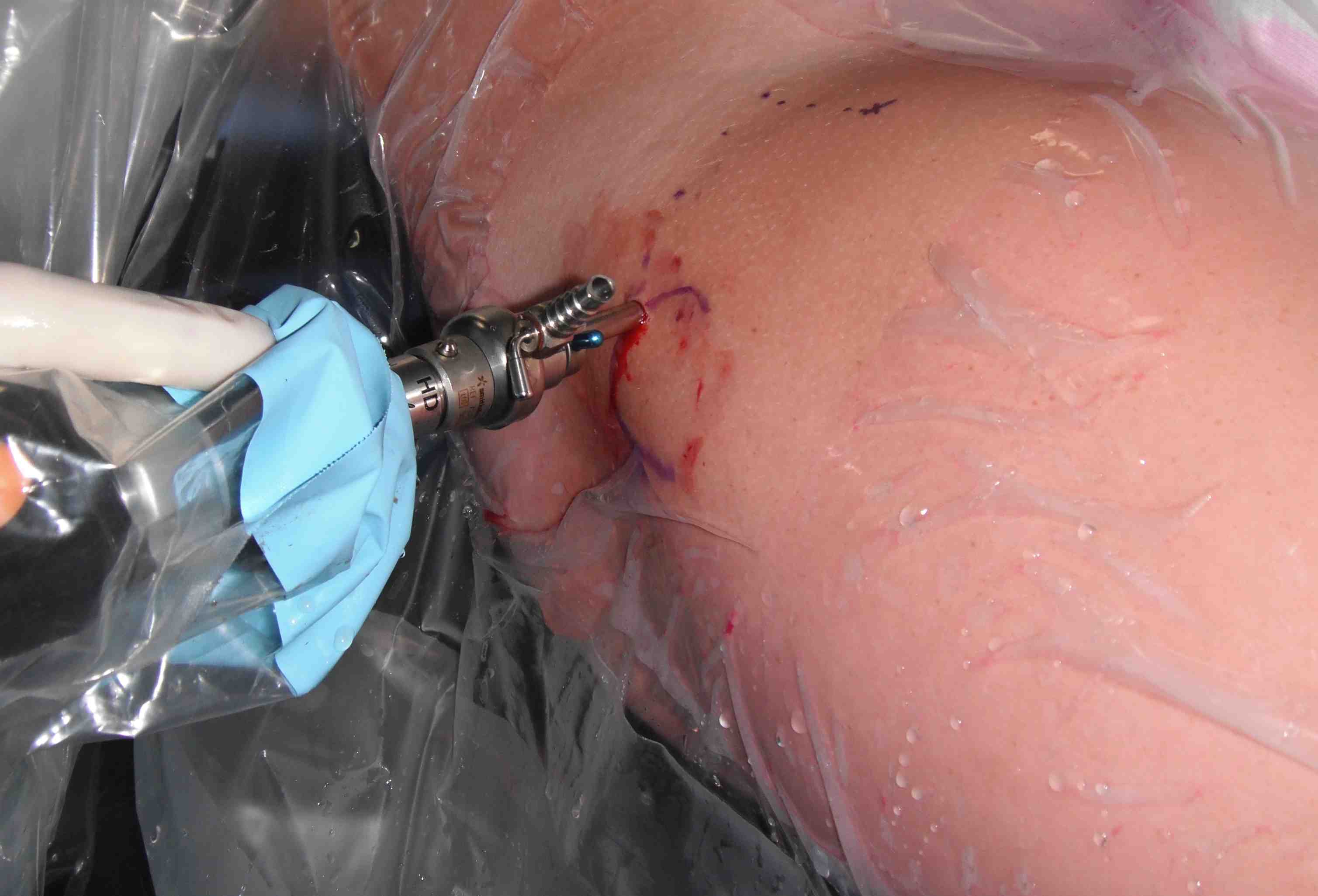
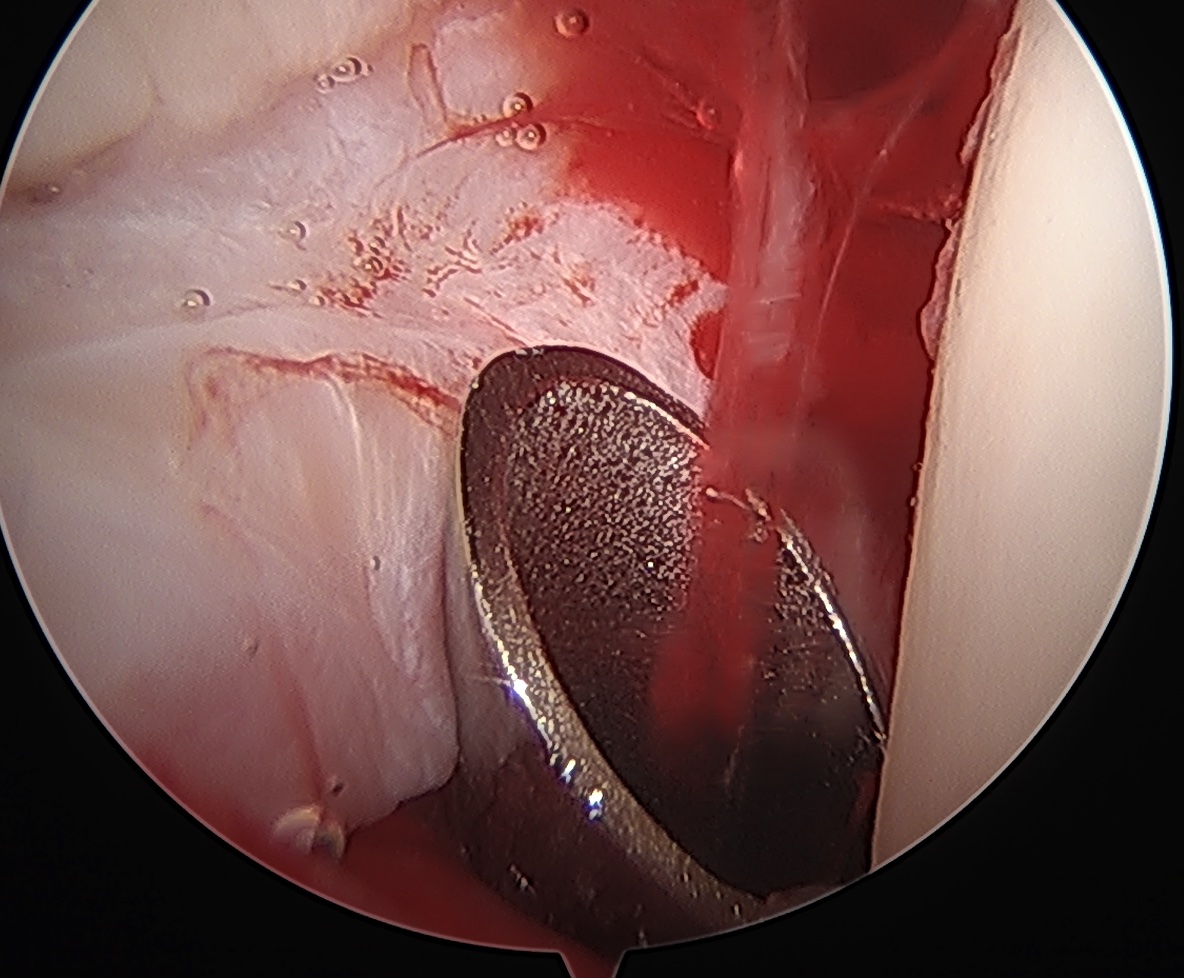
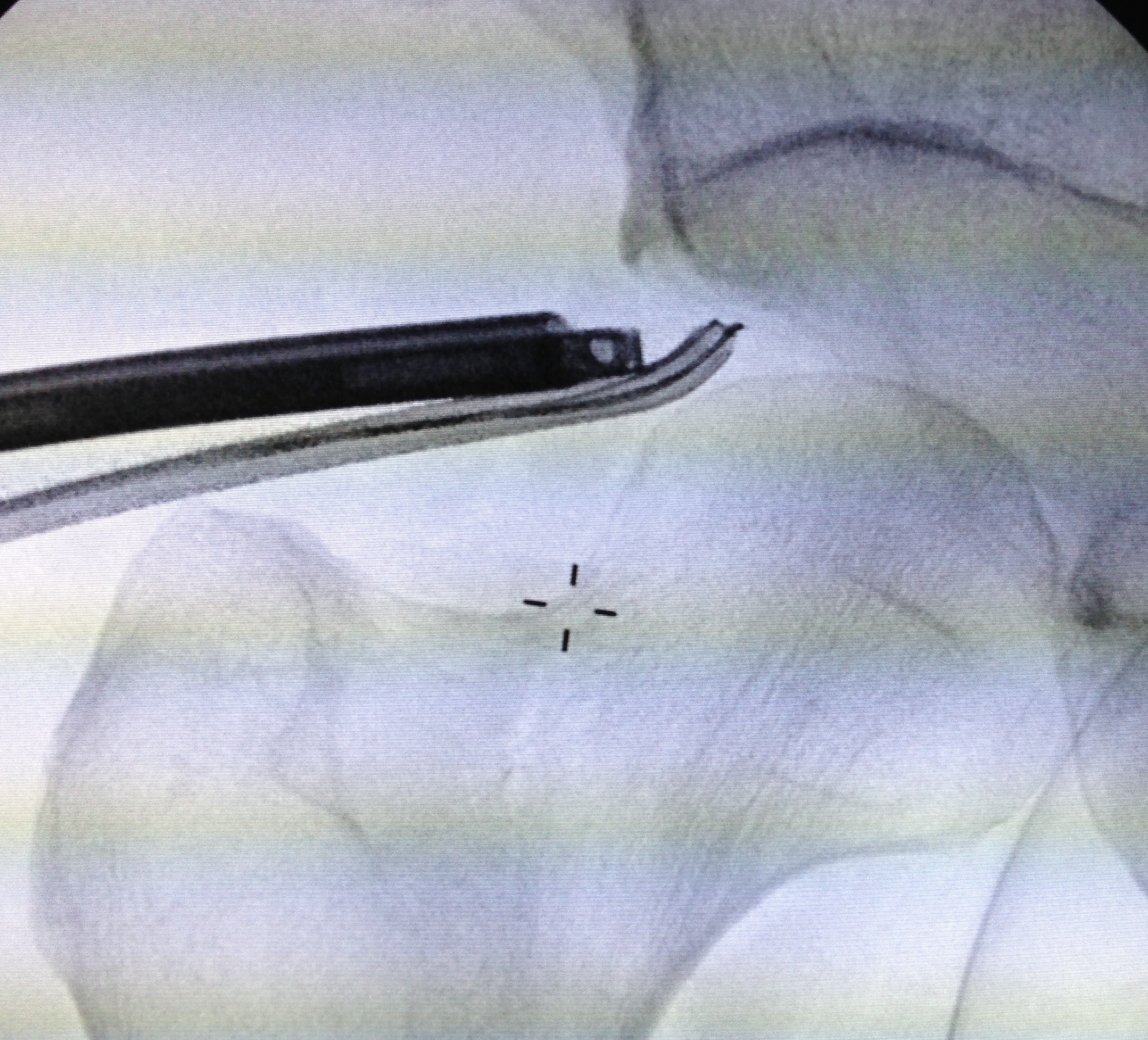
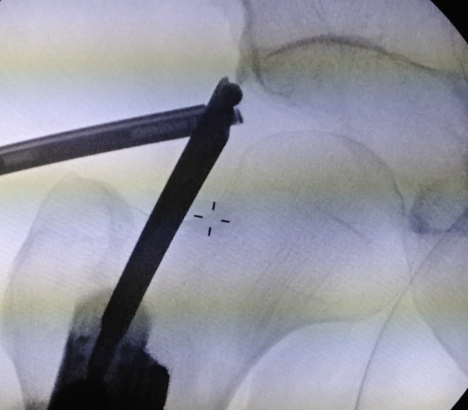
PALA
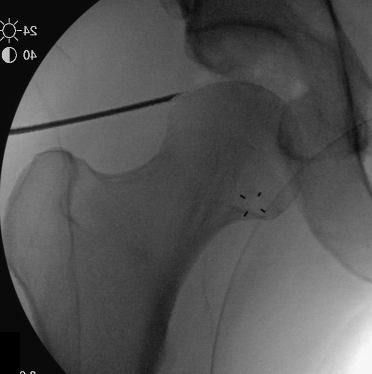
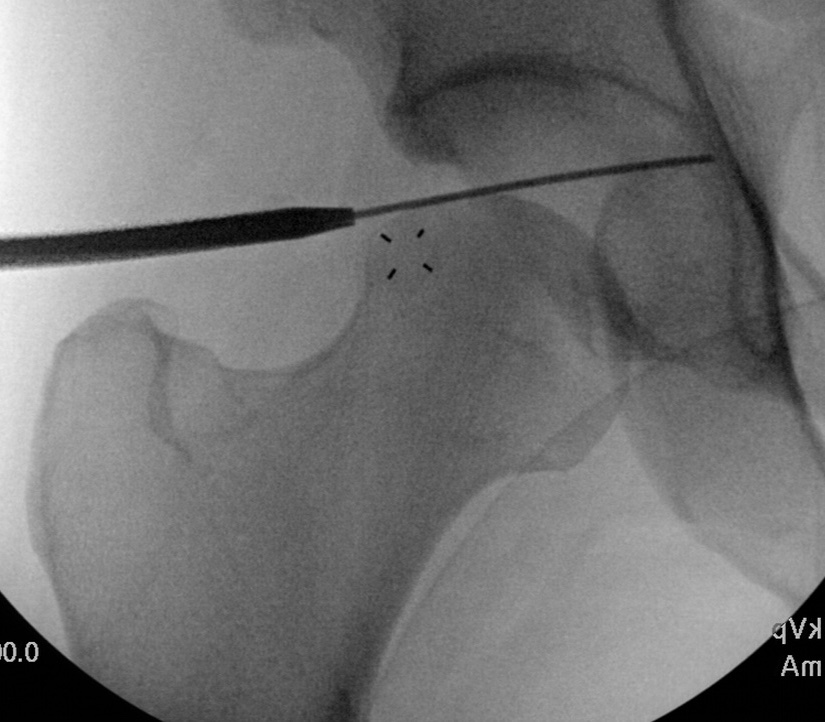
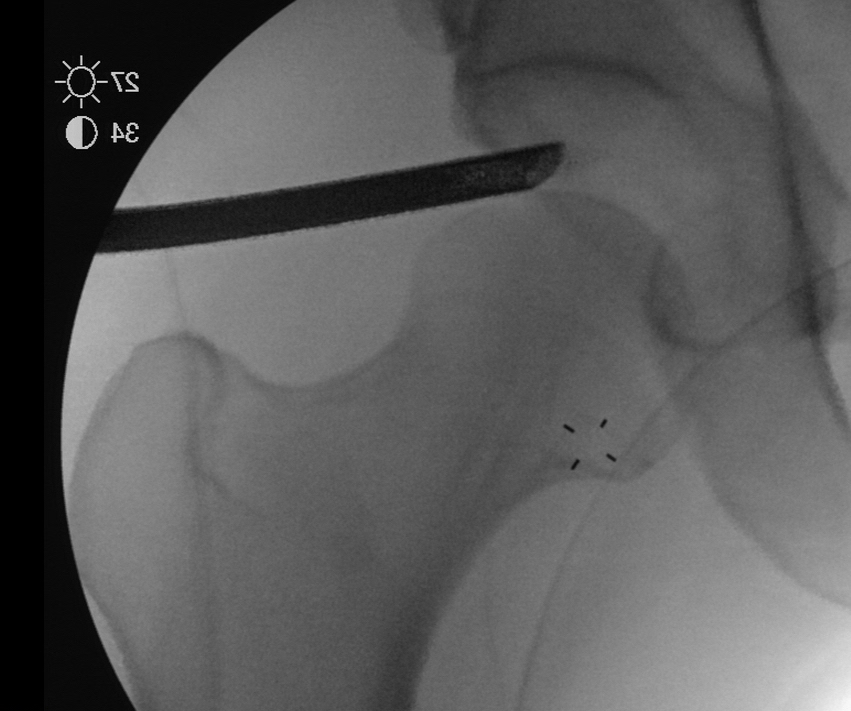
Insertion of PALA under image intensifier
Mid Anterior portal
- stay lateral to line drawn down from ASIS to prevent NV injury
- aim for tip of camera on image intensifier
- judge anterior posterior using femoral head / acetabulum
- enter capsule between labrum and femoral head
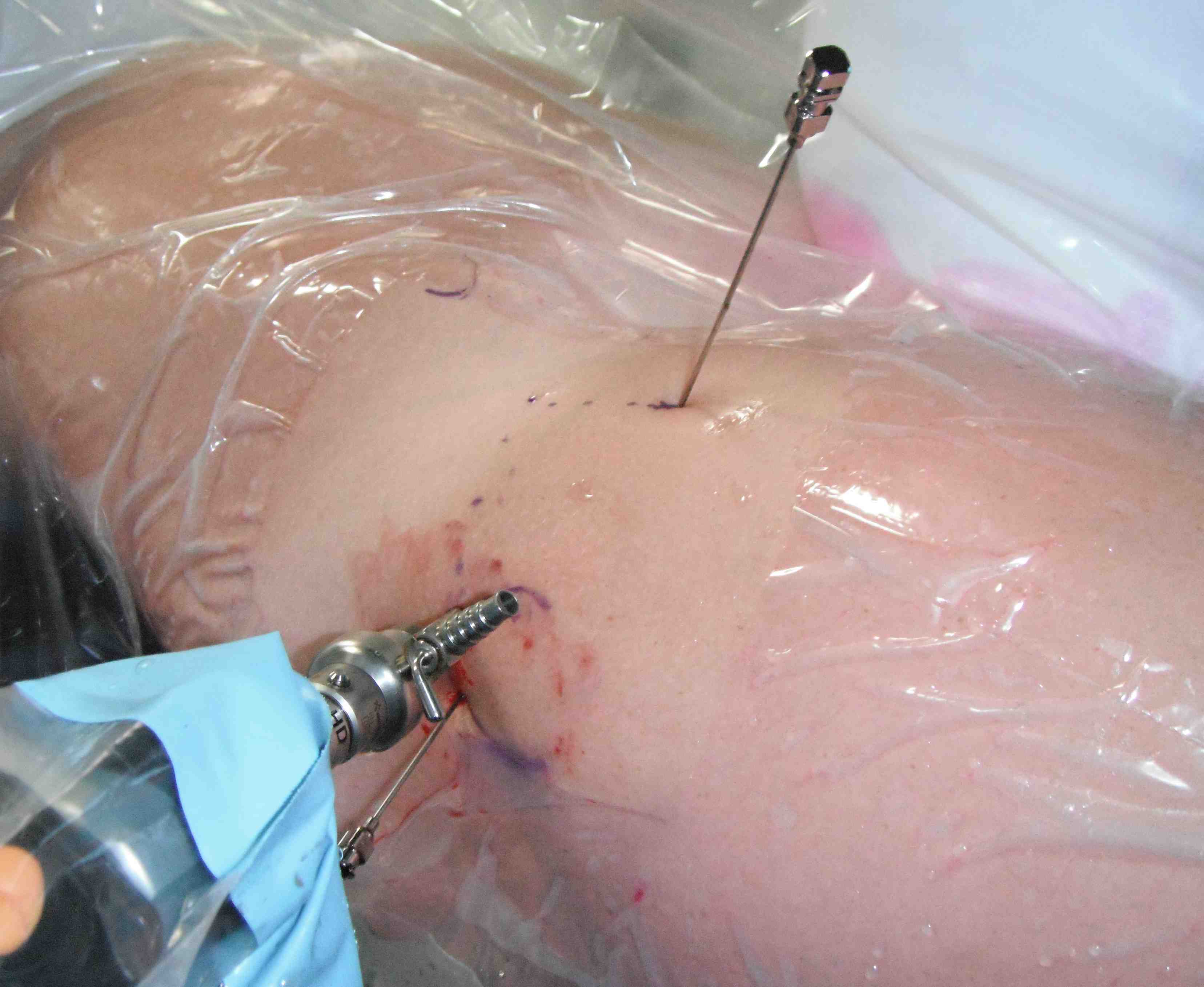

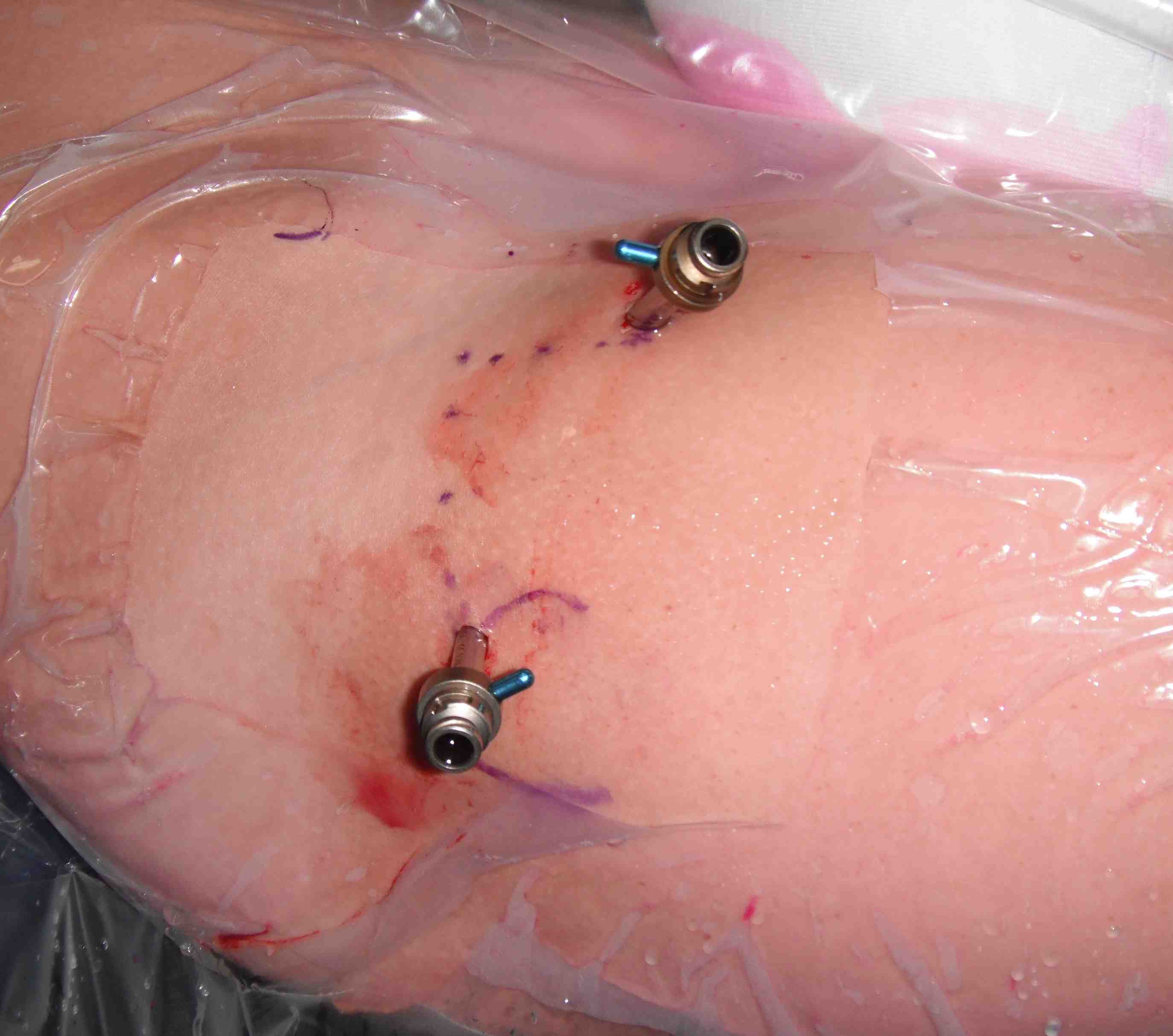
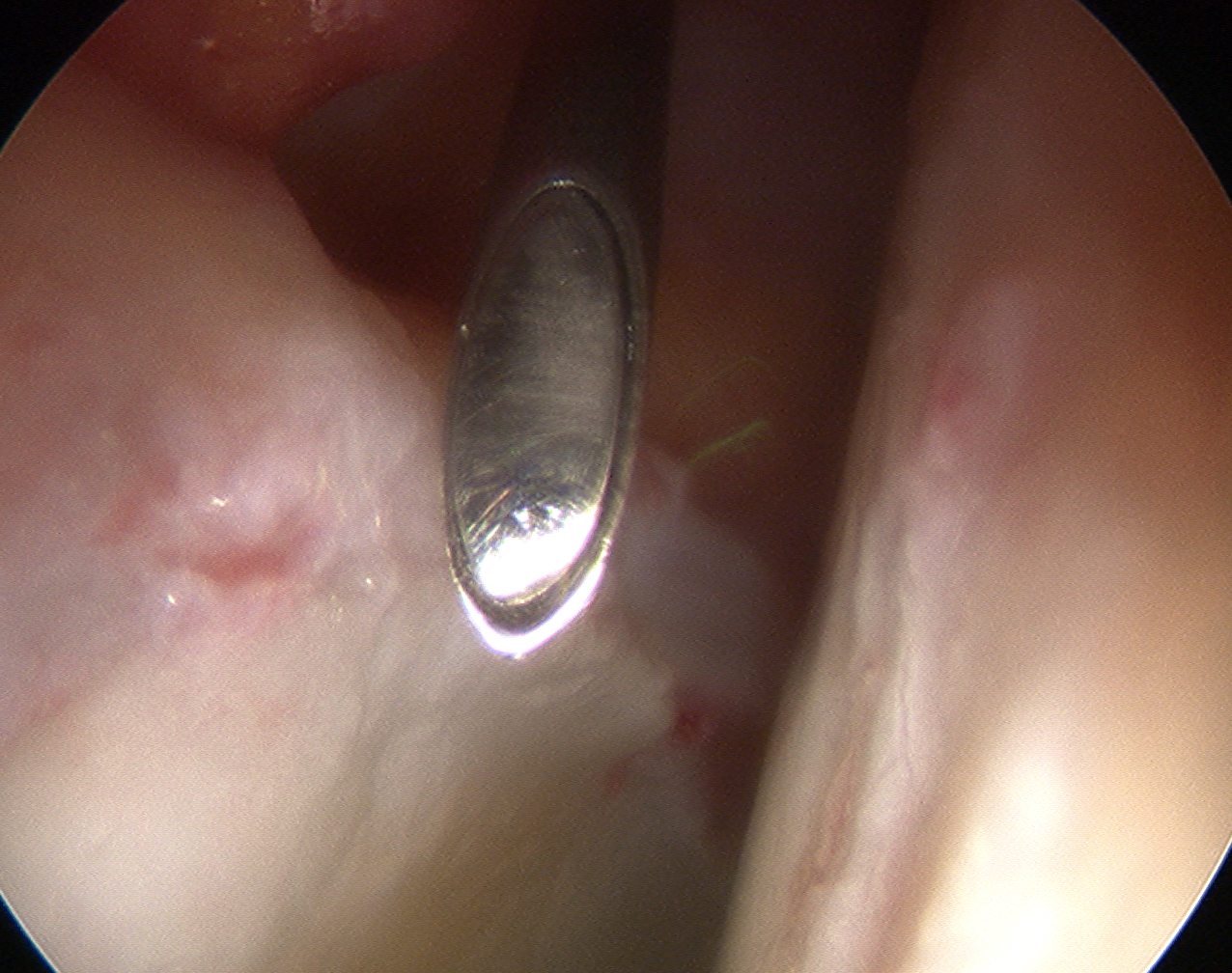
Mid anterior portal
Distal anterolateral portal
- between midanterior and proximal anterolateral
- useful for some acetabular anchors
- used to perform T capsulotomy
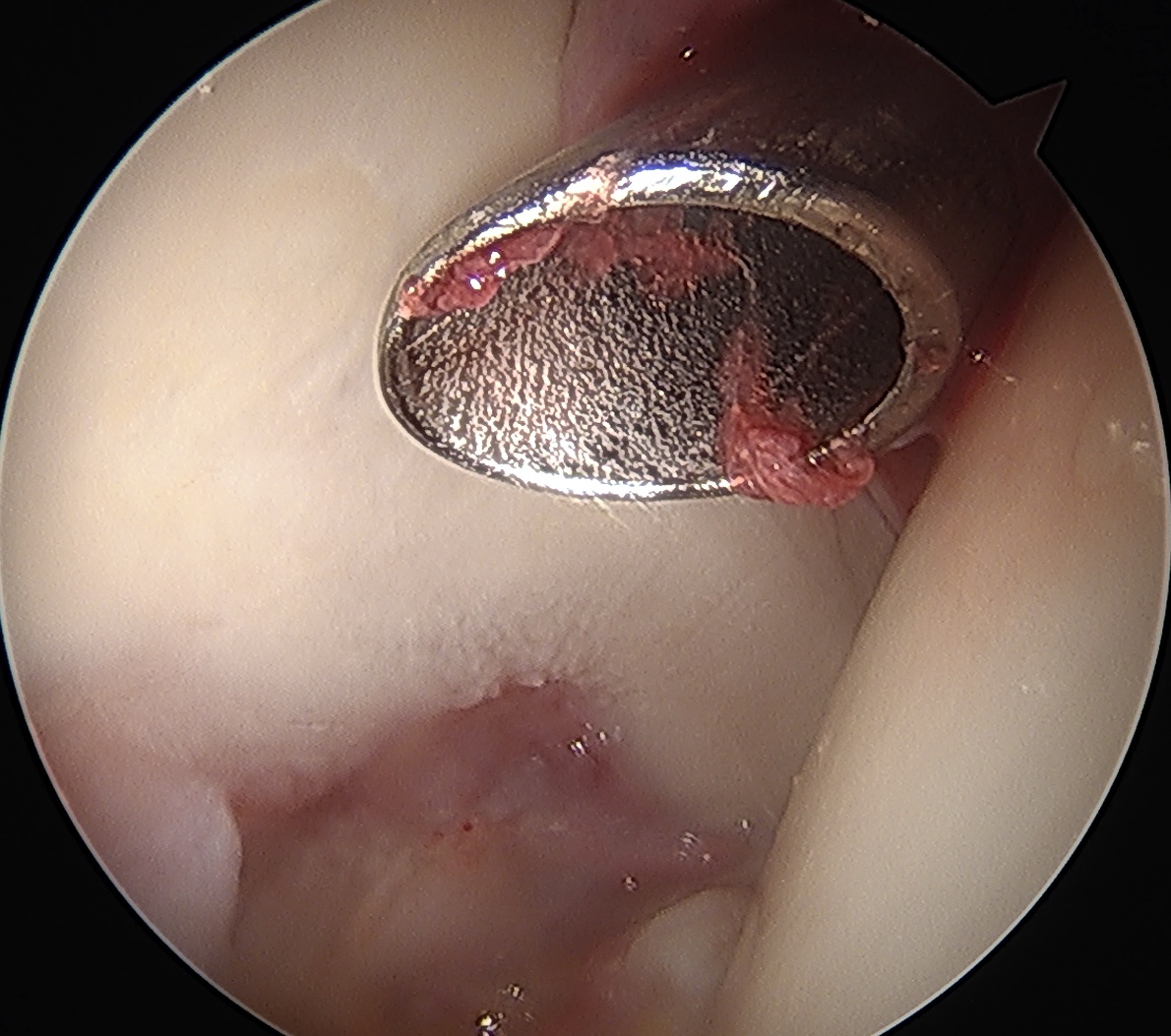
Posterolateral Portal
- 2 cm posterior to GT
- level with superior border GT
- not commonly used
- removal of loose bodies
Posterolateral portal
Interportal capsulotomy
Critical to allow instrumentation
- divide capsule between PALA and midanterior portals
- use combination of knife / diathermy
- preserve capsule for later repair
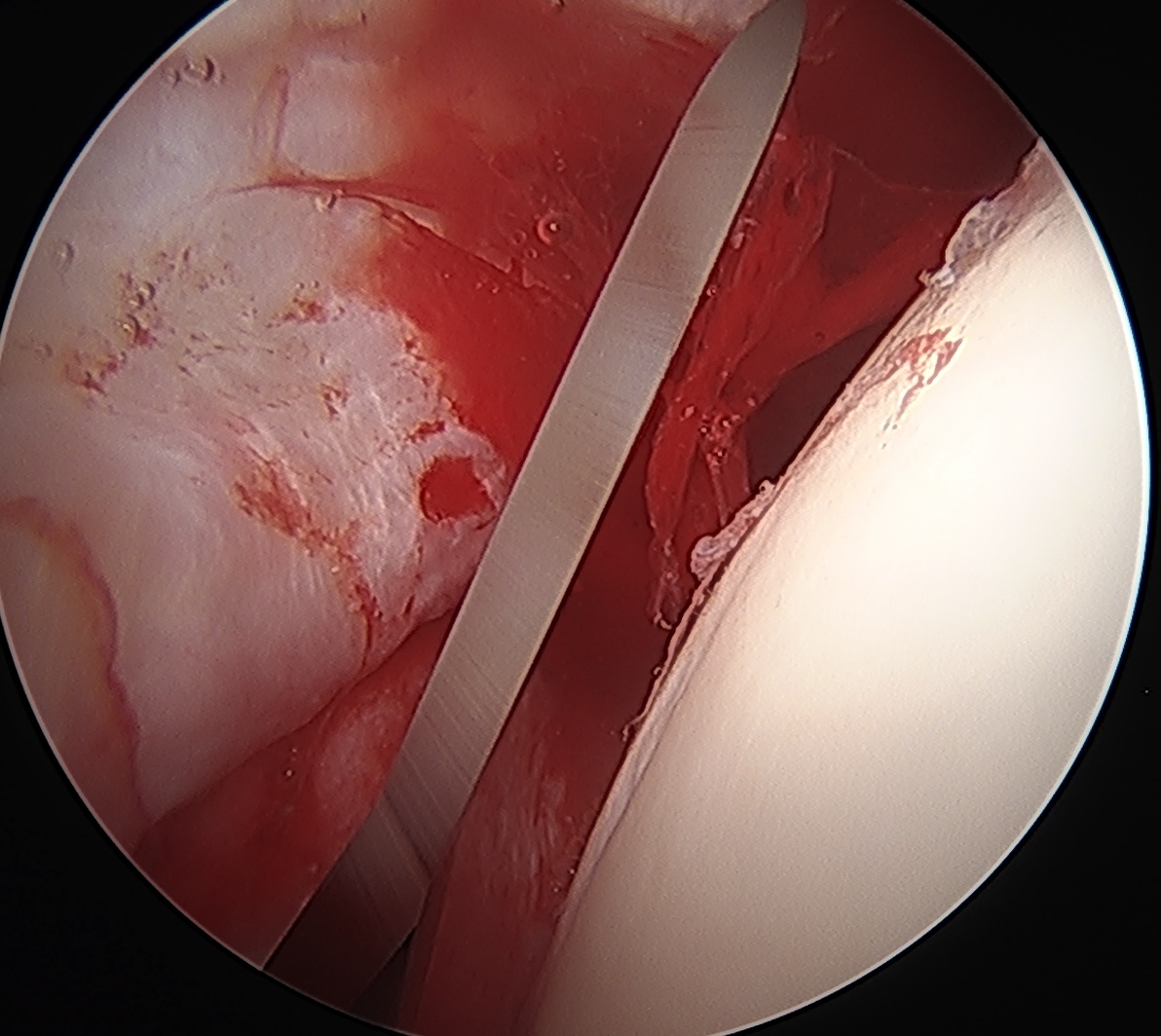
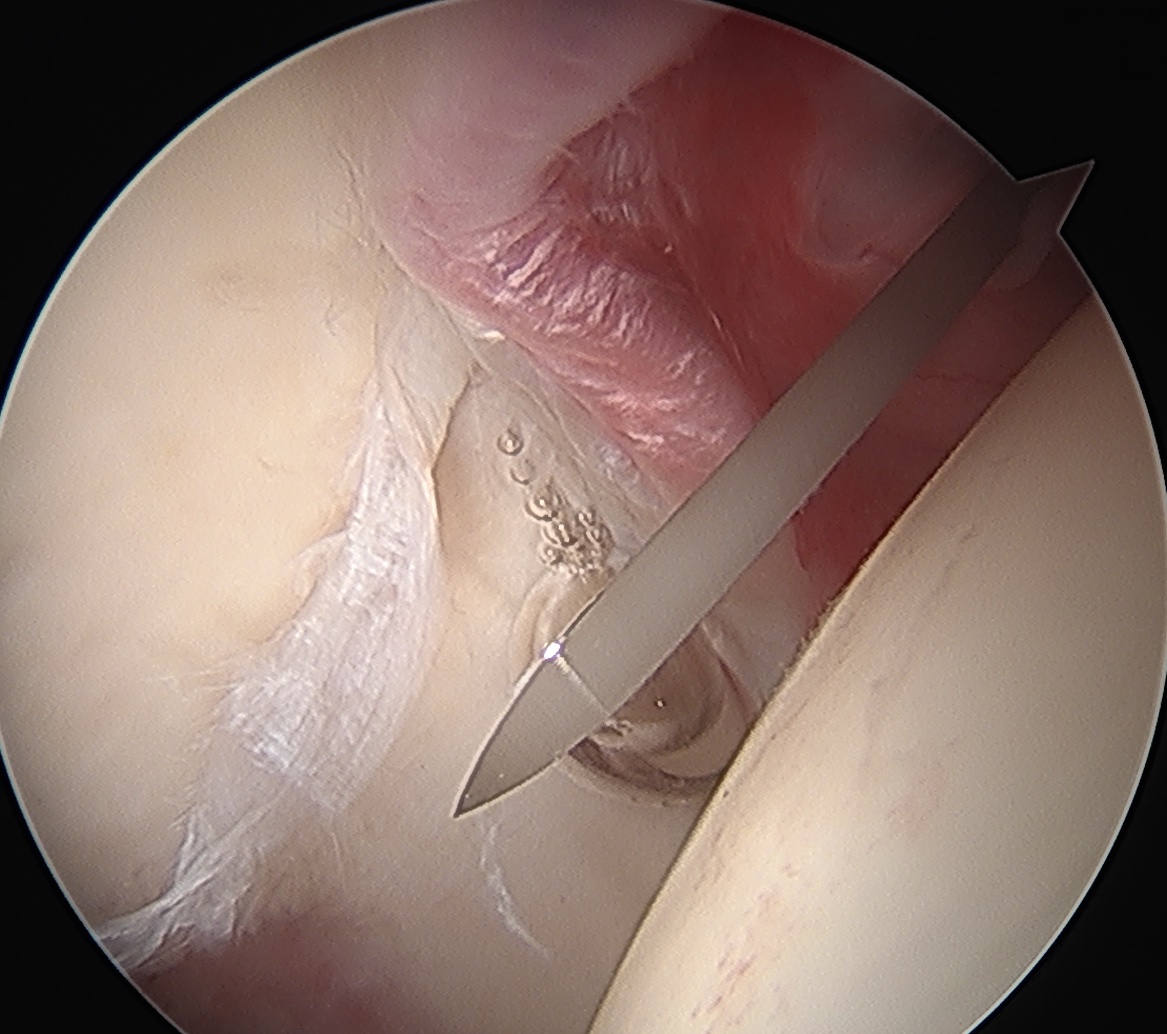
Interportal capsulotomy through PALA Interportal capsulotomy through midanterior
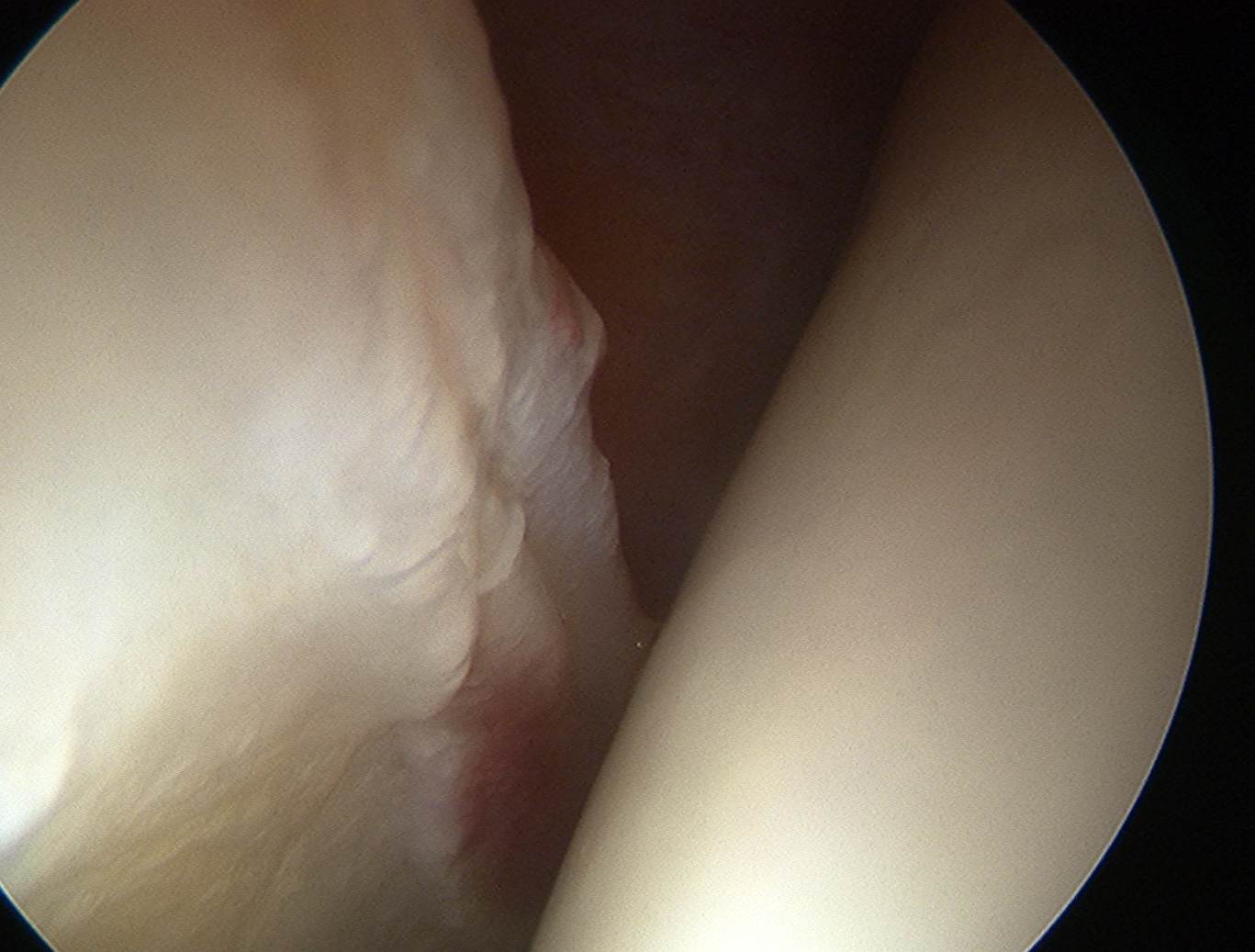
Labral Repair
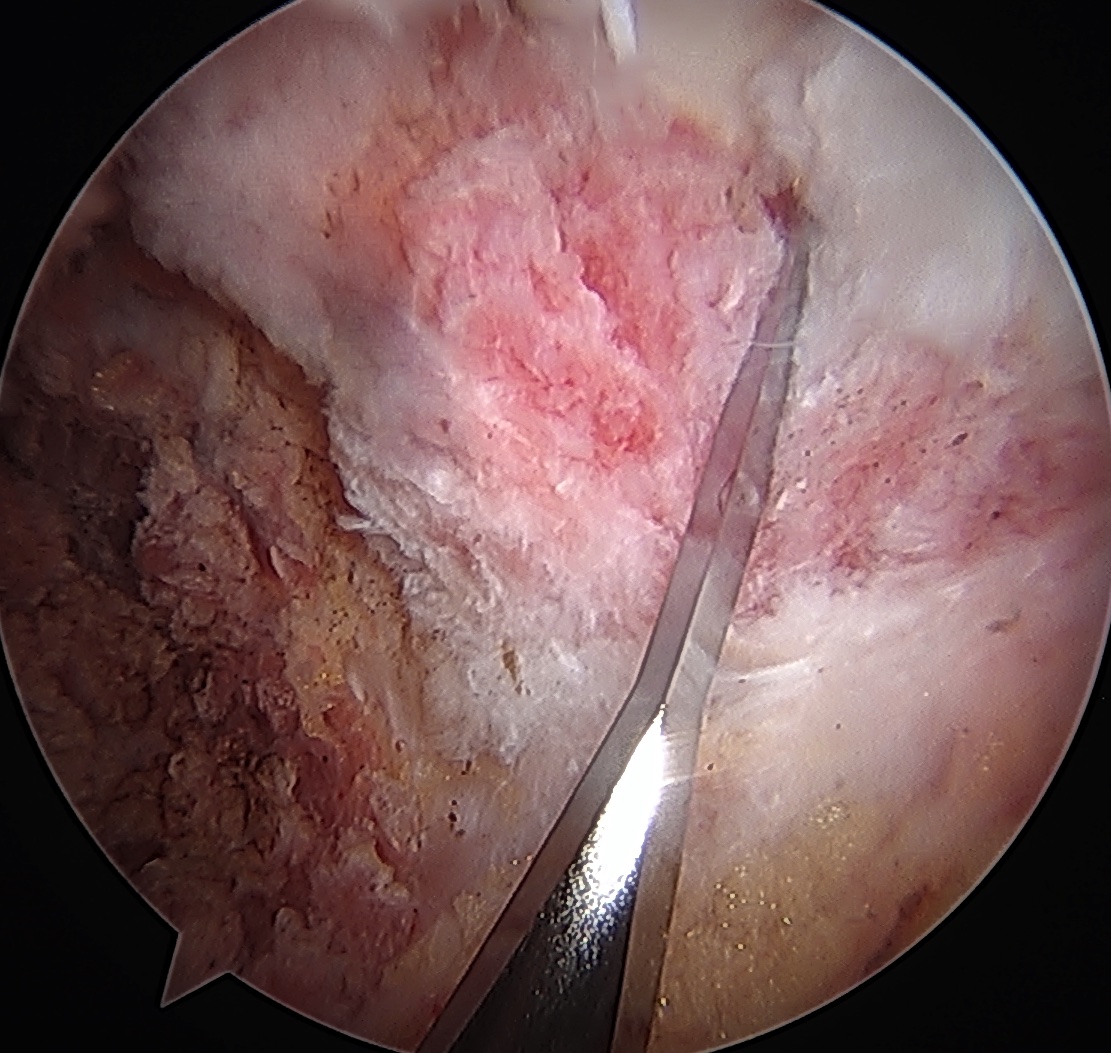
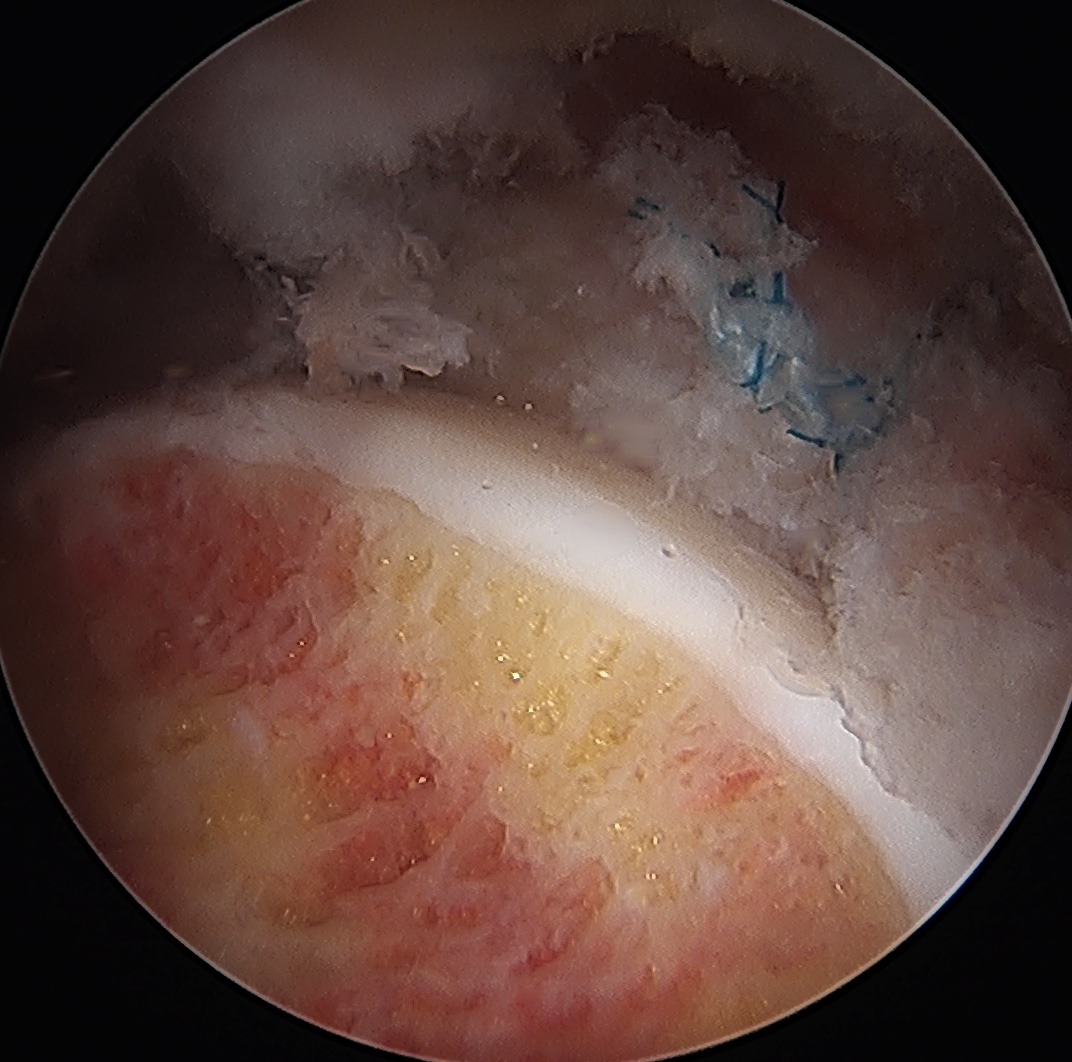
Assess for Labral Tears
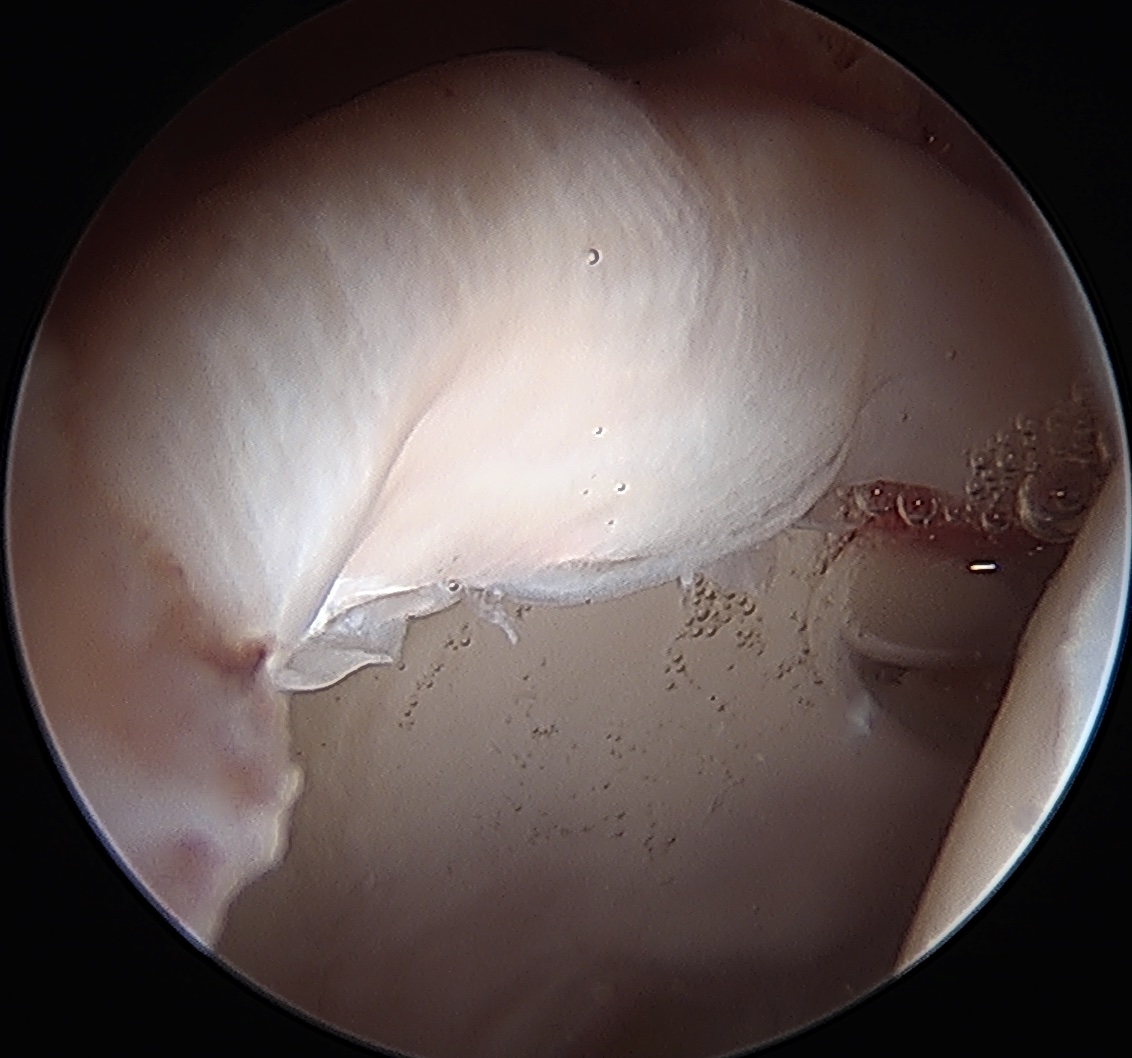
Expose acetabulum
- place proximal capsule suspension sutures
- elevate and protect proximal capsule for later repair
- use cautery to expose acetabulum while not injuring labrum
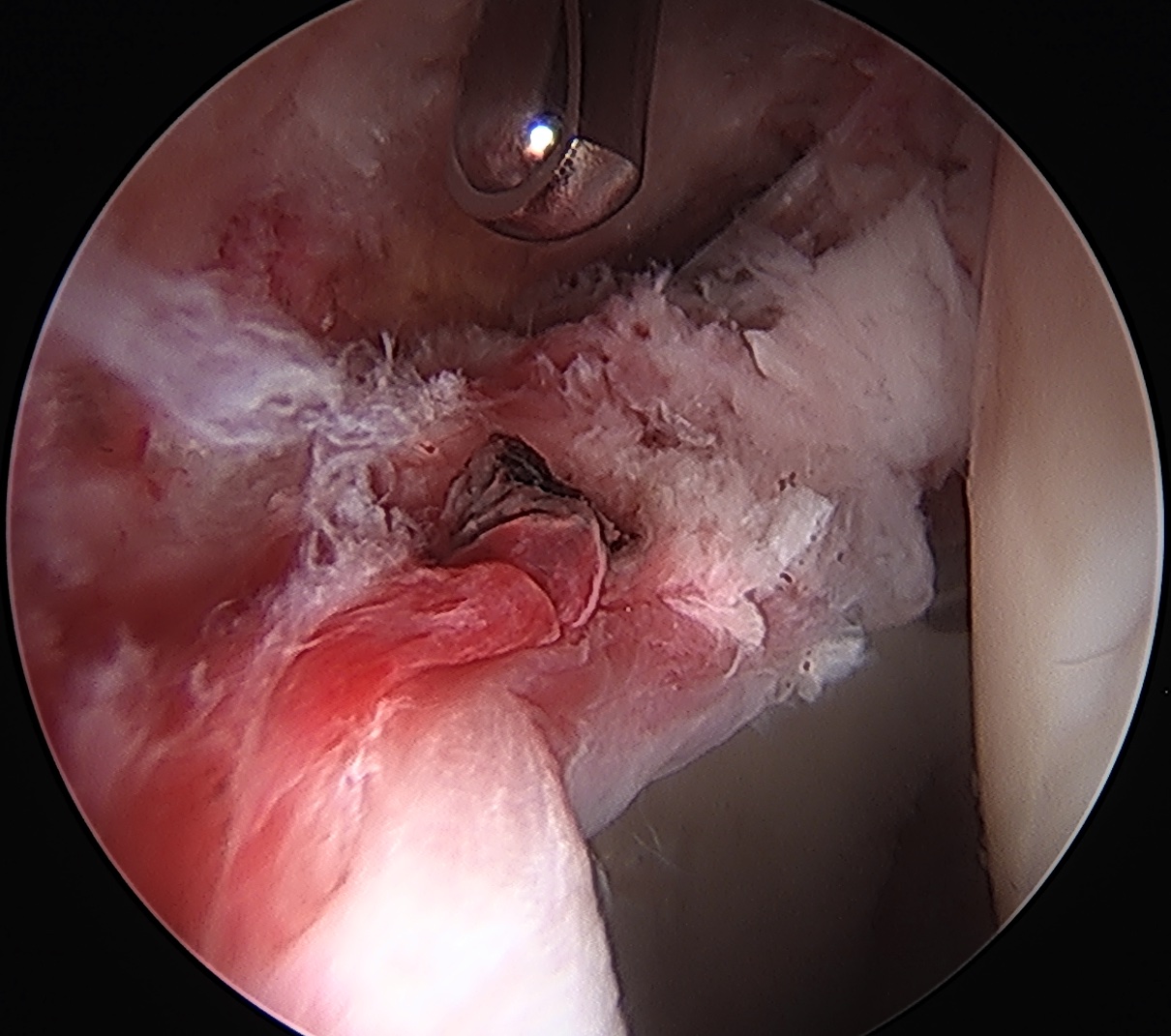
Acetabular rim trim / Acetabuloplasty

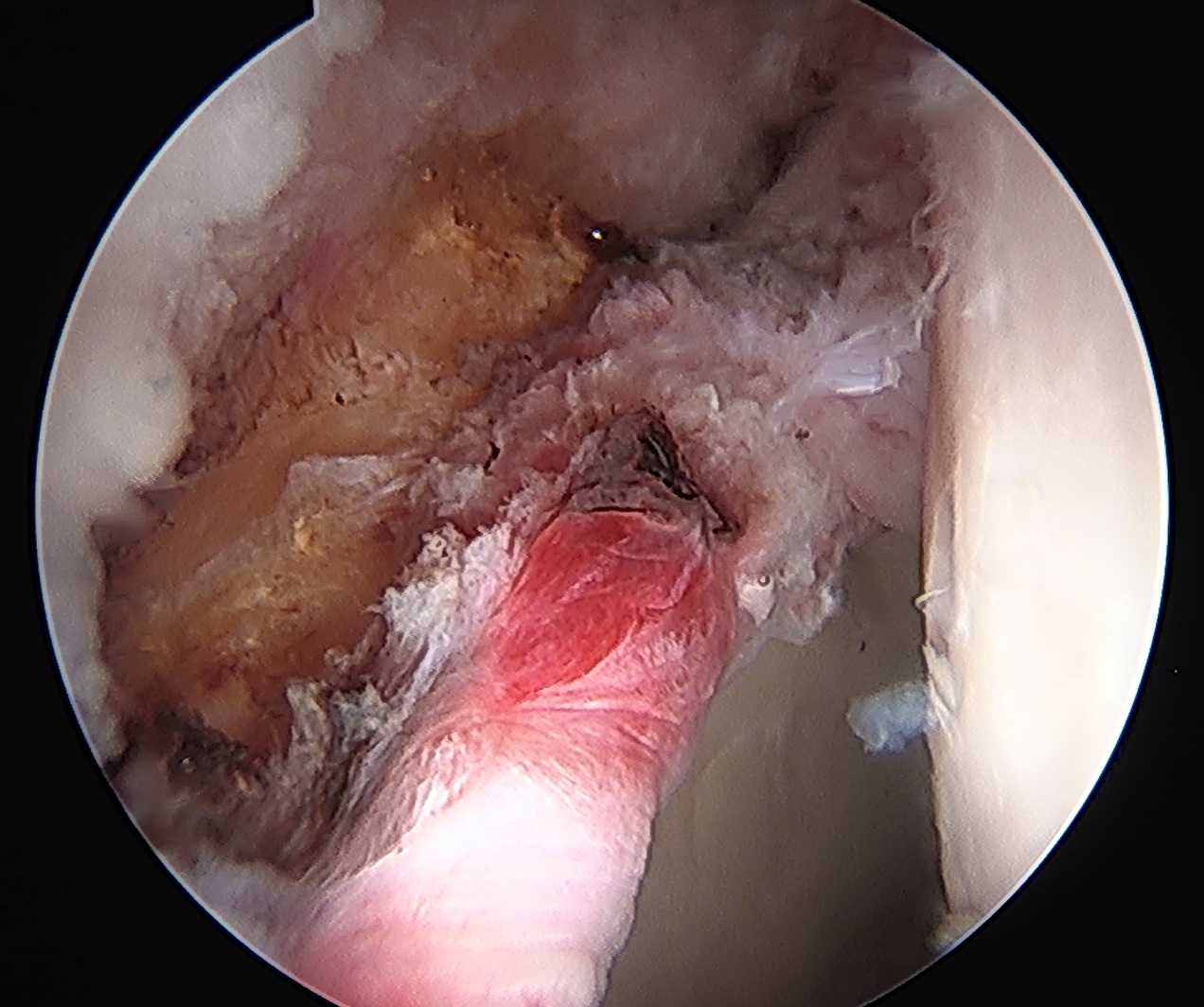
Pincer resection
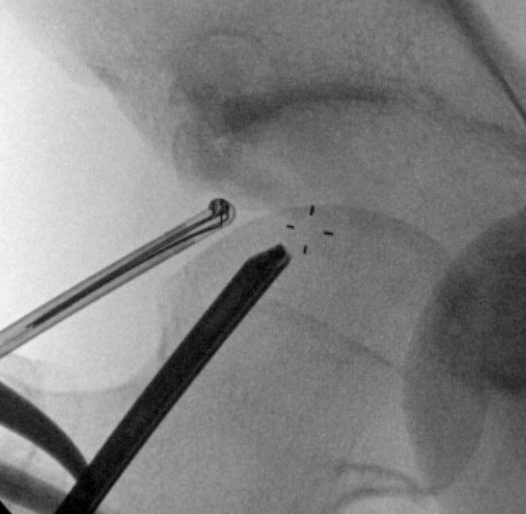
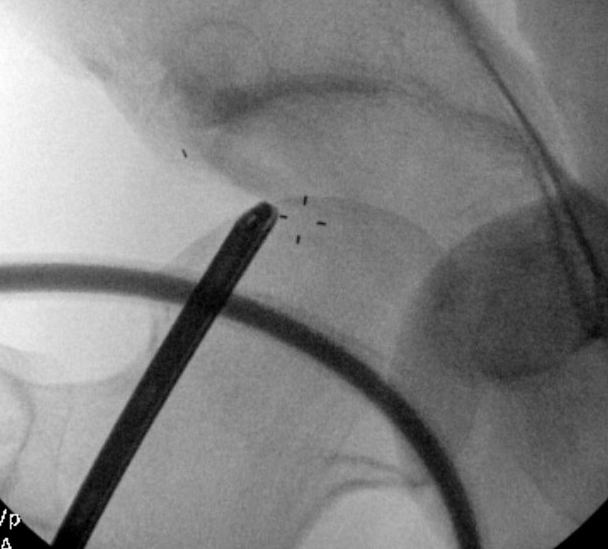
Os acetabuli resection
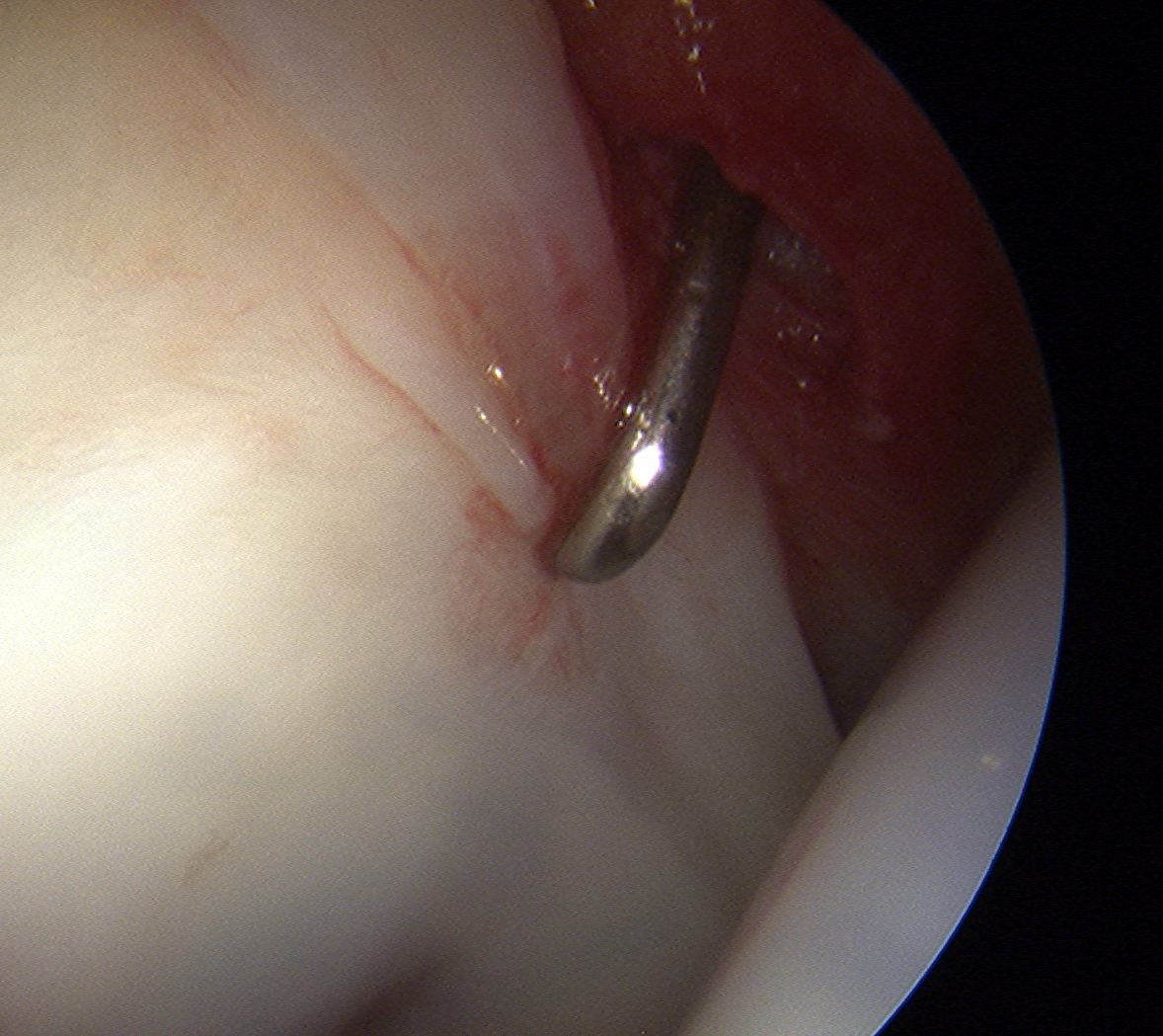
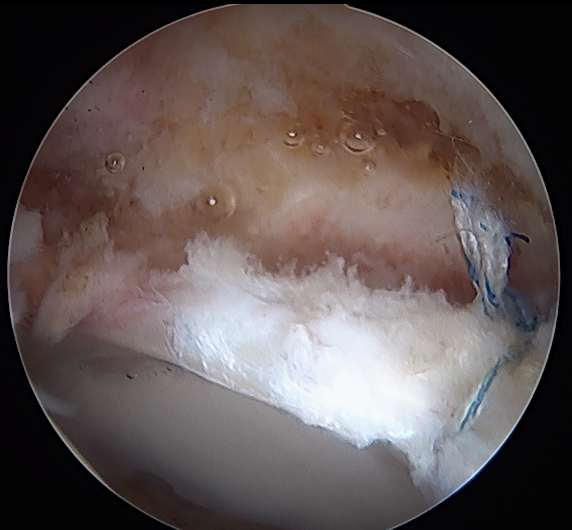
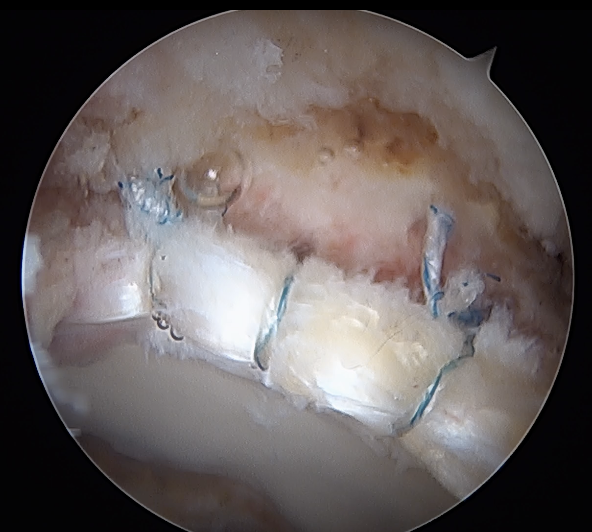
Labral repair
Options
- knotted versus knotless anchors
- straight versus curved
Must avoid intra-articular penetration
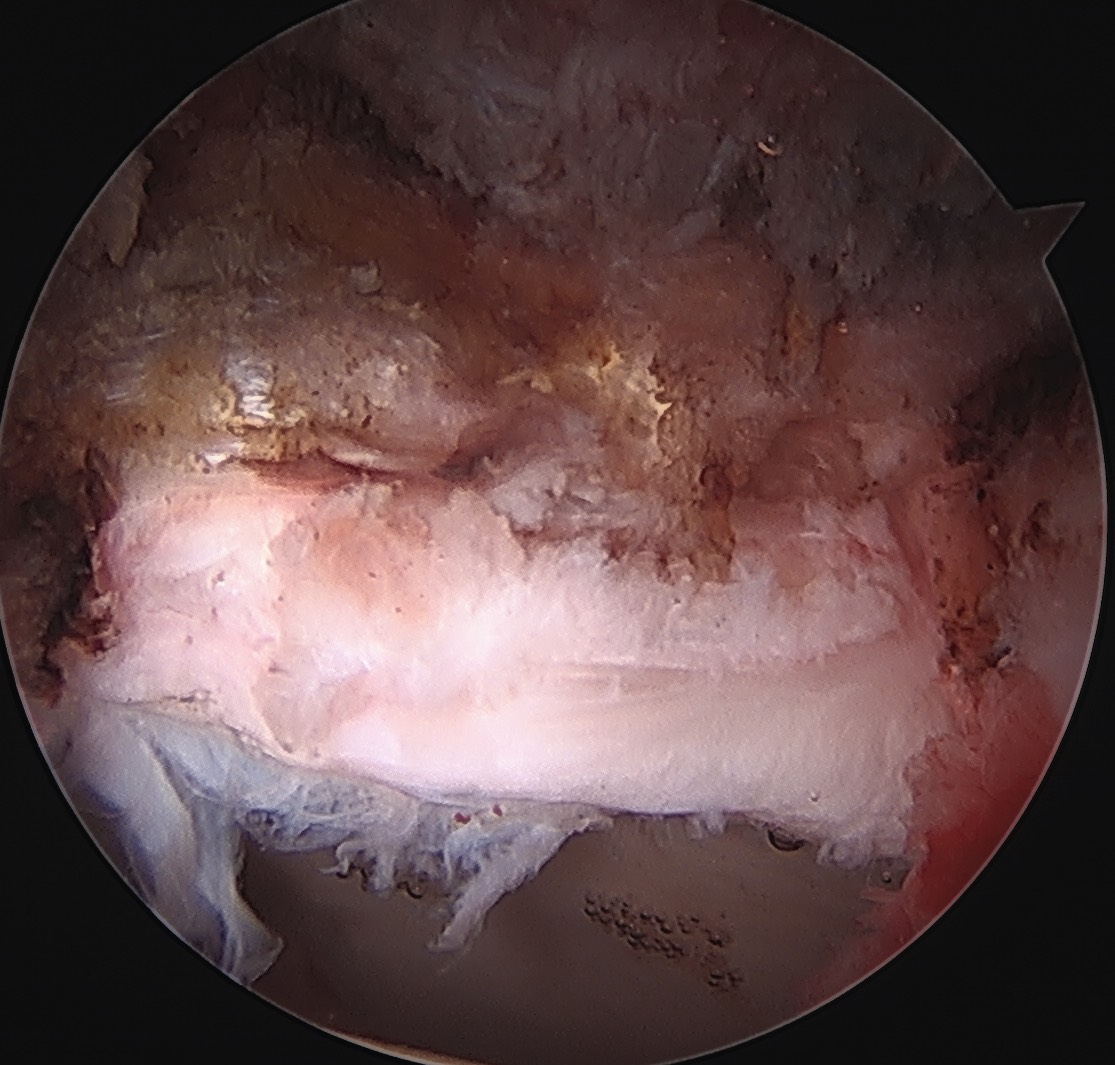
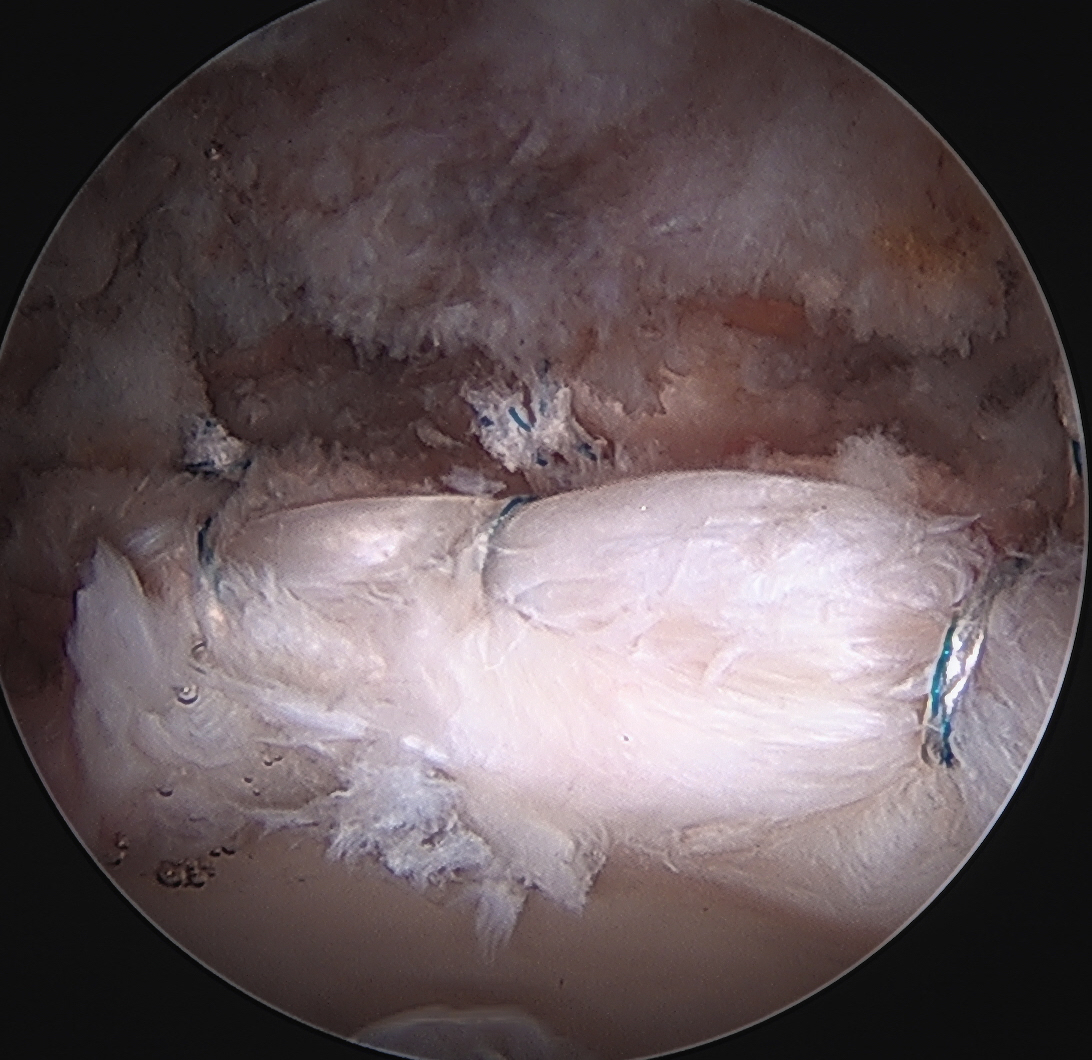
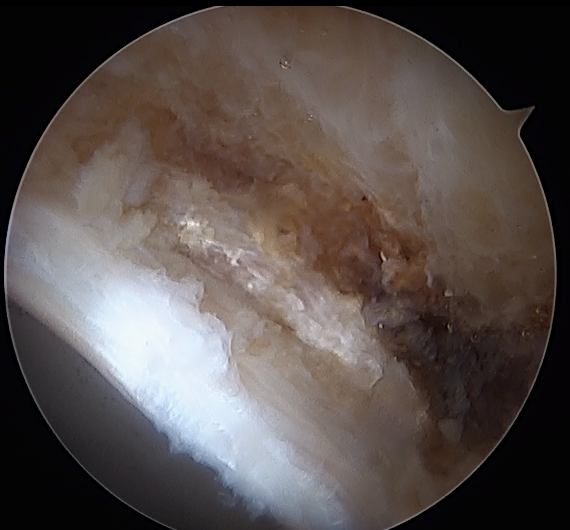
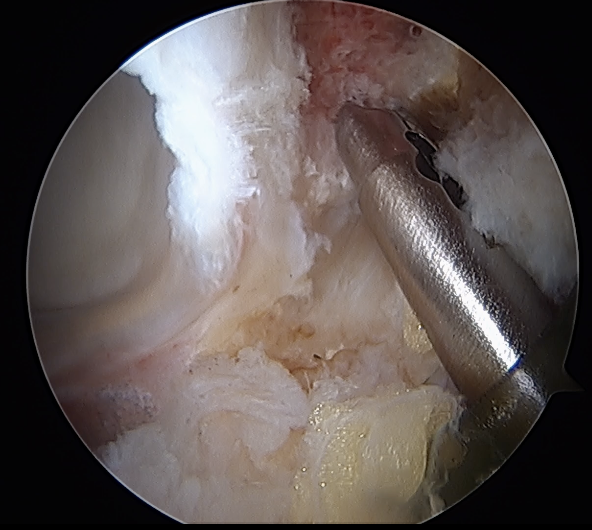
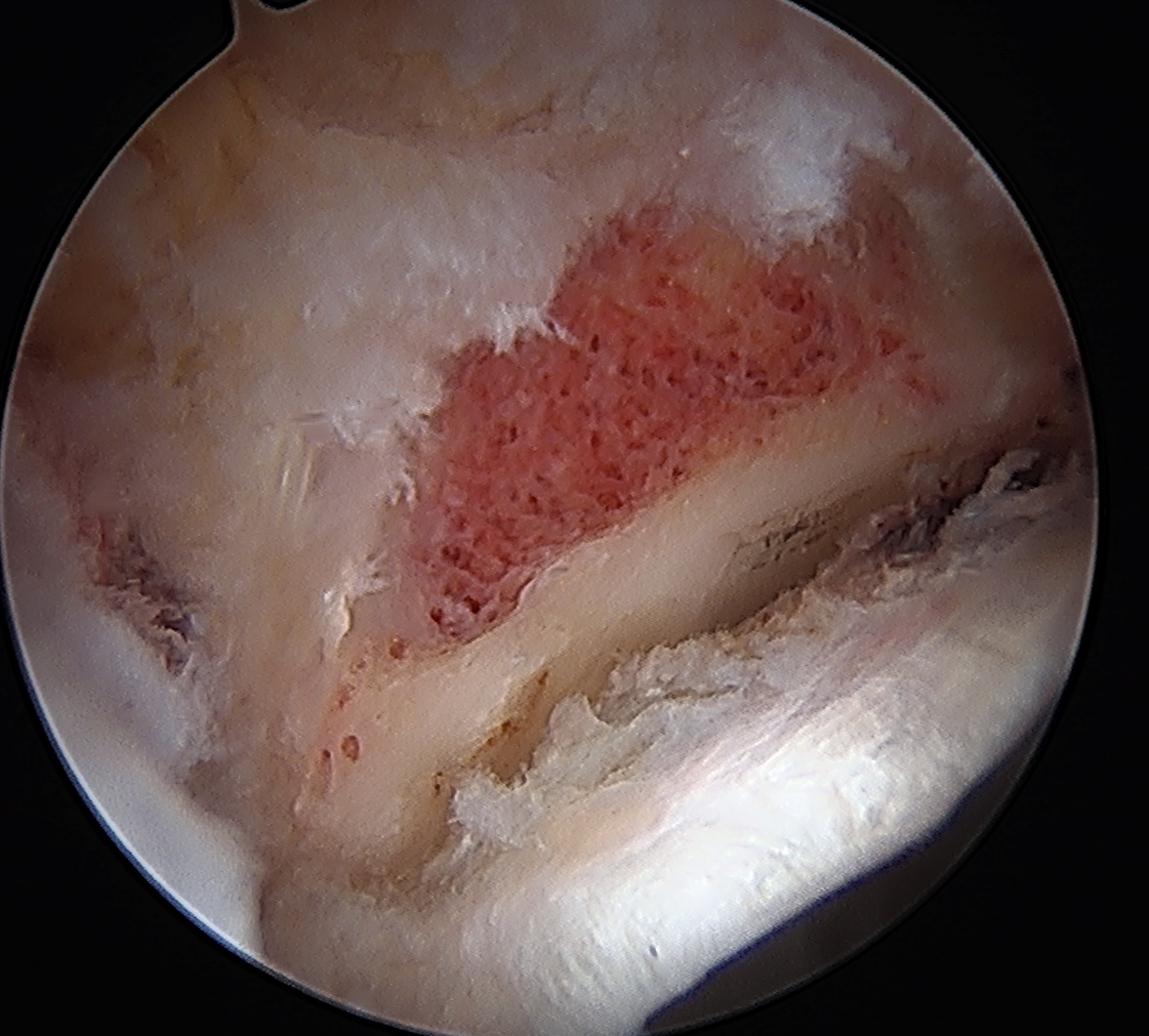
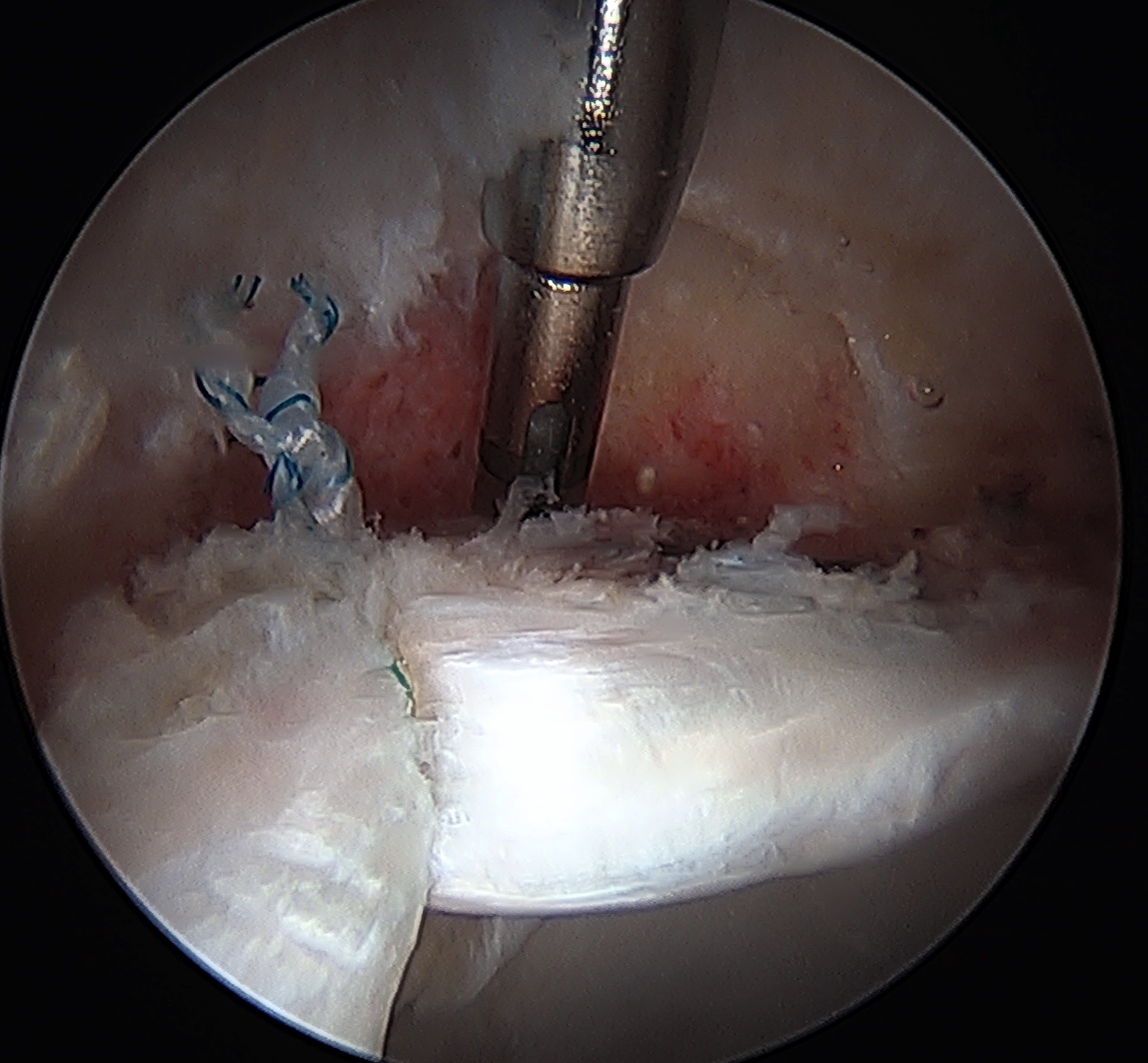
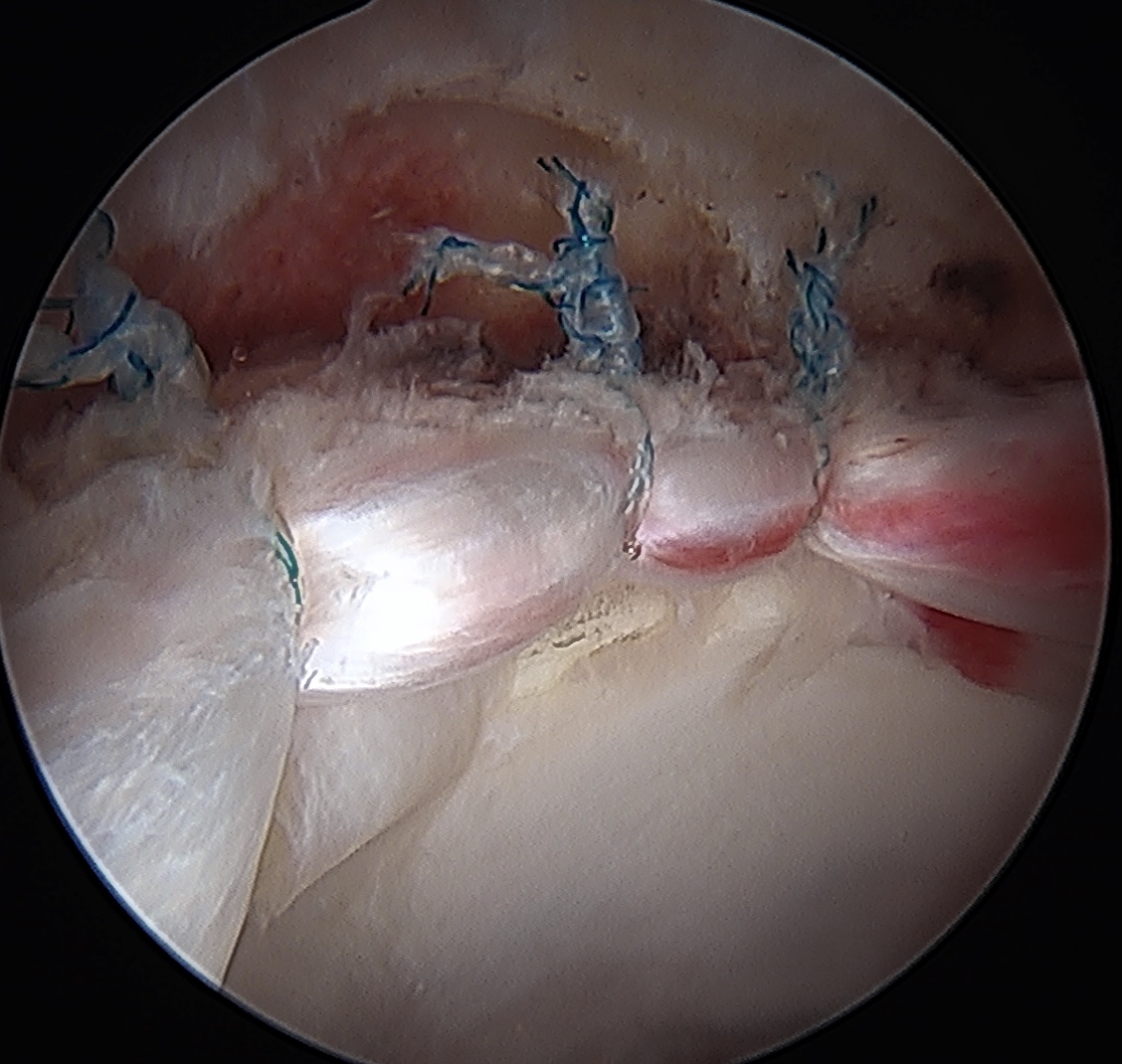
Labral debridement
- for degenerative / irreparable / ossified labrum / failed labral repair
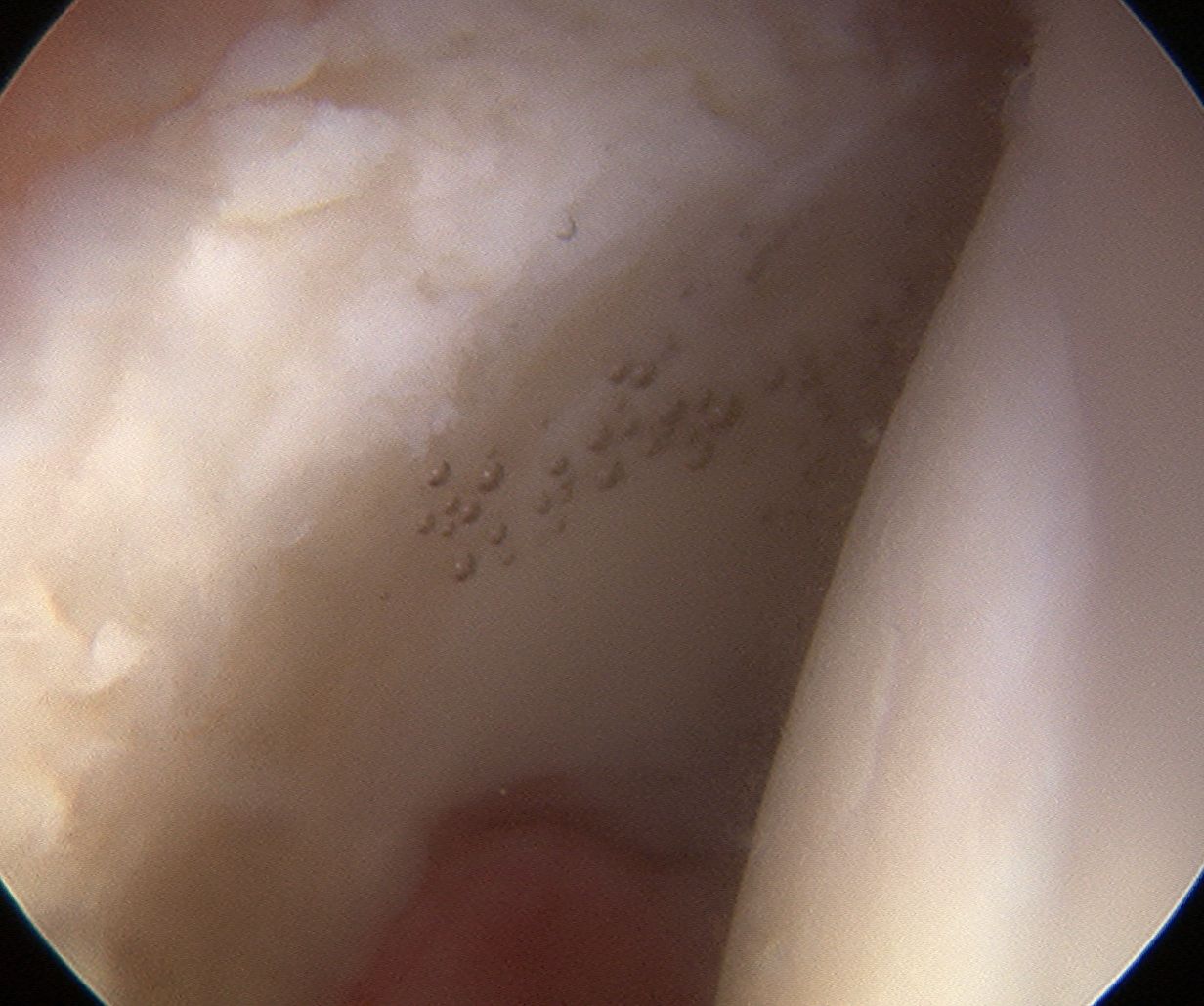
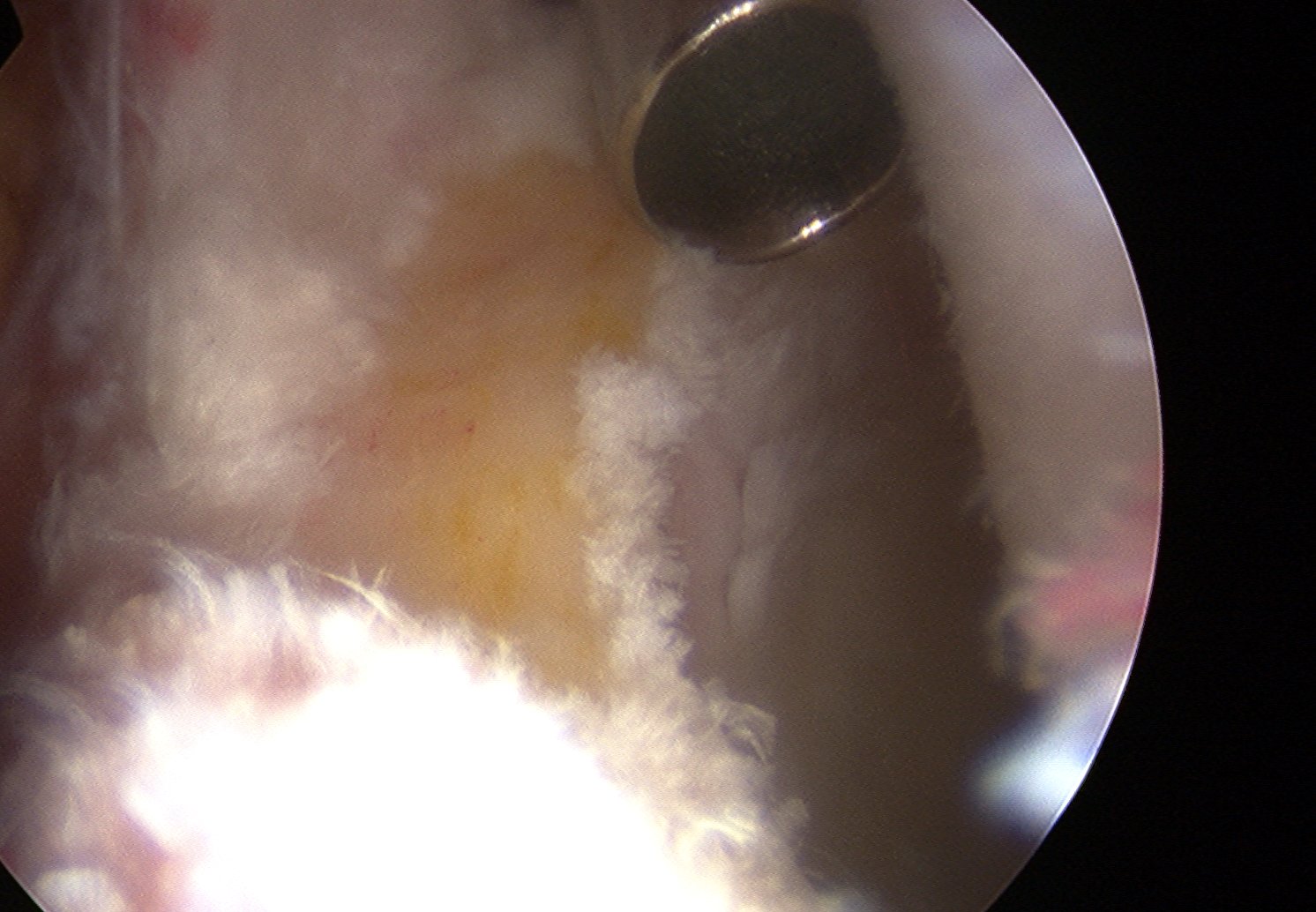
Labral debridement
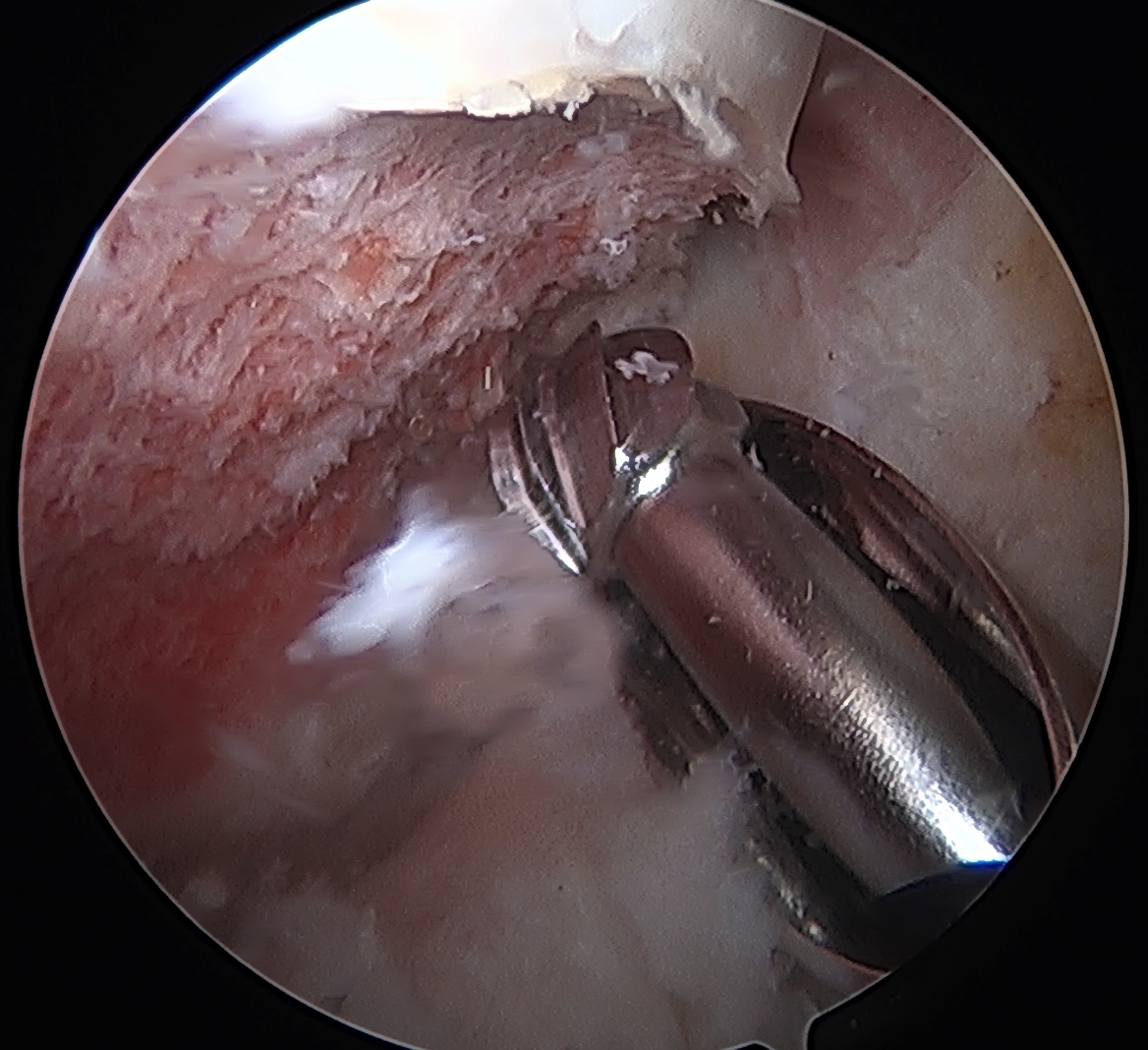
CAM resection
Capsule
- distal capsule suspension sutures / parachute technique
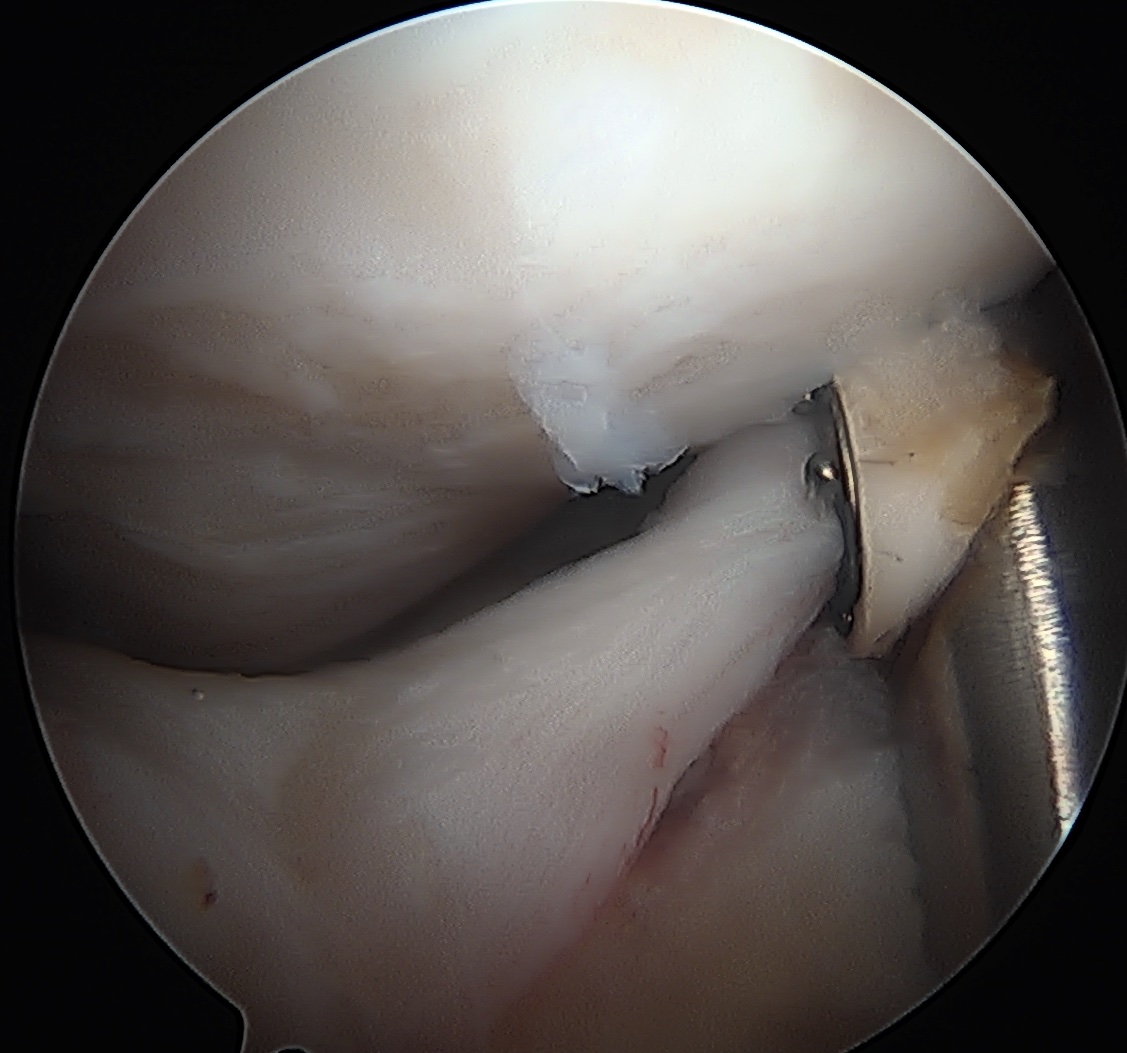
- T capsulotomy - better for large Cam lesions, needs repair
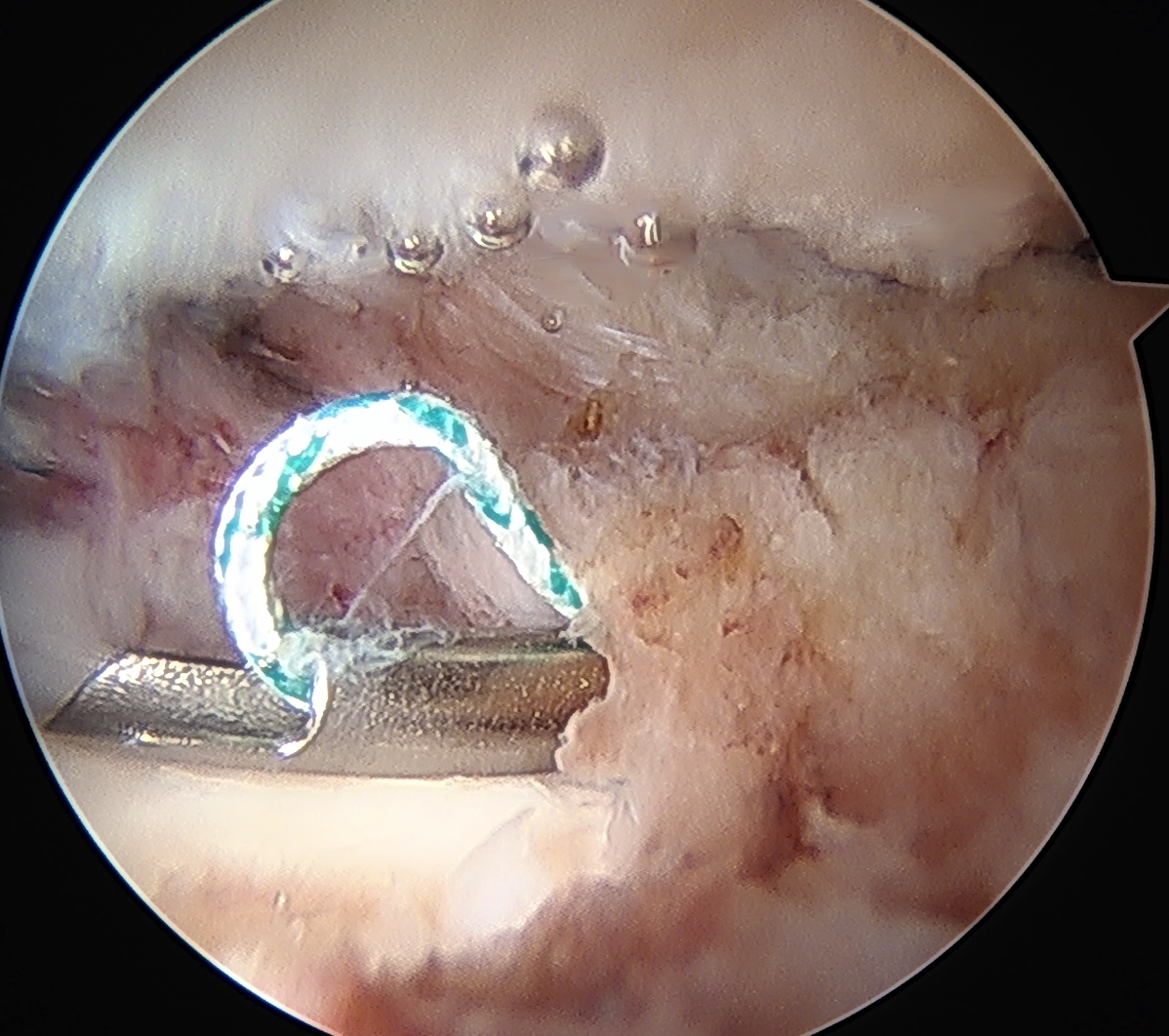
Placing distal capsule sutures to allow parachute technique / distal capsule suspension to expose Cam
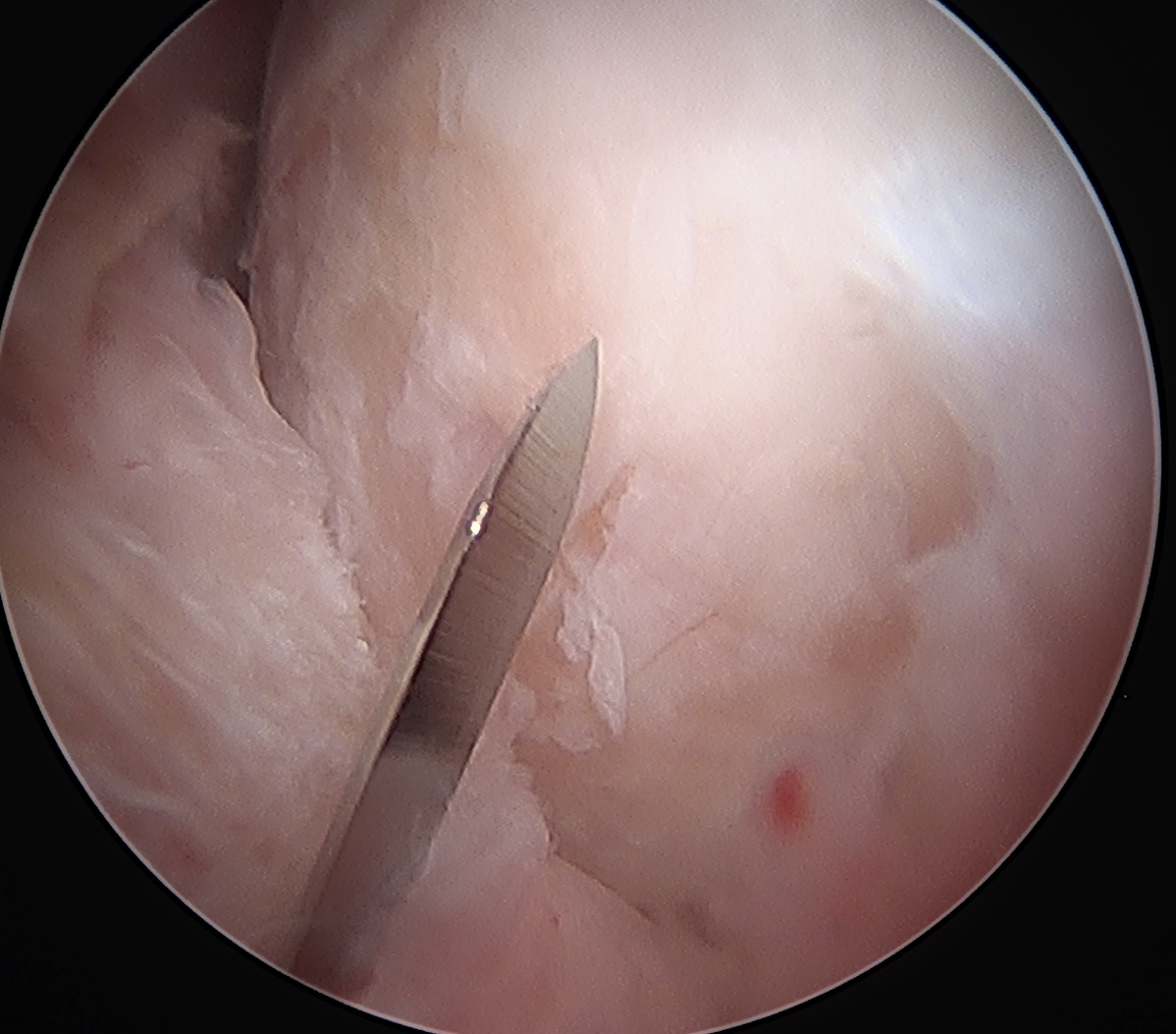
T capsulotomy to expose large Cam at head neck junction
Leg position
Anterior Cam
- hip flexed to 45 degrees
- image intensifer rotated 20 degrees posterior and 20 degrees distal to allow Dunn view
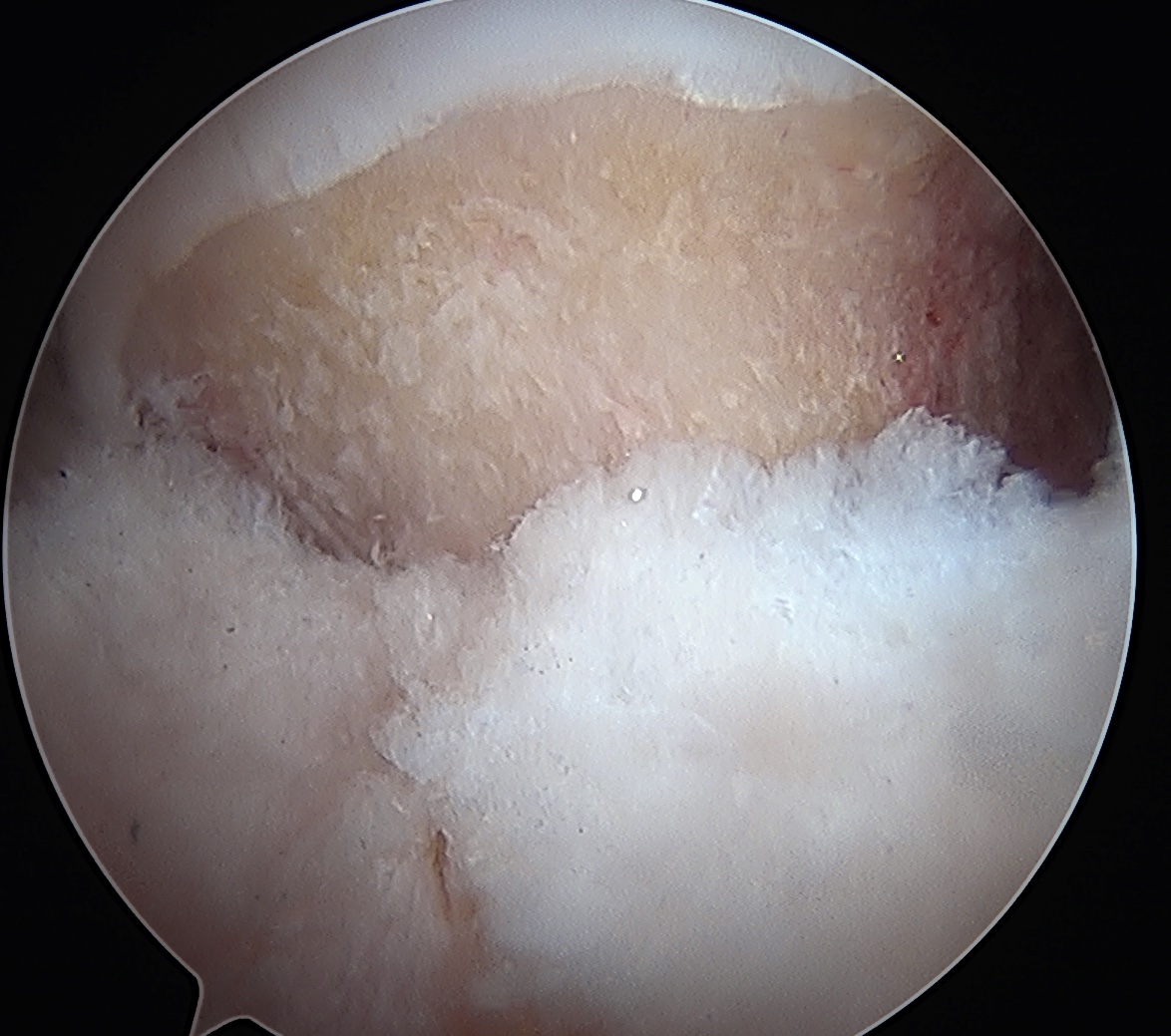
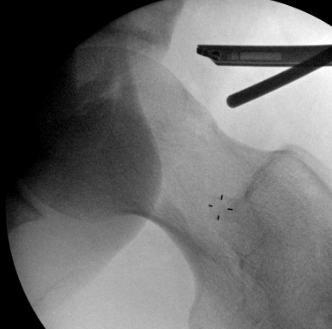

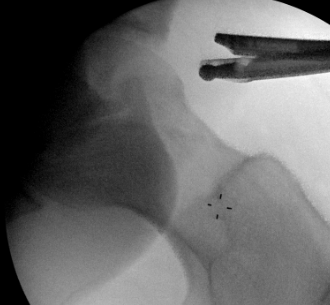
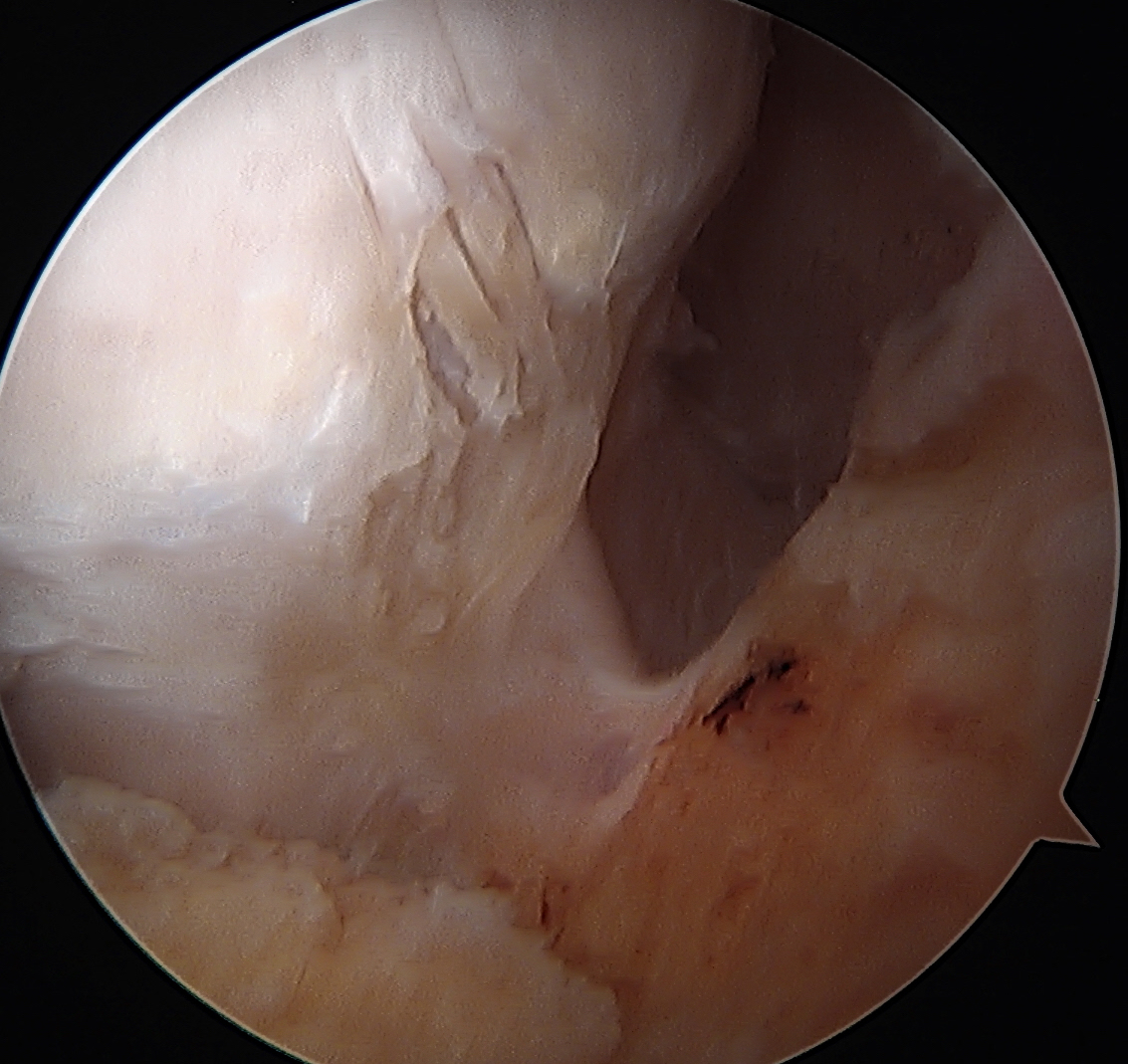
Anterior cam resection with hip flexed
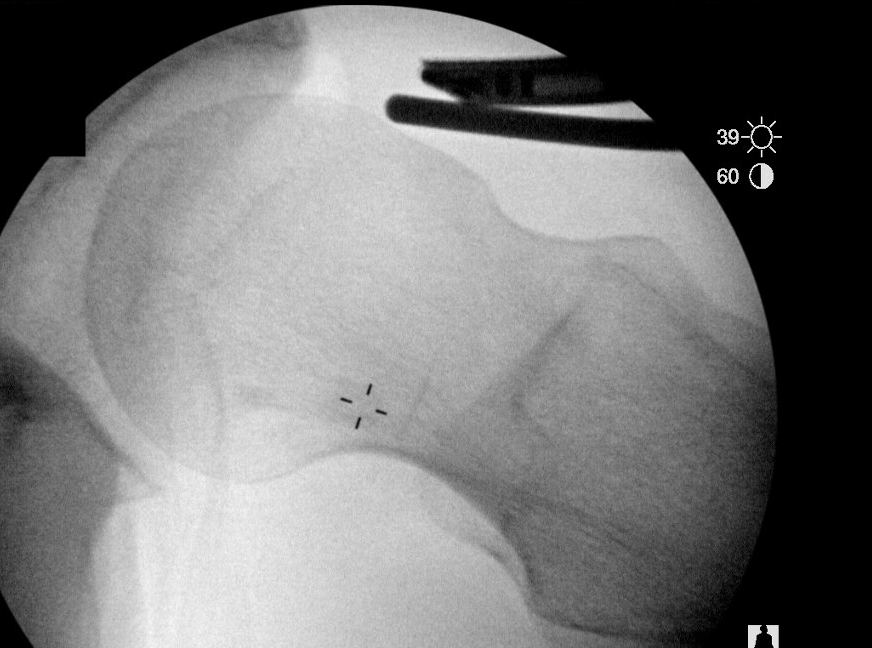
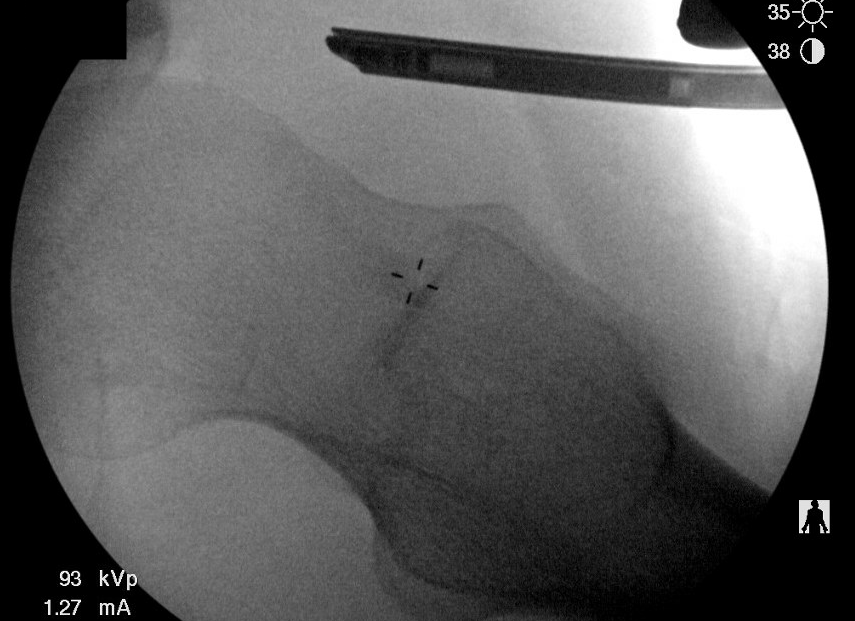
Intra-operative Cam resection using Dunn view
Lateral Cam
- hip in extension / internal rotation
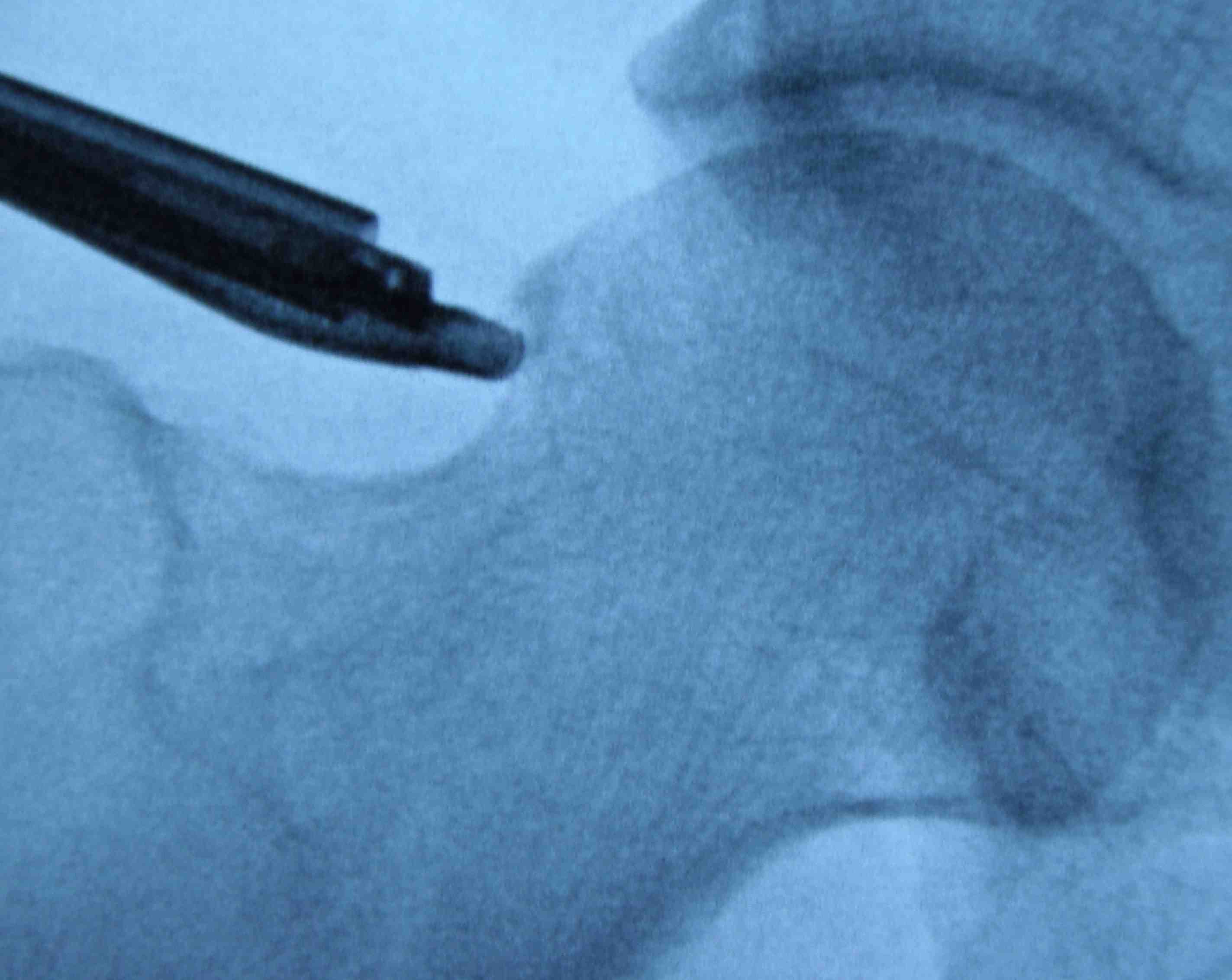
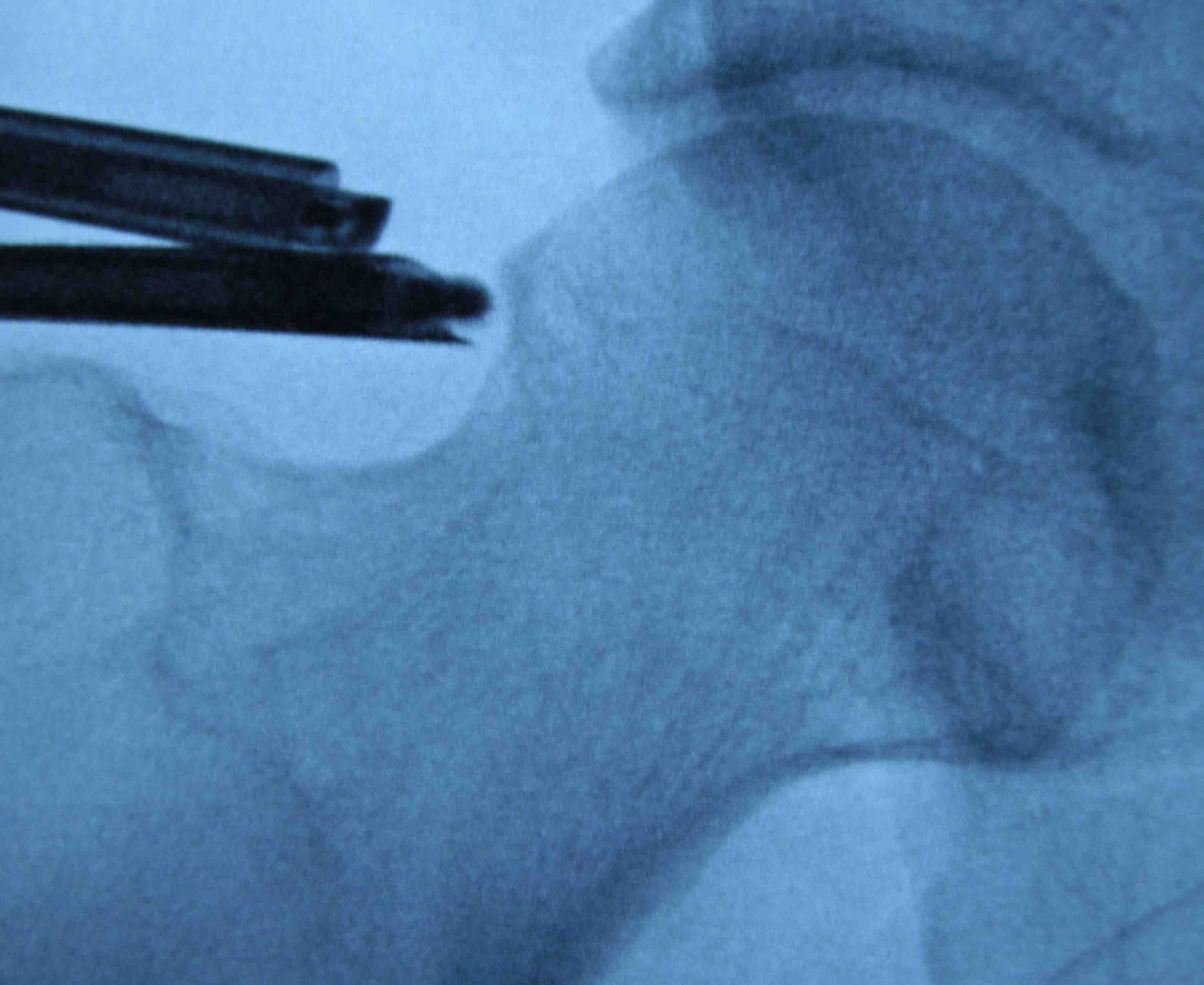
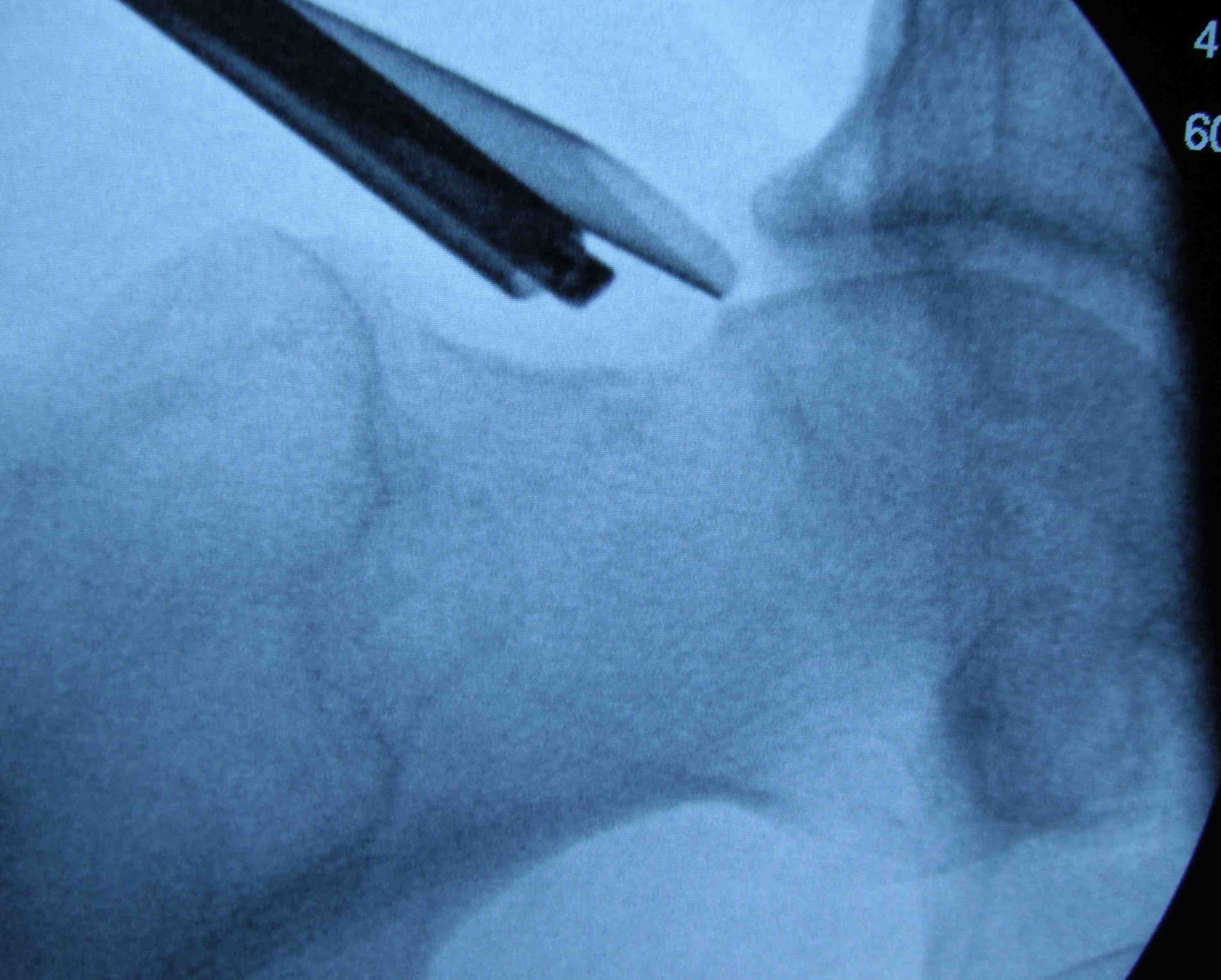
Lateral cam resection with hip in extension
Capsular Repair
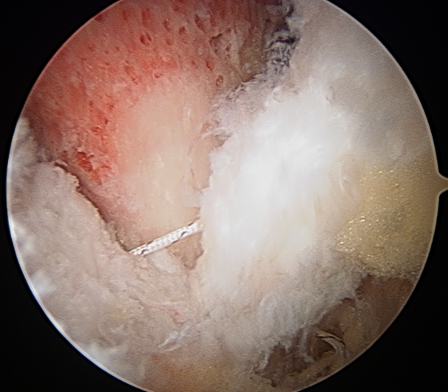
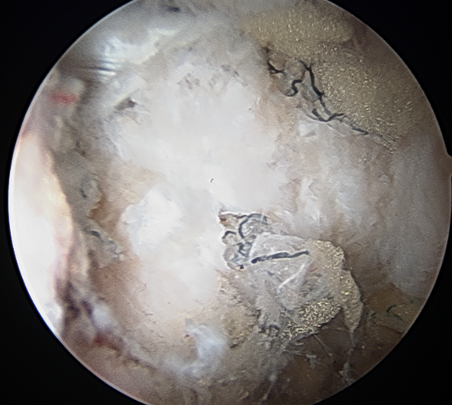
T capsule closure
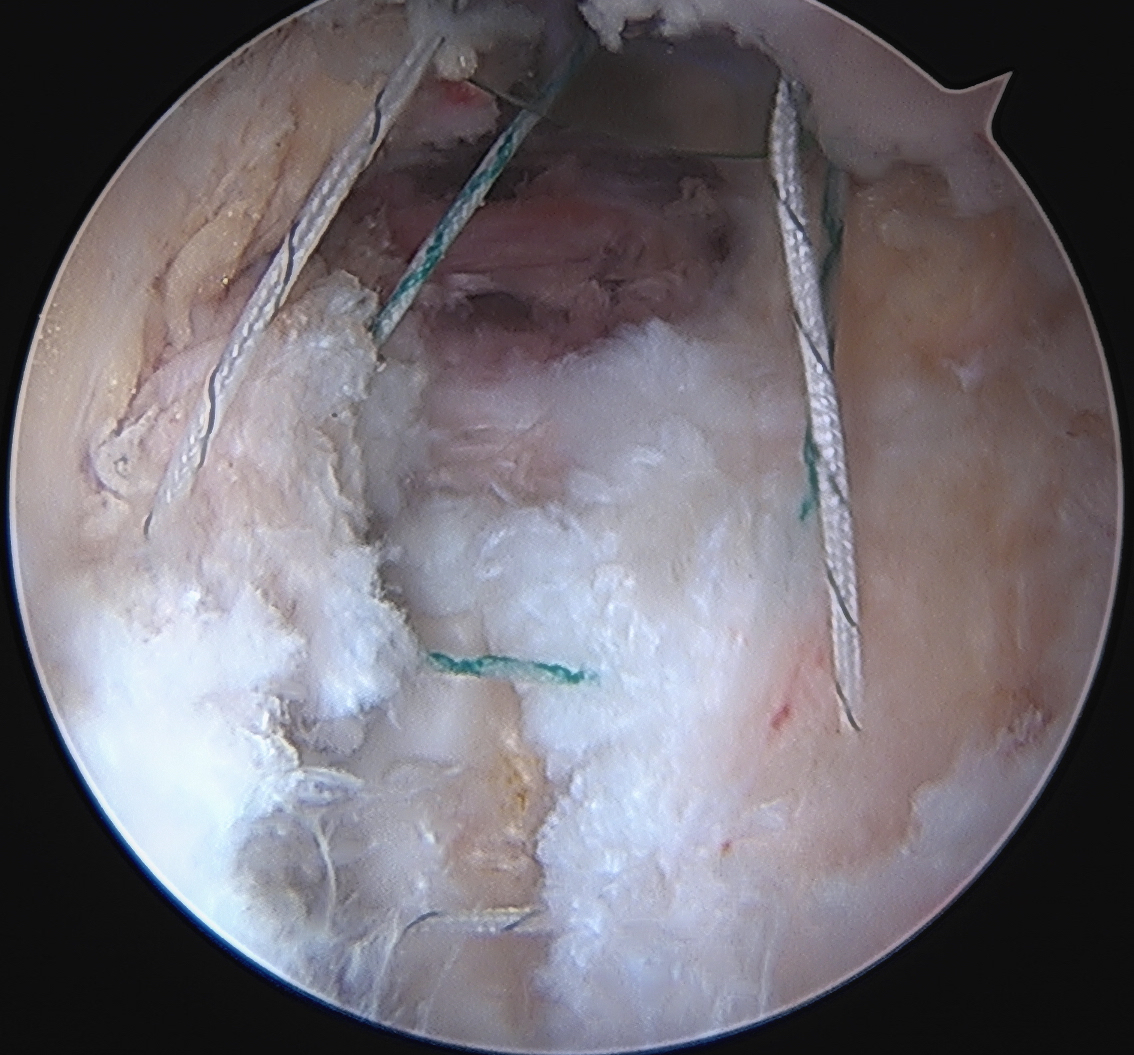
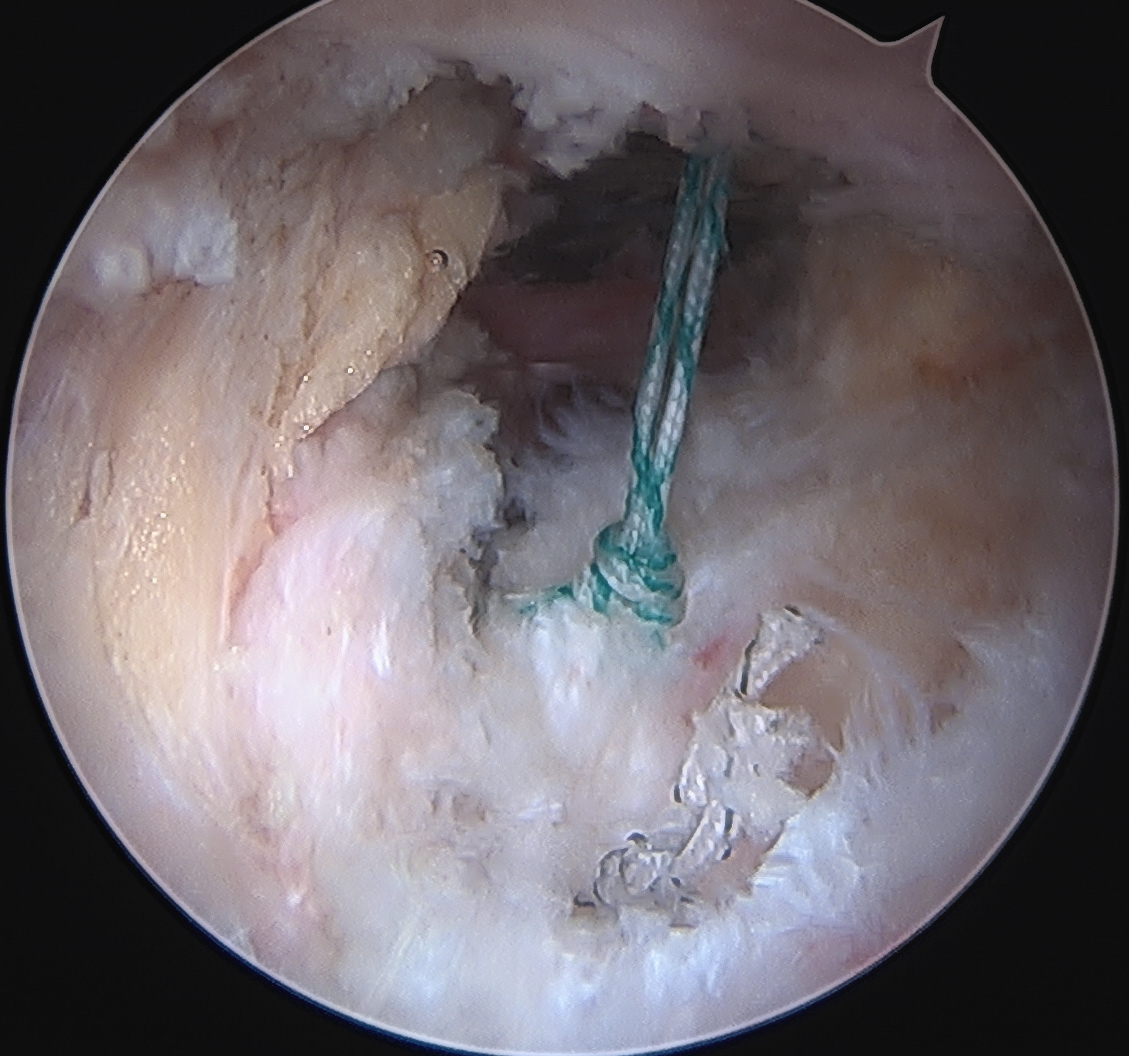
Interportal capsule closure
Complications
Infection 1/1000
DVT / PE - uncommon
Intra-articular anchors
Pudenal nerve injury
- secondary to use of post and excessive traction time / duration
- numbness in the groin / sexual dysfunction
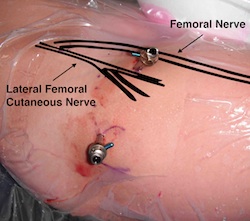
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury
- secondary to portals
- numbness outside of thigh
Numbness dorsum feet
- due to traction boots
Abdominal compartment syndrome
- extravasation of fluid
- associated with high pressures / prolonged surgery / psoas tendon release
- can be fatal
Hip fracture
- 1/1000
- excessive Cam resection
Hip dislocation
- 1/1000
- increased risk with ligamentous laxity / DDH / reduced LCEA / capsulotomy
Heterotopic ossification - 1%
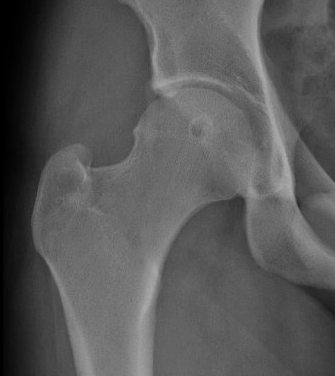
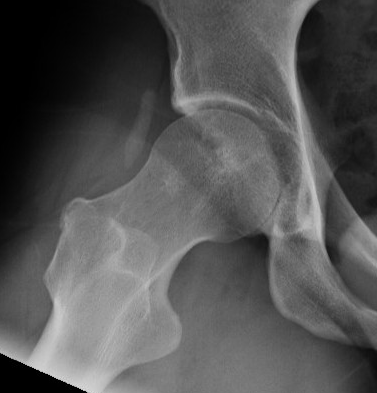
Heterotopic ossification anterior capsule
Capsular retear / deficiency
- may cause microinstability / pain
- most studies point towards superior outcomes with capsular repair
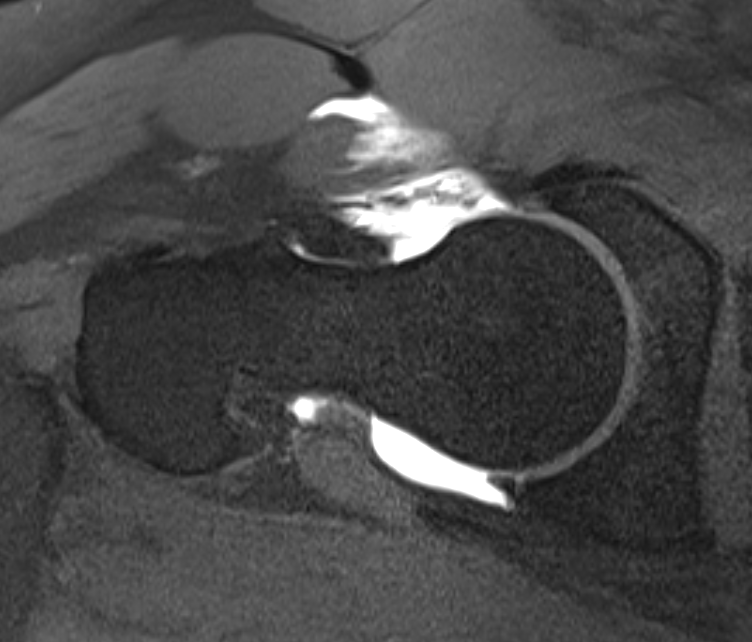
Anterior capsular deficiency on MRA post hip arthroscopy
