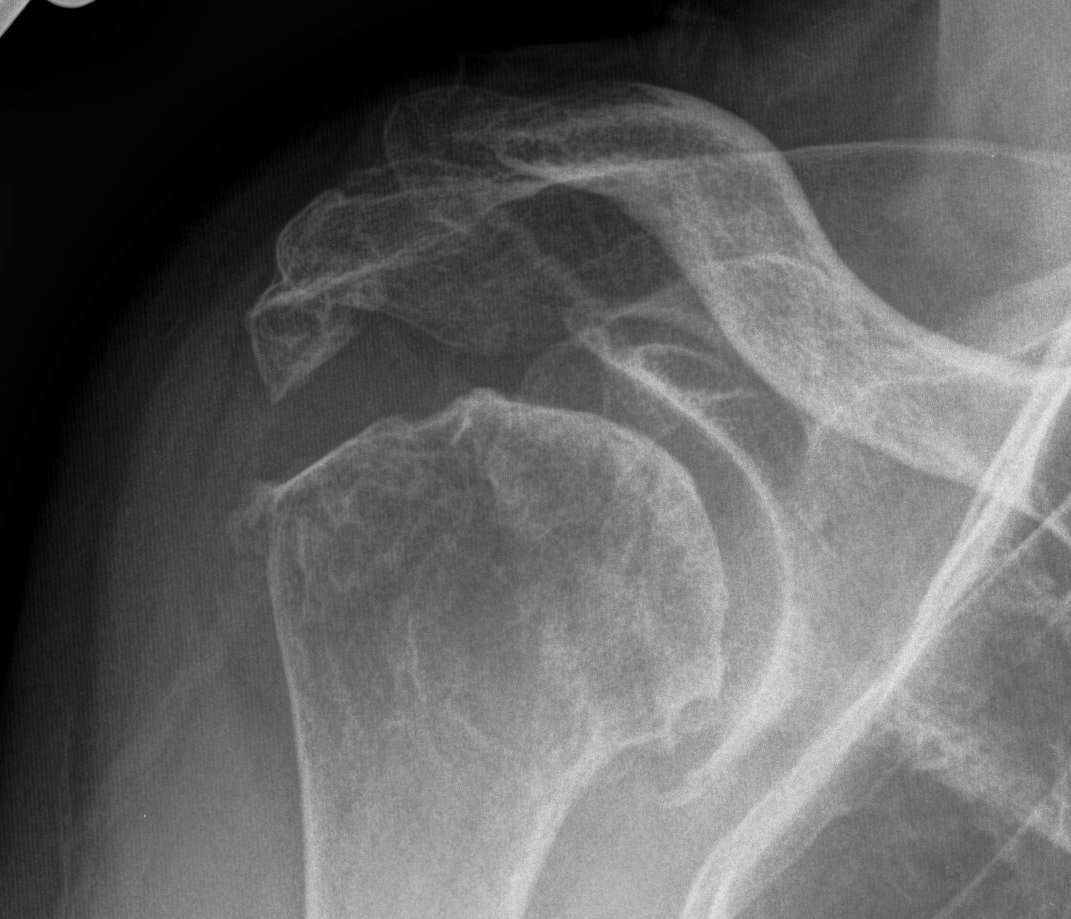
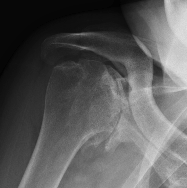
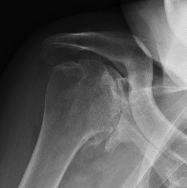
Xray
Typical changes of RA
- regional osteopenia
- marginal erosions and cysts
- humeral head erosions
- medial migration / protrusio
DDx
- septic arthritis
- gout / pseudogout
- Milwaukee shoulder (calcium hydroxyapatite crystals)
- rotator cuff arthropathy
- OA (beard osteophytes)
Issues
Rotator cuff deficiency
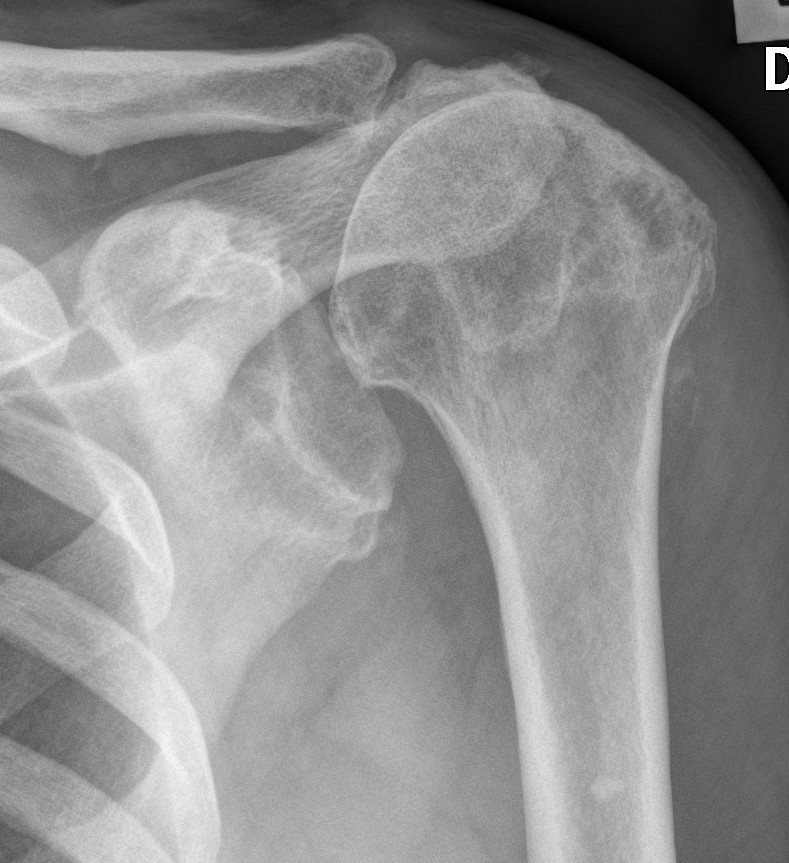
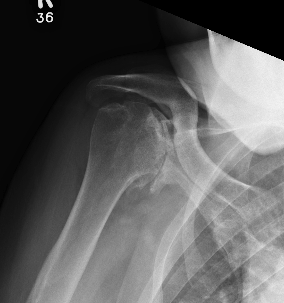
Proximal migration on the humeral head on xray
75% of patients will have rotator cuff pathology
Incidence of full thickness tears varies 20 - 50%
Glenoid deficiency
Levigne and Franceschi Classification
Three main patterns
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 |
|---|---|---|
|
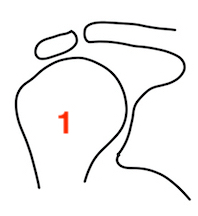
Upward migration Superior glenoid wear |
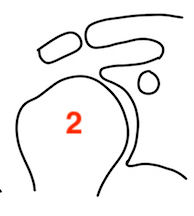
Concentric medial migration Deficient medial bone stock |
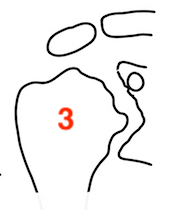
Destructive |
|
Due to rotator cuff insufficiency Most common pattern |
||
 |
 |
 |
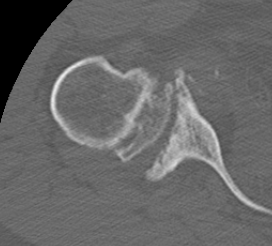
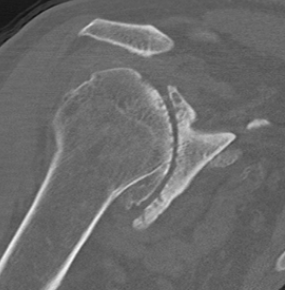
Rheumatoid arthritis with superior and medial wear
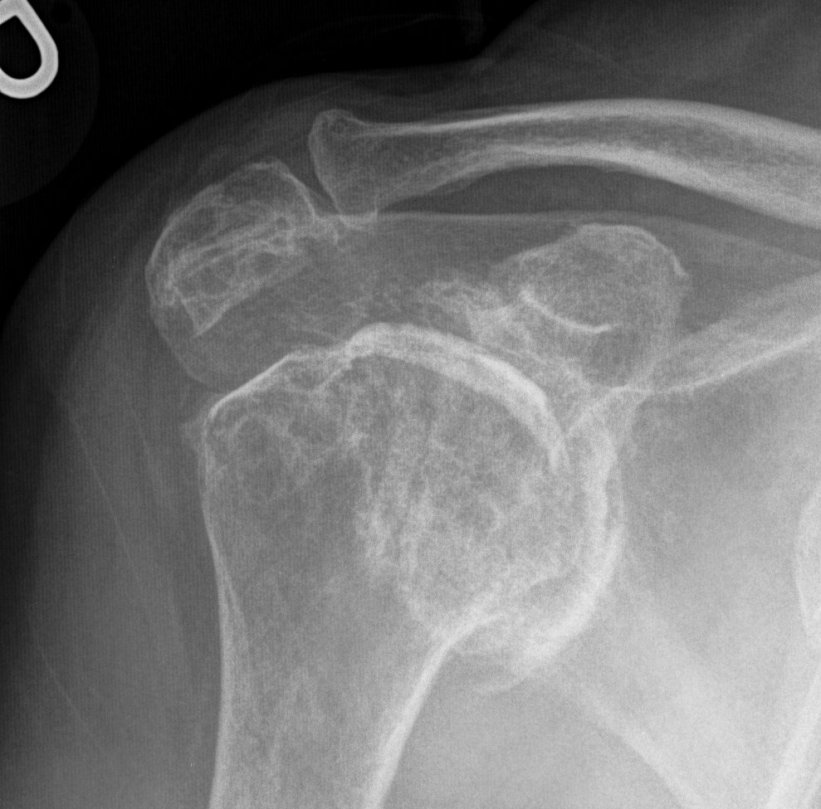
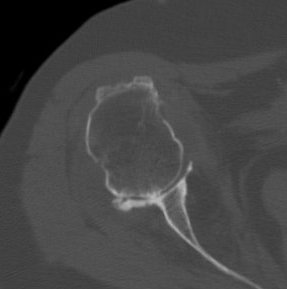
Medial migration with extremely deficient medial bone stock
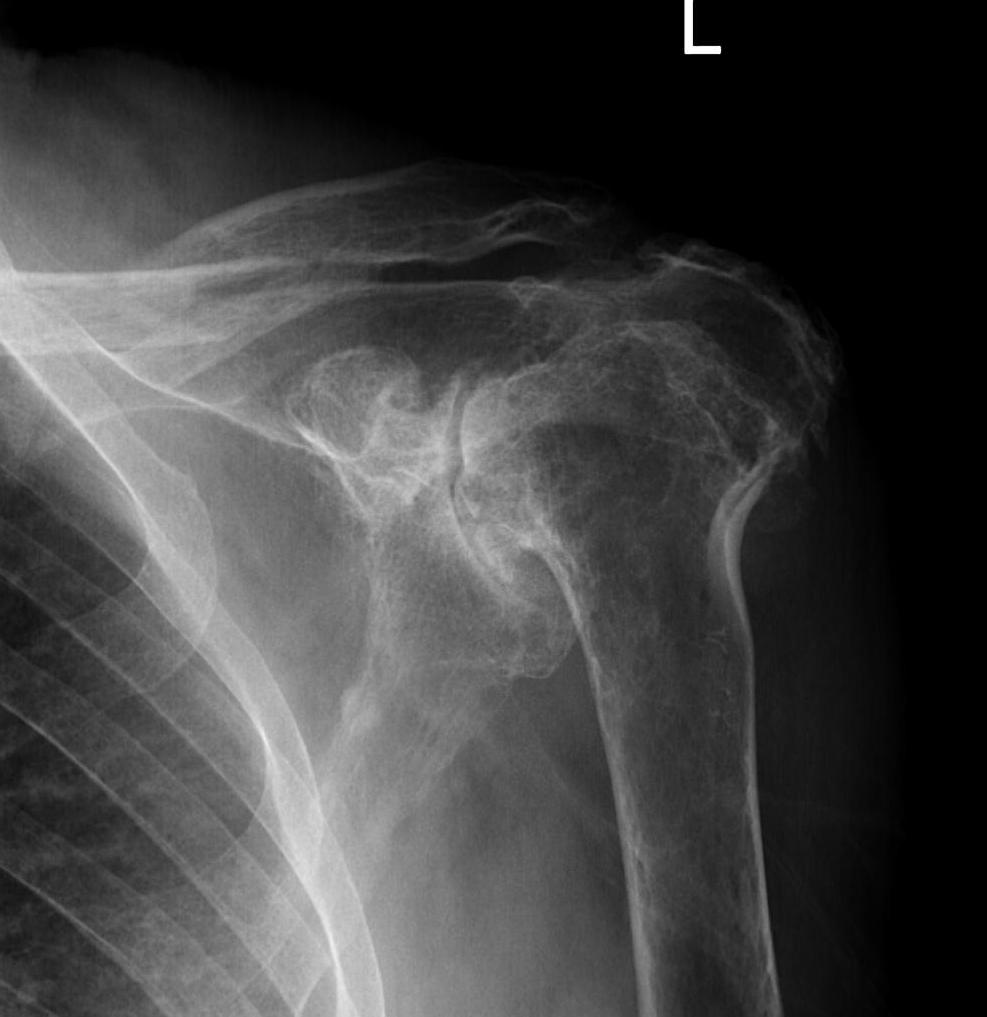
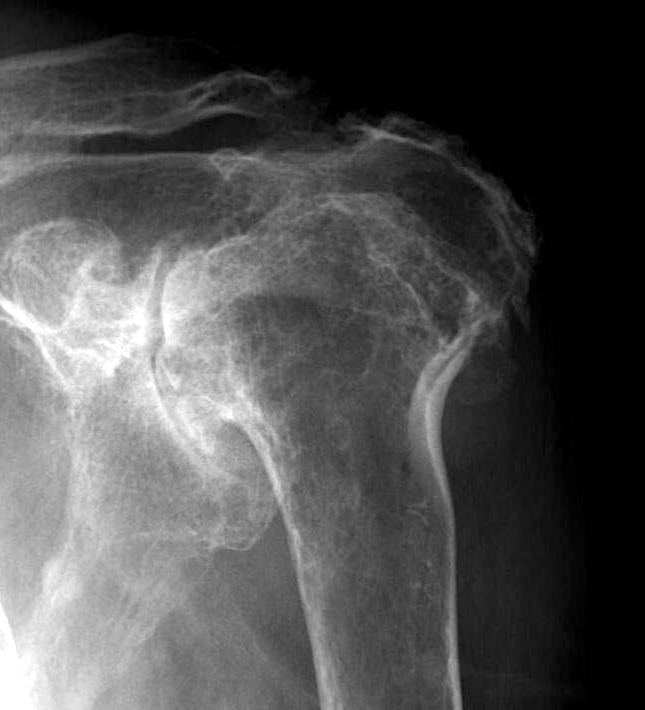
Destructive RA
Non operative Management
Injections
Cortisone / Hyaluronic acid / PRP
Medications
www.boneschool.com/rheumatoid-arthritis
Steroids
Methotrexate
Biologics
Anti-TNF - Adalimumab / Etanercept / Infliximab
IL - 1 receptor blocker - Anakinra
IL - 6 receptor blocker - Tocilizumab
Operative Management
Options
Arthroscopic Synovectomy
Hemiarthroplasty
Anatomic TSA
Reverse TSA
Arthroscopic Synovectomy
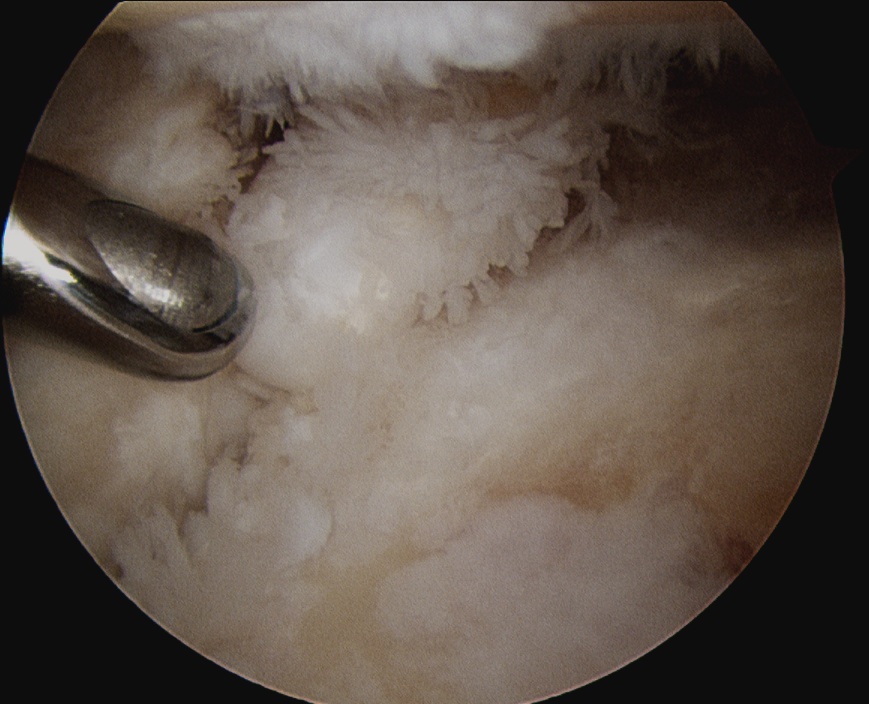
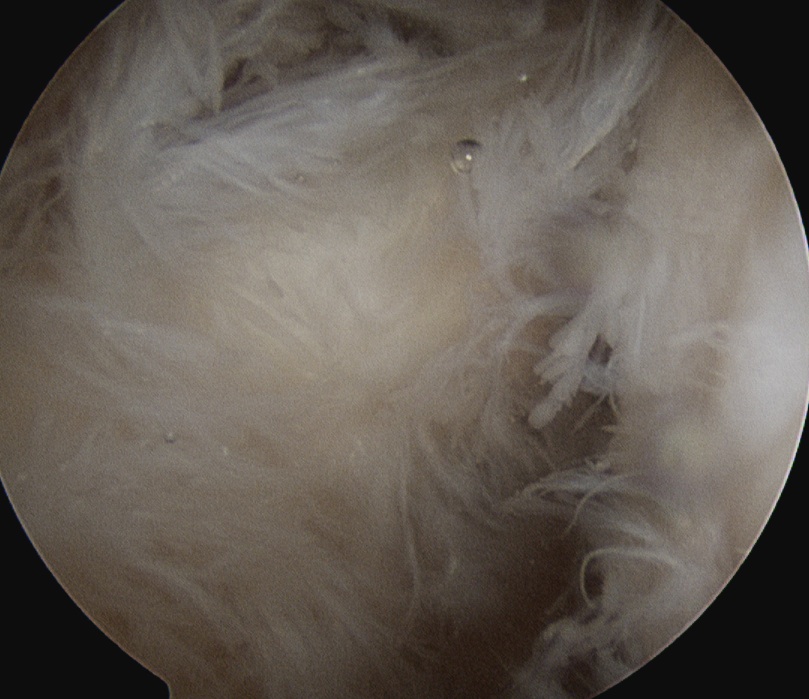
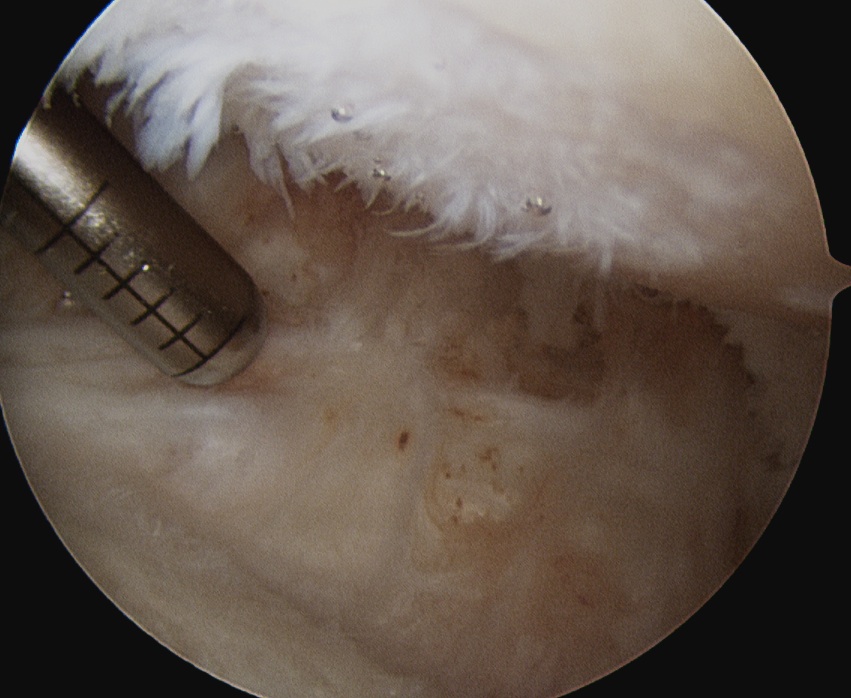
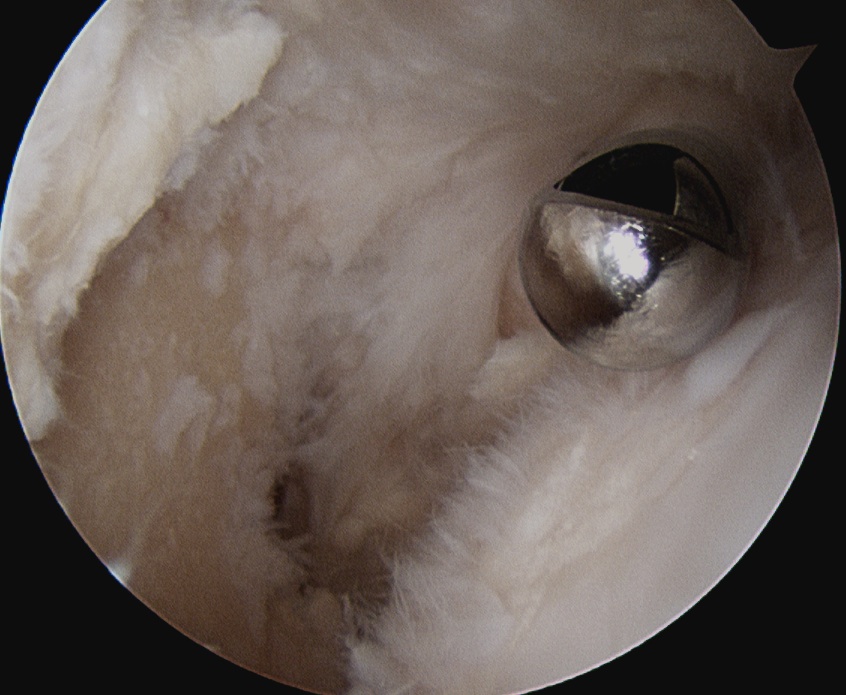
Kanbe et al. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2015
- arthroscopic synovectomy and capsular release for 54 RA shoulders
- mean follow up 5 years
- 67% receiving biologic treatments
- improvements in function and ROM
Arthroplasty
Options
Hemiarthroplasty - young, poor glenoid bone stock
aTSA - intact rotator cuff
rTSA - deficient rotator cuff
Hemiarthroplasty versus anatomic TSA
Barlow et al J Should Elbow Surg 2014
- 195 aTSA and 108 hemiarthroplasties with minimum 5 year follow up
- improved pain relief and abduction, and lower revision rate in aTSA compared with hemiarthroplasty
- 70% of glenoid components had lucencies
- 33% of glenoid components had shift in position
Anatomic TSA versus Reverse TSA
Haleem et al. Shoulder Elbow 2022
- systematic review of aTSR for RA
- 10 studies with 279 shoulders
- mean follow up 10 years
- revision rate 8%
- radiolucency seen in 70%
Cho et al. Clin Orthop Surg 2017
- systematic review of rTSR in RA
- 7 studies with 128 shoulders
- revision rate 7%
- 11% had intra-operative or postoperative fracture
- infection rate 3.3%
Reverse TSA in OA versus RA
Australian Joint Registry 2024
| Indication | 1 year | 5 year | 10 year | 14 year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis (n=23,000) | 2.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 6.7 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 2.3 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 6.1 |