Aetiology
Intrinsic
Infection
Loosening
Thigh pain in uncemented
- micro motion at distal end of stem
- modulus mismatch
Stress fracture / insufficiency fracture
- pubic rami, sacral
Intra-operative fracture
Prosthesis failure
Subtle instability
Extrinsic
Psoas tendon
Muscular tendonitis
- irritation of Psoas
- stretching of Adductors
- vas lateralis herniation
Trochanteric bursitis / tear G medius
Non-union of Trochanteric Osteotomy
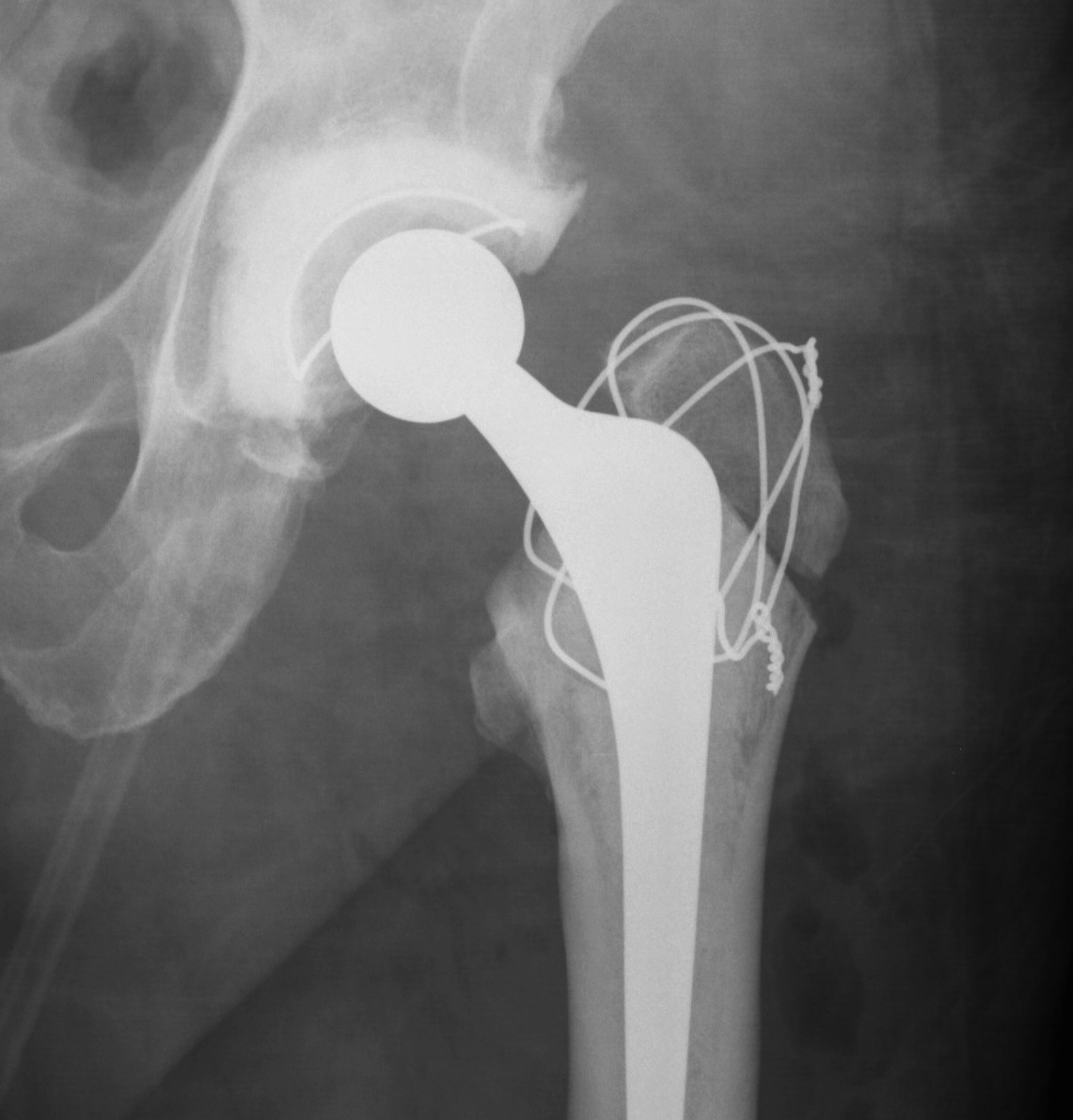
HO
Lumbar / Knee / Pelvic / Abdominal pathology
History
Nature of Pain
°Pain-free interval
- indolent infection
- pathology elsewhere (pain same as pre-op)
- poor implant fixation
- impingement
Pain-free interval
- loosening
- infection
- implant failure
Mechanical pain
- loosening
Start up pain
- pain with initial movement
- recedes as implant settles
- loosening symptoms
Rest pain / night pain
- infection
- tumour
Location
Buttock / groin pain
- cetabular pathology
Thigh / knee pain
- Femoral pathology
Pain over GT suggests
- trochanteric bursitis / tear G medius
- Non-union of trochanteric osteotomy
Pain in other locations
- spinal stenosis
- knee OA
Radiating below knee
- radiculopathy
Infection
Drainage postoperative suggests +++ infection if > 1/12 post-op
History of bacteraemia suggests infection
Prolonged in hospital ABx treatment
Examination
Pain with ROM
- loosening - extremes of motion
- infection - pain throughout motion
- implant failure
Tenderness over GT
Wound
- induration, erythema & drainage
Spine, knee & vascular exam
Groin for inguinal hernia
Xray
Problems
1. May be normal in face of pathology
- serial comparison very important
2. Difficult to differentiate infection v loosening on XR
Infection
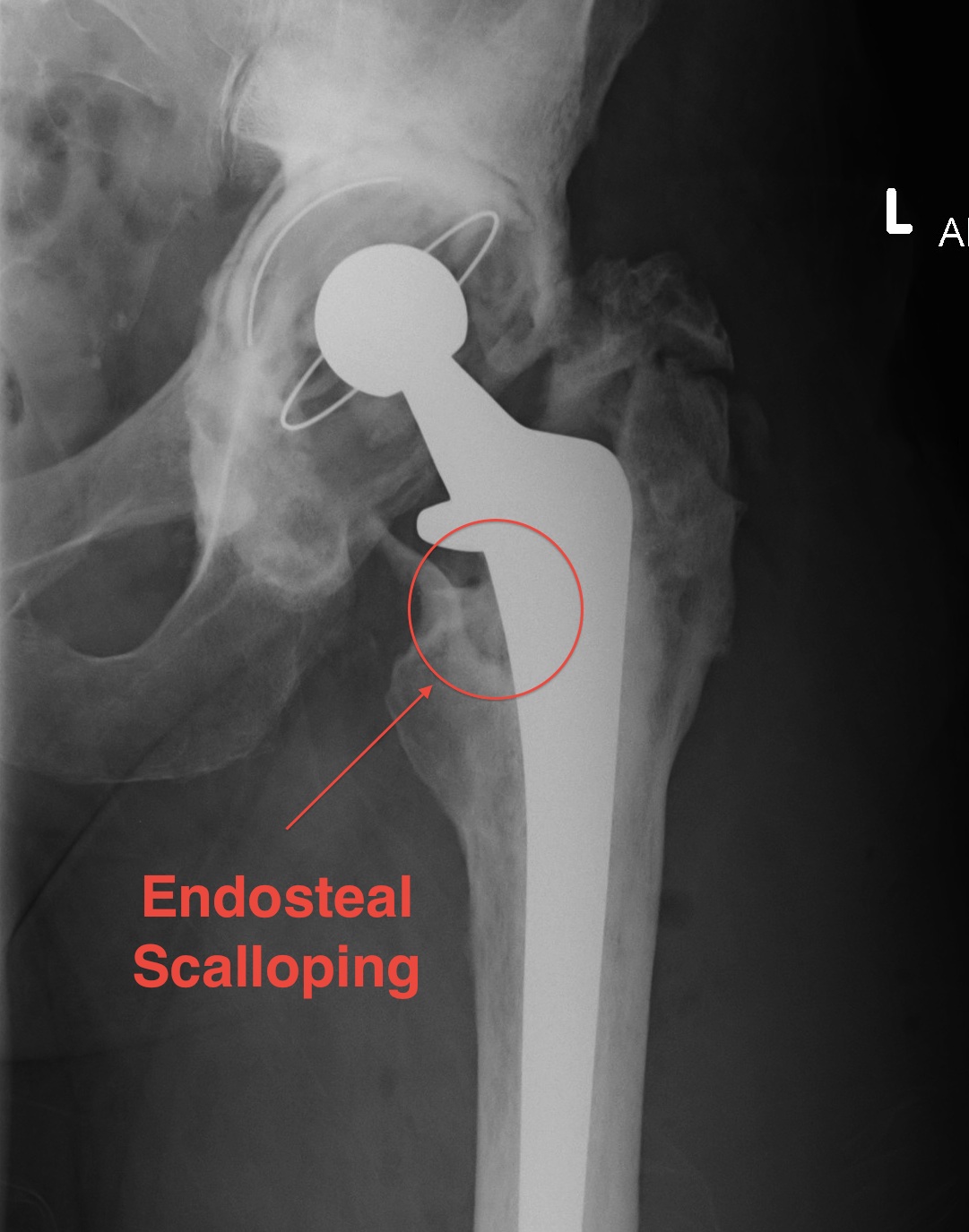
1. Radiolucent lines
2. Focal Osteolysis with Endosteal scalloping
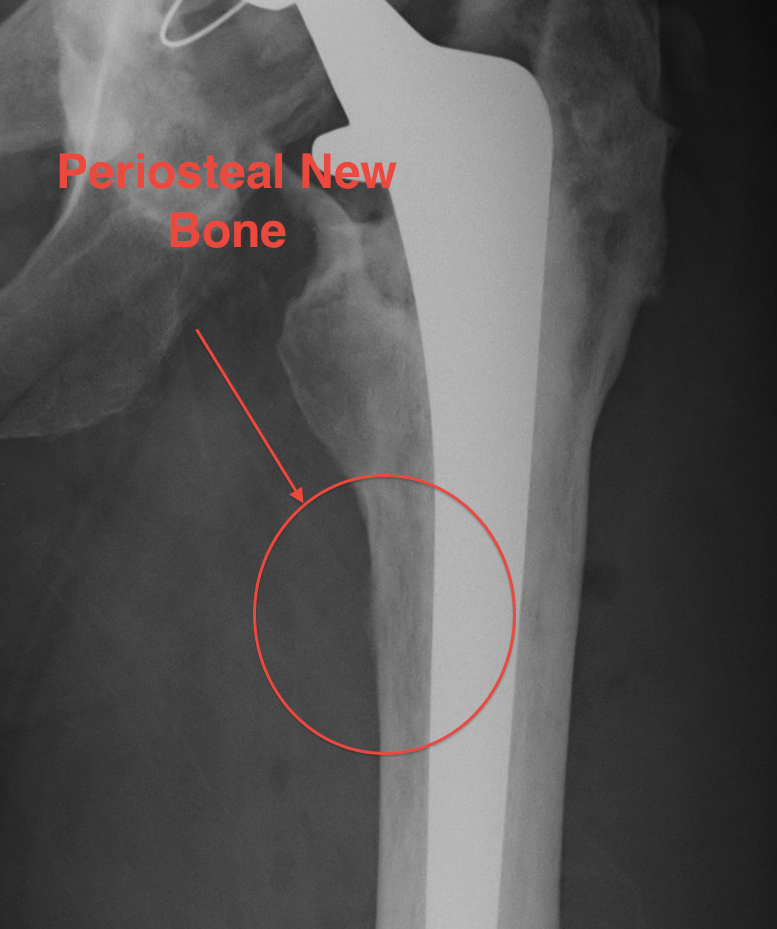
3. Periosteal new bone
- almost pathognomonic
- usually at junction meta / diaphysis on medial side
- only seen in 1-2%
Loosening
Easier to identify loosening in femur than acetabulum
- femur 90% accuracy
- acetabulum 65% accuracy
Lucent lines don't necessarily represent problem
- may be present in well-fixed prosthesis (retrieval studies)
- due to remodelling
WCC
Little value
- increased in 15%
- raised only if sepsis +++
ESR
> 30 mm = 80% sensitivy & specificity for infection
Problems
- takes 6 - 12 / 12 to normalise post OT
- very non specific, increased in RA and remote pathology
- can be raised in aseptic loosening
CRP
> 10 mg/l = 90% sensitiviy & specificity
- rarely increased with loosening
More predicable response post OT
- peak 2/7 (~400)
- normal after 3 /52
In the absence of other causes of elevation
If CRP is negative can be confident is no infection
- negative predictive value 99%
If CRP is positive is still a 20% chance that is no infection
- positive predictive value 75%
IF both ESR > 30 and CRP >10, 84% probability of sepsis
Te99 Scan
Bone scan may show increased uptake from
- infection
- loosening
- HO
- Paget's
- stress fracture
- large uncemented stem (modulus mismatch)
- tumors
- RSD
Advantage
- pathology unlikely if negative
Disadvantage
- very sensitive
- poor specificty
- doesn't differentiate cause
Lieberman et al JBJS Br 1993
- no benefit of NMBS over x-ray in diagnosis of infection or loosening
Residual activity
Cemented
- majority return to normal by 1 year
- 20% remain hot at portions of stem / GT / LT past 1 year
Uncemented
- can remain hot for 2 years
- can remain hot at distal stem for many years
Infected prosthesis
All phases increased & usually diffuse in 3 phases
- highly suggestive of infection
- can get focal uptake similar to loosening but rarer
Loose prosthesis
- localised increased uptake on delayed phase only
- motion of prosthesis causes increased bone turnover due to bone resorption
- increased uptake @ GT & LT alone may be normal post op change
- well advanced loosening can show diffuse uptake as for an infected hip
Stress sites
- will see localised area of uptake on scan
- corresponds with cortical thickening on plain XRs
Insufficiency fracture
- occur in osteopaenic patients
- pubic rami fractures may cause groin pain
- sacral fractures may cause posterior hip pain
Indium 111 Labelled WC Scan
Uncertain role
- expensive, difficult
- have to harvest WC
More specific for infection
- especially when combine with bone scan
- sensitivity 92%
- range specificity 75 - 100%
Aspiration
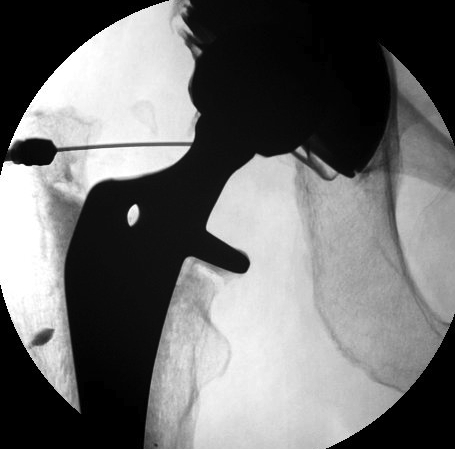
Technique
- no Abx >4 weeks
- II control & with contrast / confirm in joint
- no LA (bacteriostatic)
- aspirate hip joint x 3 specimens
- if only 1 specimen positive then repeat
If dry, inject normal saline & aspirate
- controversial
> 65% PMN infection likely
> 1600 white cells microlitre
Results
Harris & Barrack JBJS 1996
- 2% positive rate if aspirate all hips
- therefore be selective
Lachiewicz et al JBJS Am 1996
- hip pain and elevate ESR
- 92% sensitivity & 97% specificity
HCLA
Crawford et al JBJS 1998
- 95-100% sensitivity
- ff good results from LA expect same from THR
- demonstrates that the pain is from the hip
Intra-Operative Frozen Section
PMN Cell Count
- 40x power, count white cells in that field
- average over 10 fields
Mirra 1976 > 5phpf
- 84% sens, 96% spec
Lonner 1996 > 10phpf
- 84% sens, 99% spec
Intra Operative gram stain & m/c/s
Gold Standard
- 10% false positive
- Gram stain sensitivity < 20%, but very specific
All revisions no antibiotics for 4 weeks prior
Surgical Opinion
Sensitivity 70%
Specificity 85%
Management
Algorithm
Xray N / Scan N / ESR & CRP N
- not infected
- explore extrinsic causes
Xray Loose / ESR & CRP raised
- infected
- 2 stage revision with intra-operative M/C/S
Xray normal / Hot scan / Raised ESR & CRP
- infected
- 2 stage revision
- intra operative FFS to confirm
Xray / Scan / ESR / CRP all equivocal
Aspirate
