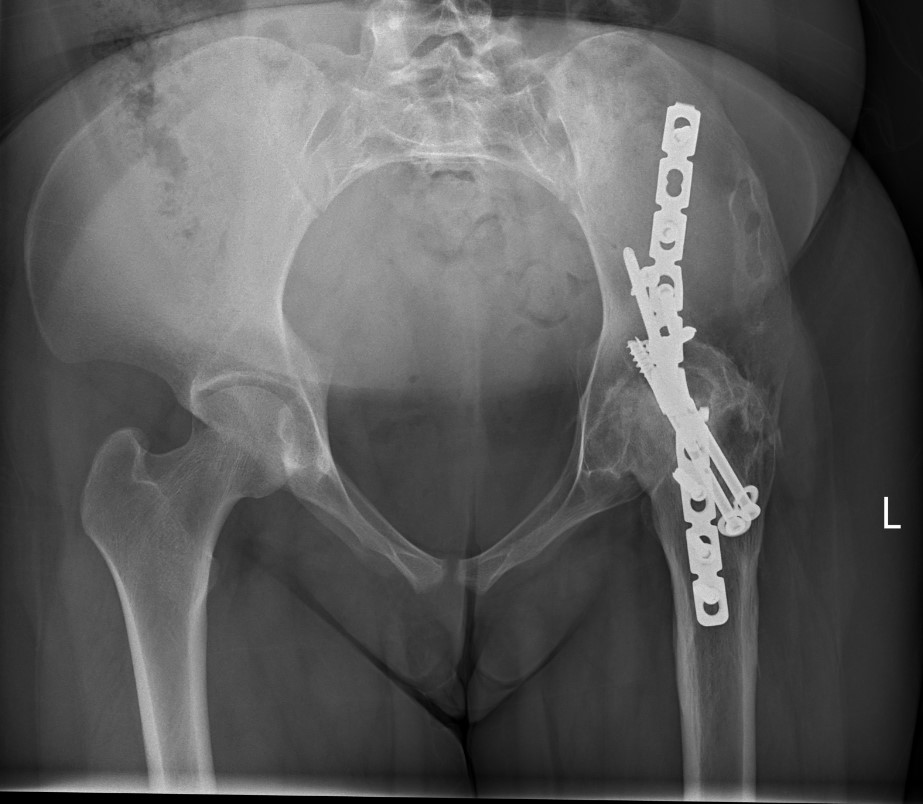
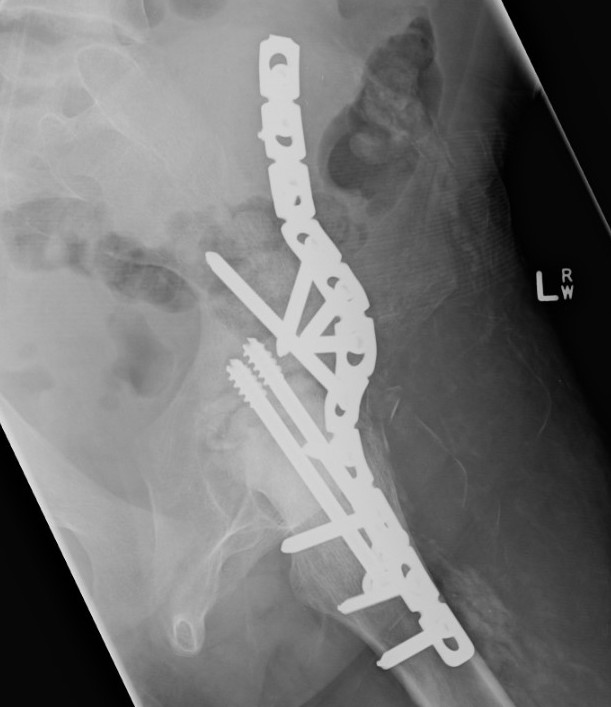
Indications
Young adult / children / adolescents with end stage OA
High risk of THA failure / multiple revision surgeries
Aims of arthrodesis
Minimise shortening
Facilitate future conversion to THR
Contraindications
Poor bone stock
- i.e. AVN
Bilateral hip disease
- need ROM in other hip 90o in order to compensate in gait
Polyarticular disease i.e. Rheumatoid arthritis
- likely to develop hip / knee / back OA
Degenerative disc disease
- lumbar spine ROM important to compensate in gait and ability to sit in chair
Stiff ipsilateral knee or contralateral hip
Disadvantages
Functionally inferior to THA
Increased stress on other joints
1. Lumbar spine pain
- most common reason for converting to THA
2. Ipsilateral knee pain
3. Contralateral hip pain
Difficulties with certain activities
Squatting
Running
Sitting erect in chair
Difficulty putting on shoes
Gait abnormalities
Decreased stride length / shortened stance phase
Increased energy requirements / increased oxygen consumption
Surgery
Concepts
Retain option of conversion to THR
- avoid old techniques involving pelvic osteotomy
- preserve abductors
Types
1. Intra-articular
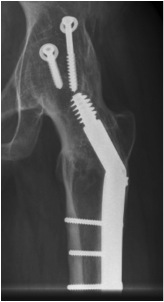
2. Extra-articular
3. Combined
Position
Sagittal / 20° flexion
- <20° flexion - difficult to sit
- >25° flexion - difficult to walk due to LLD
Coronal / 0° adduction / abduction
- never abduction: can't walk, fall over even with 5° abduction
- too much adduction: LLD
Rotation / 15° ER
< 2 cm LLD
Complications
Pseudarthrosis - 10%
Mal-positioning
Options
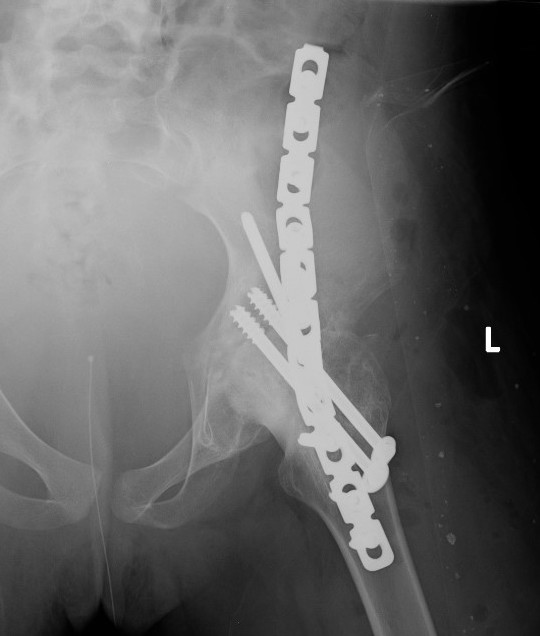
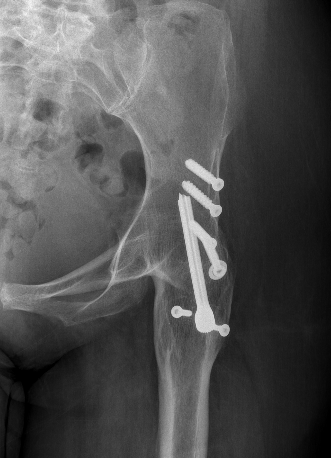
| Extra-articular | Intra-articular | Combined intra-articular + anterior plate |
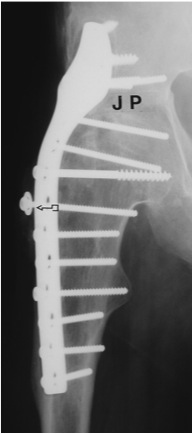 |
 |
  |
Technique
Surgical technique tntra-articular + anterior plate PDF
Technique
Radiolucent table with image intensifier
Supine
Smith Peterson approach
- leave abductors intact
- dislocate hip anteriorly
- between sartorius and TFL
- between G medius and Rectus femoris
- take off reflected head of rectus, remove direct head to AIIS
Remove cartilage from head & acetabulum
- cup arthroplasty instruments useful for acetabulum
- approximate raw surfaces
- pack cancellous autograft
- position hip & hold with guide-wires temporarily
- place one guide wire central in head
Check position of hip
- need to be able to do intra-operative Thomas test
- Flexion 20o / Add 0o / ER 15o
Fixation
- 150° DHS / 6.5 mm cannulated screws
- through joint into thick supra-acetabular area of ilium
- supplement with additional screws as necessary
Anterior plate onto lateral aspect of iliac crest
TWB 3 months
Consider late plate removal to reduce risk peri-prosthethic fracture
Results
Banksota et al Bone Joint J 2022
- 20 year follow up in 26 patients
- mean age at fusion 14
- Harris hip score good / excellent in 57%
- Harris hip score fair in 42%
- 20% moderate back pain
- 4% moderate knee pain
- 35 fusions with anterolateral fusion plate
- nonunion 2/35
Ipsilateral TKA with fused hip
Issue
- cannot flex hip
- impossible to flex knee when supine on bed
Solution
- knee over end of bed
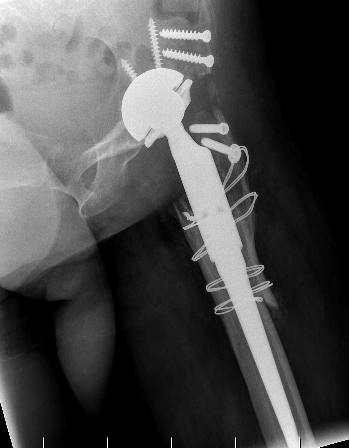
Conversion to THA

www.boneschool.com/arthrodesis-conversion-THA
