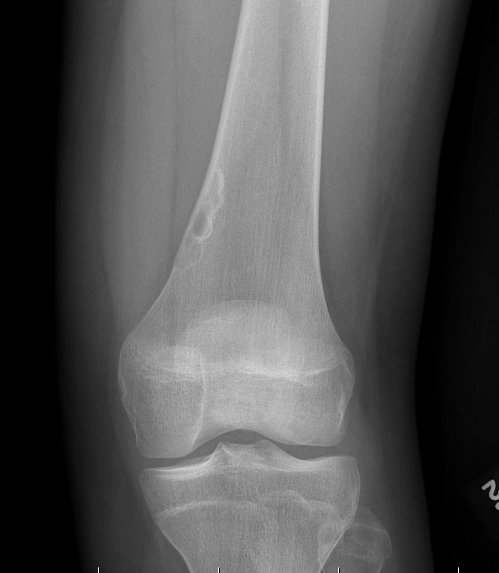
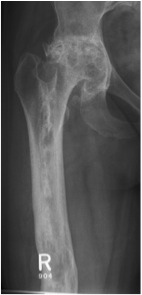
Periosteal Chondroma
Definition
Metaphyseal Enchondroma
Site
Arise from the metaphyseal cortex of long bones
- most common in the proximal humerus
Histology
Difficult to DDx from Chondrosarcoma
Masses of cartilage nestling in a shallow crater in the periphery of the cortex
NHx
Don't ossify
- remain as immature cartilage