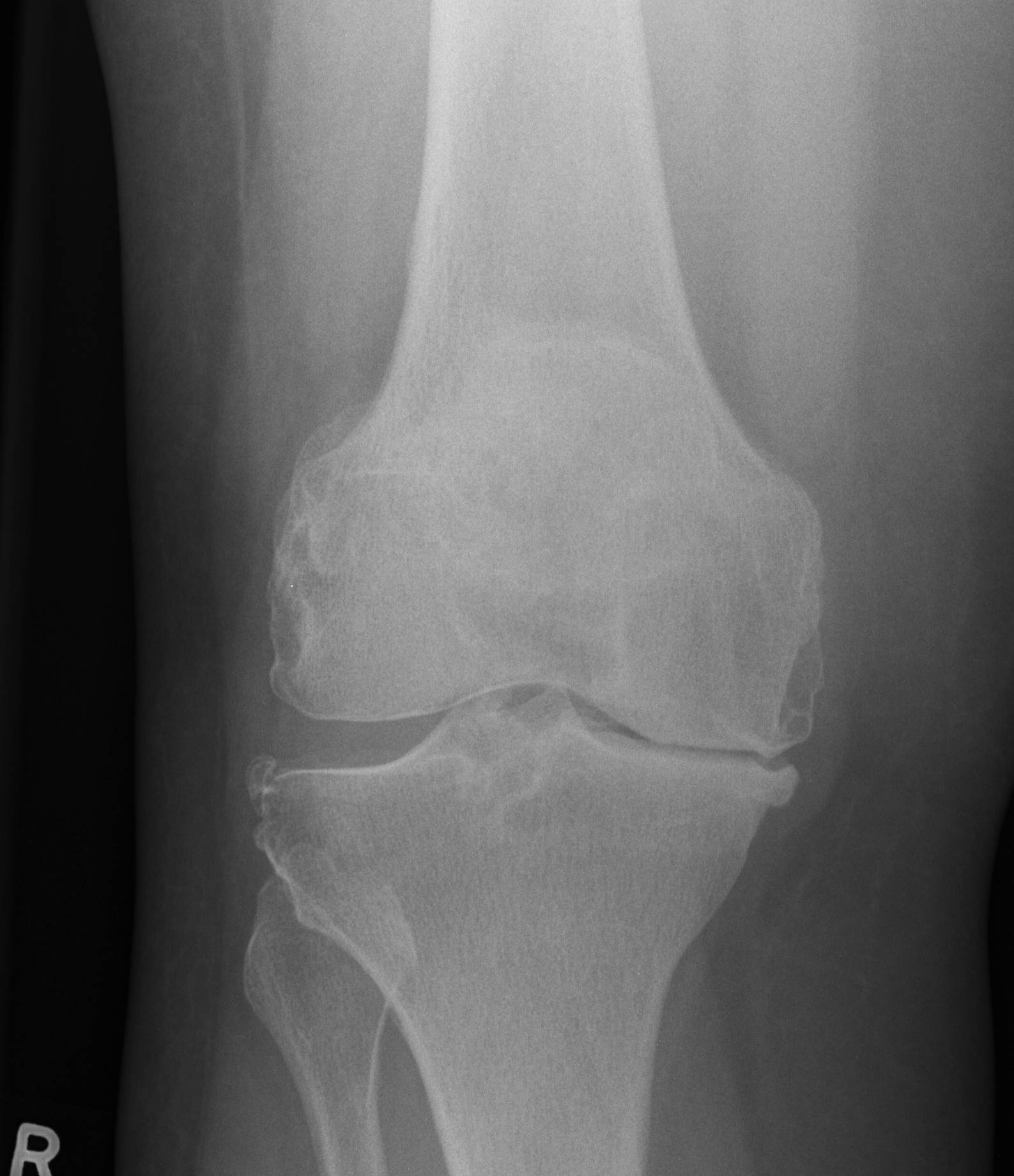
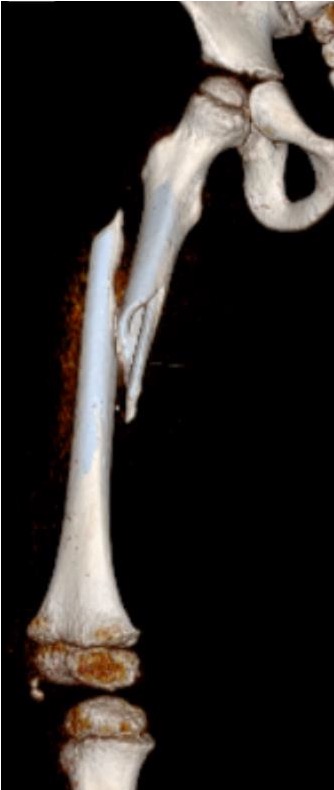
Distal Humerus Fractures
Epidemiology
2 groups
- young patient with high velocity injury
- older patient with comminuted, osteoporotic fracture
In the second group fixation can be very difficult
Anatomy
Hinged Joint
- trochlea axis is centre of rotation
- 40o anterior angulation in sagittal plane