Proximal Humerus Fracture
Epidemiology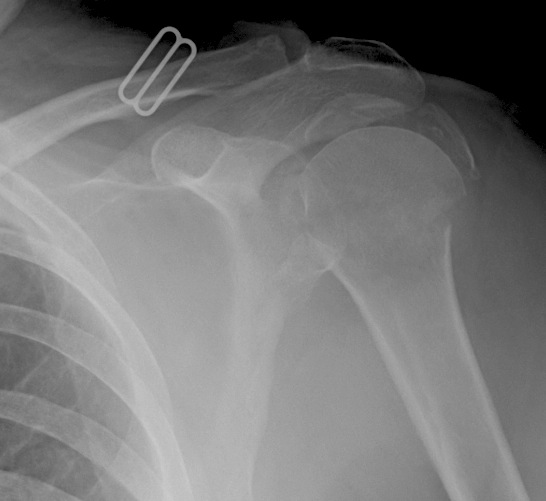
>65
Third most common fracture after hip and distal radius
Anatomy
Neck shaft angle 130o
Head retroverted 20o relative to shaft
Anatomical neck (junction of head and metaphysis)

>65
Third most common fracture after hip and distal radius
Neck shaft angle 130o
Head retroverted 20o relative to shaft
Anatomical neck (junction of head and metaphysis)
< 20o sagittal
< 30o coronal
< 3 cm of shortening
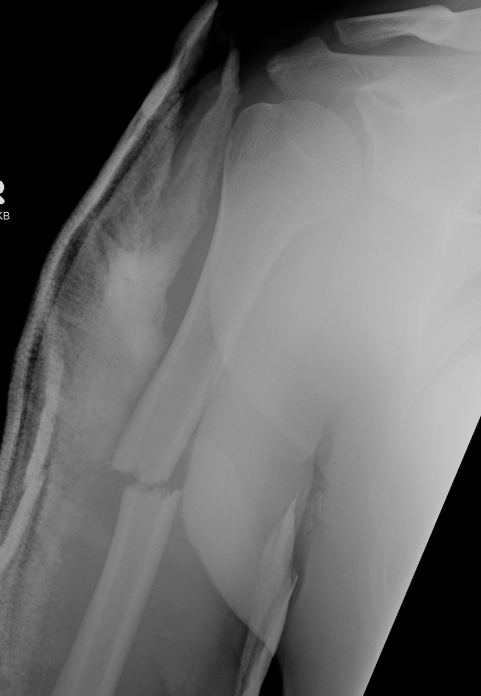

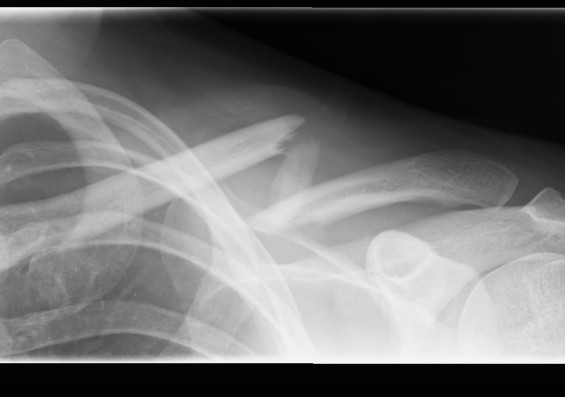
Usually a direct blow
- less commonly a fall on the outstretched hand
RTA / sporting accidents commonest causes
Can be pathological as a result of radionecrosis
- eg following radiotherapy for breast cancer.
Fractures of the clavicle are common
Failure of fusion of adjacent ossification centers
Incidence 3%
Bilateral in 60%
4 ossification centers present in acromion
- pre-acromion
- mesoacromion
- metaacromion
- basiacromion
FOOSH
- axial load with a valgus force
1. Provides Valgus stability
- especially if MCL deficient
2. Longitudinal stability
- aided by interosseous membrane
3. Load Transfer
- 60% of load at elbow
Intra-articular proximal ulna fracture
Articulates with trochlea
- may have a central bare area
Triceps insertion
- via broad aponeurosis which blends with anconeus and CEO
Undisplaced fracture
- need to ensure triceps mechanism is intact
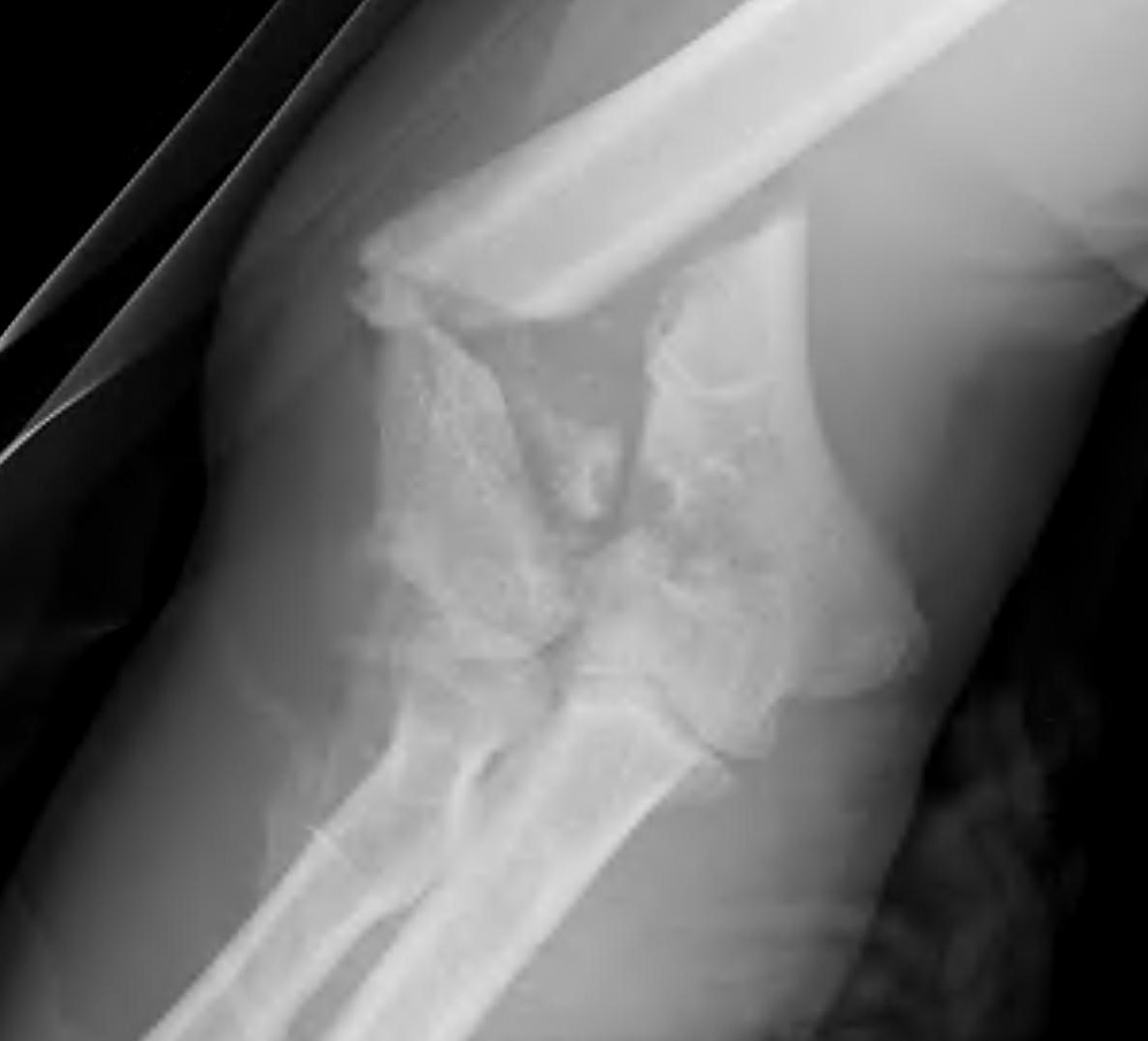
2 groups
- young patient with high velocity injury
- older patient with comminuted, osteoporotic fracture
In the second group fixation can be very difficult
Hinged Joint
- trochlea axis is centre of rotation
- 40o anterior angulation in sagittal plane
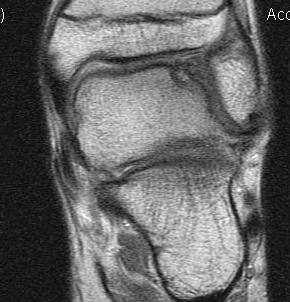
Fracture talus through articular cartilage into subchondral bone
- 2° force transmitted from distal tibia
Osteochondritis dissecans v osteochondral fracture
6% ankle sprains
Average age = 25
M > F
1. Dorsal lip fracture / Tuberosity fracture
- avulsion fractures
- most common
- beware avulsion T post
2. Body fracture
3. Stress Fractures
Types
A. Transverse fracture in coronal plane
B. Transverse from dorsolateral to plantarmedial
C. Central or lateral comminution