mechanism
Background
Epidemiology
National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (2021) Facts and figures at a glance
- road traffic accident 40%
- falls 30%
- sports 10%
Chen et al Arch Phys Med Rehab 2016
- 80% male
- cervical (60%), thoracic (30%), lumbar (10%)
Vertical Shear
Definition
Unstable injuries
Complete disruption of both the anterior and posterior ring
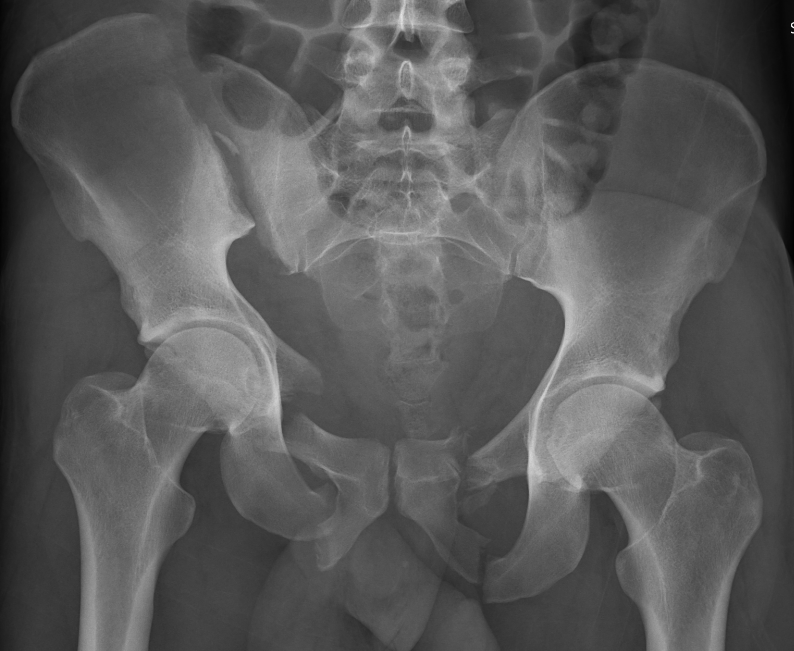
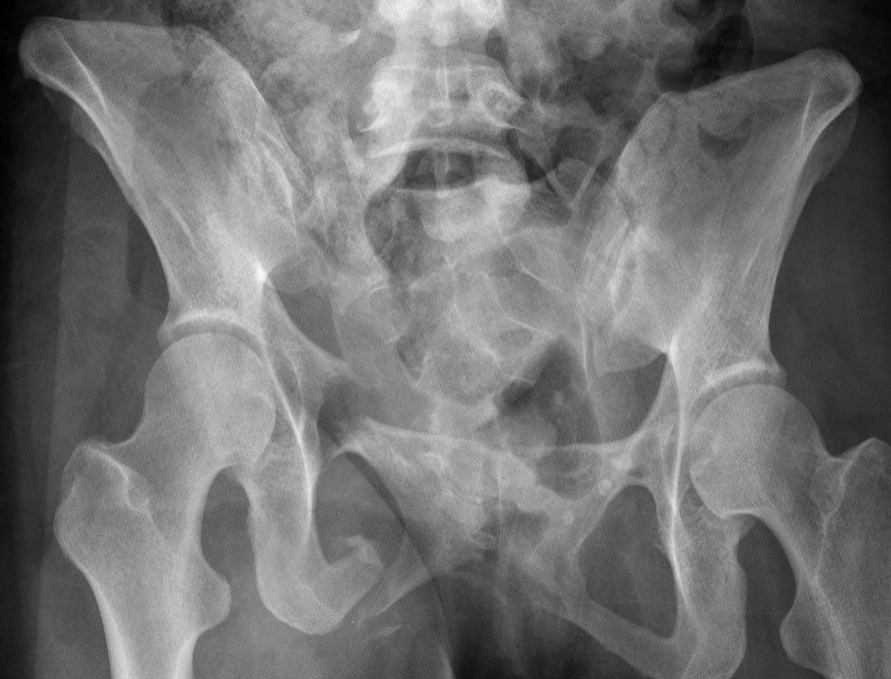
Internal snapping hip
Cause
Movement of iliopsoas tendon over femoral head / iliofemoral ridge / iliofemoral ligament
Cuboid Fractures
Types
1. Capsular avulsions
2. Body / Nutcracker fracture
Nutcracker fracture
Epidemiology
- rare
Mechanism
- forced eversion / abduction of forefoot
- cuboid crushed between 4th and 5th MT and calaneum
Pathology
- displaced cuboid fracture with subluxation of tarsus
Hoffa fracture
Definition
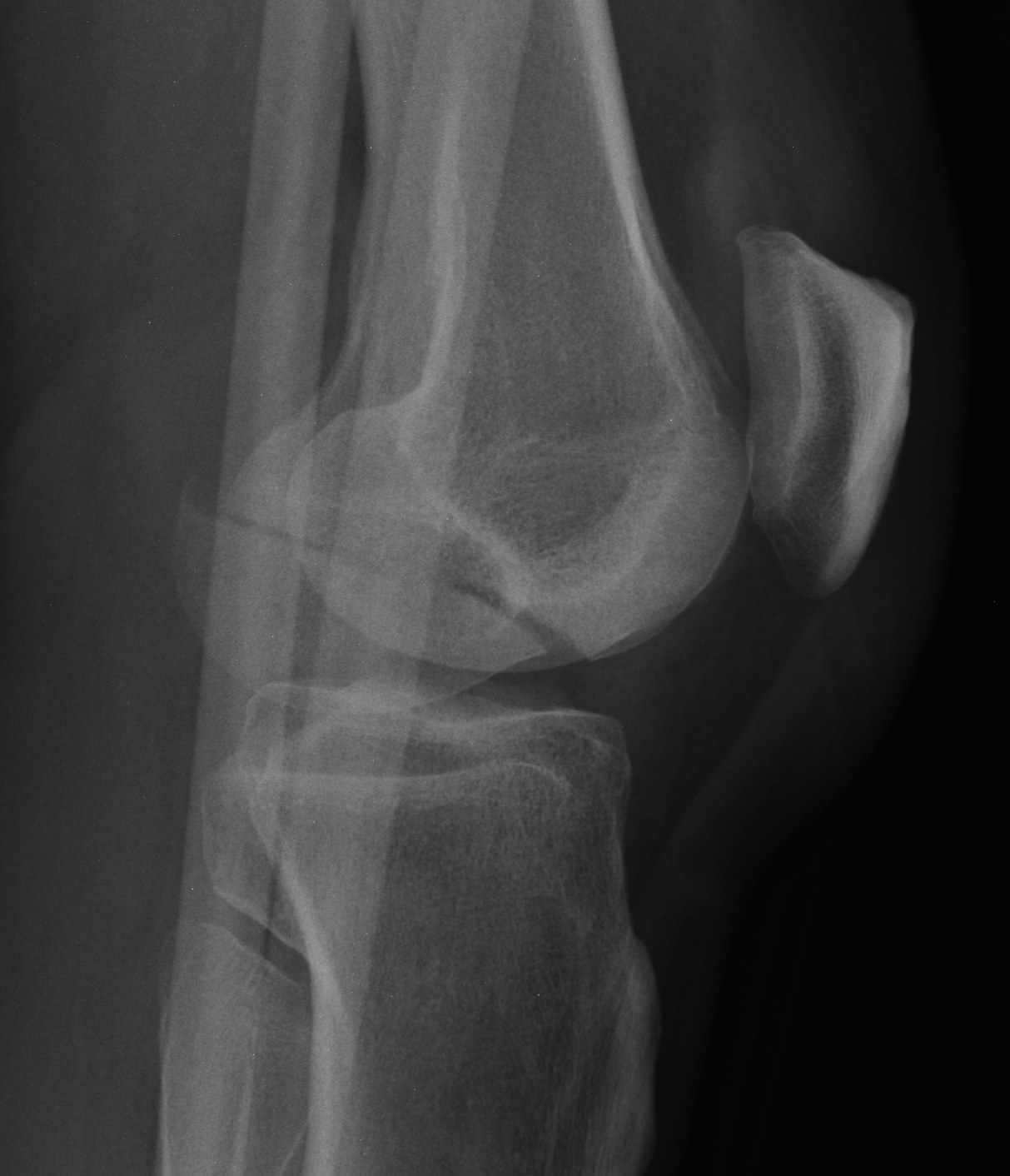
Coronal plane fracture of distal femoral condyle
- intra-articular
- often only attachment is posterior capsule
Epidemiology
Rare
Mechanism
Usually a severe valgus trauma
Xray
Tibial tubercle fractures
Epidemiology
Adolescent boys
Ossification
Proximal tibia / primary ossification centre
Tibial tuberosity / secondary ossification centre
- eventually merges with primary ossification centre
Ogden Classification
Type I - Tibial tuberosity ossification only