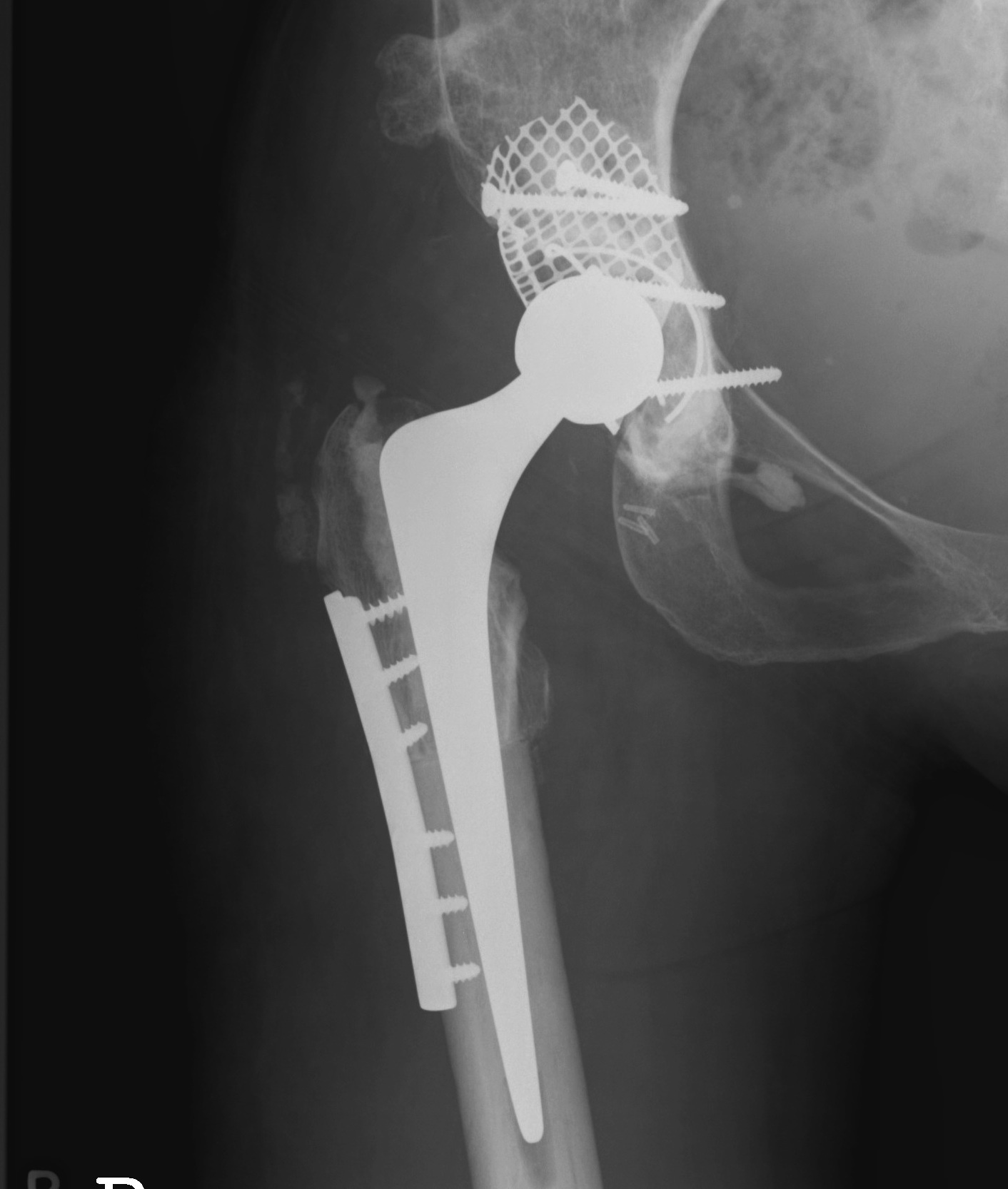
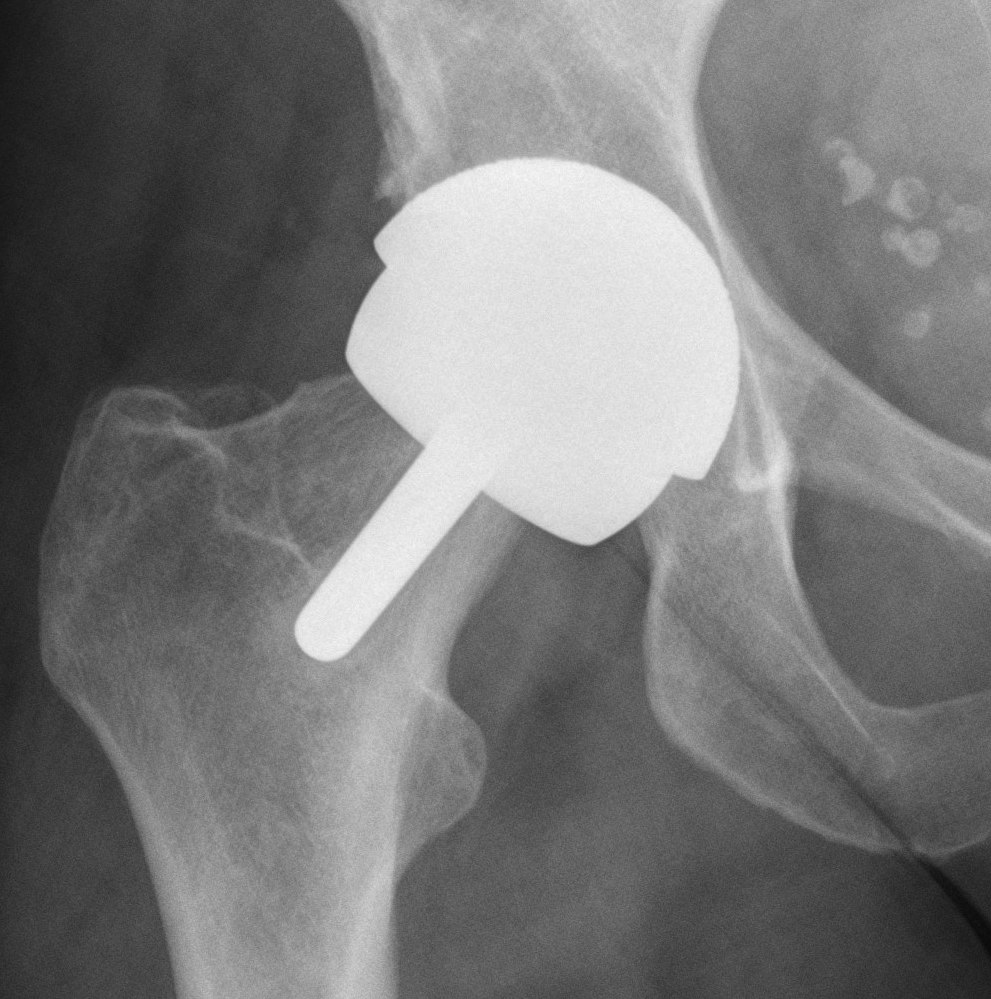
Bearing Surfaces
Wear
The removal of material, with the generation of wear particles under an applied load and in relative motion
Tribology is the study of wear and lubrication
Wear mechanisms
Adhesion
- bonding of the surfaces when pressed together
- may pull away material from the weaker surface
Abrasion
- asperities on the harder surface cut and plough