Paget's Disease
Definition
Chronic, non metabolic bone disorder
Characterised by increased bone resorption, bone formation and remodelling
Epidemiology
Rare < 40
1 – 3 % population over 60
M > F
Aetiology
Unknown
Paramyxovirus implicated
- measles
- RSV
- canine distemper virus
Electron Microscope

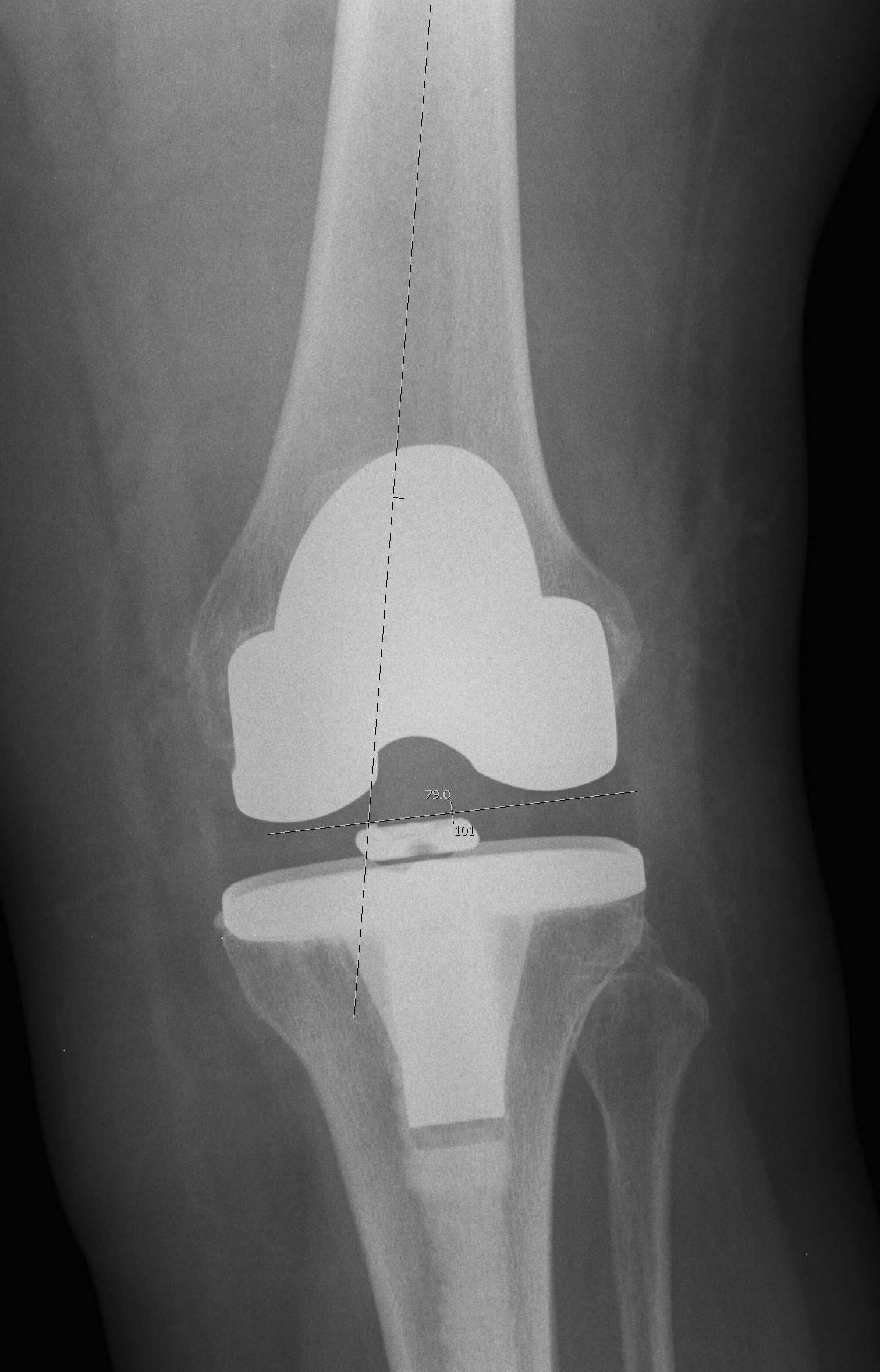
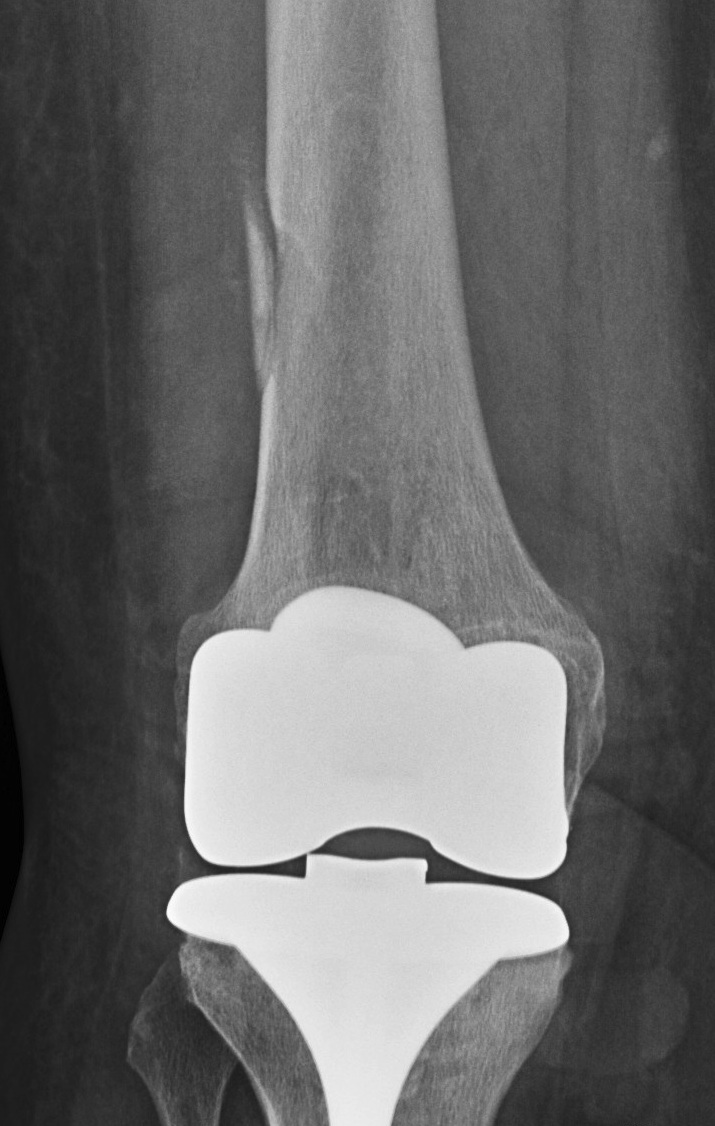
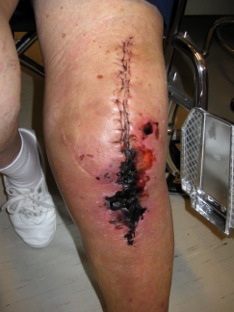 Incidence
Incidence