diagnosis
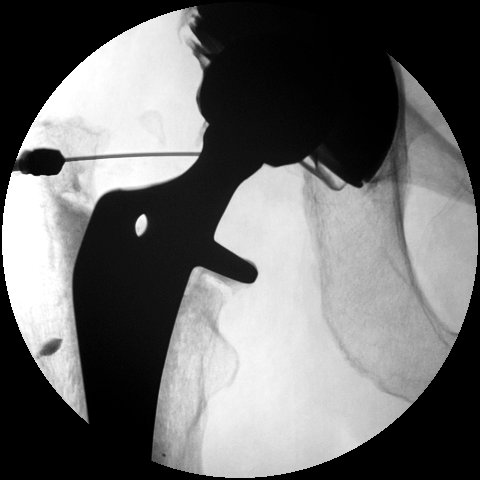
Internal snapping hip
Cause
Movement of iliopsoas tendon over femoral head / iliofemoral ridge / iliofemoral ligament
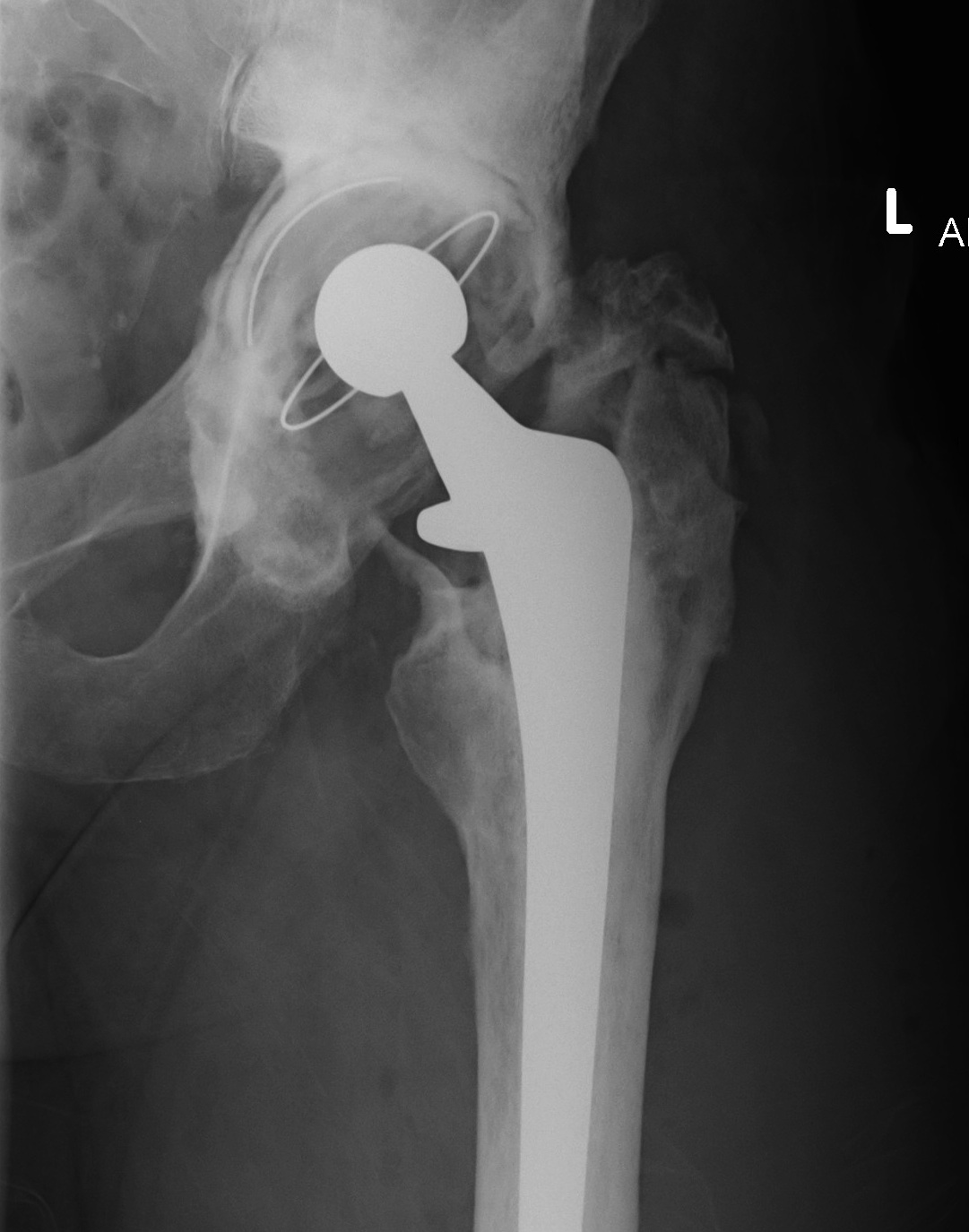
Patella Baja
Patella Baja
Aetiology
Congenital
Acquired
- trauma
- post ACL reconstruction / TKR
- chronic quadriceps rupture
Issues
Decreases ROM
Associated with early OA of the PFJ
Diagnosis
Blackburne-Peel ratio at 30 degrees flexion
Cuboid Fractures
Types
1. Capsular avulsions
2. Body / Nutcracker fracture
Nutcracker fracture
Epidemiology
- rare
Mechanism
- forced eversion / abduction of forefoot
- cuboid crushed between 4th and 5th MT and calaneum
Pathology
- displaced cuboid fracture with subluxation of tarsus
DIC
Definition
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Pathology
Results from excessive activation of either extrinsic or intrinsic coagulation pathway
- multiple small clots
- consumptive coagulopathy
1. Excessive Extrinsic Activation
Secondary to extensive cellular destruction
- thromboplastins +++ released into circulation
Necrotising Fasciitis
Definition
Infection of skin and subcutaneous tissue
- spreads across fascial planes
- many microbes can be responsible
Types
Type 1 Polymicrobial
Type 2 Monomicrobial
Aetiology
Group A Beta Hemolytic Strep (S. pyogenes)
- most common cause monomicrobial
S. Aureus / MRSA
Vibrio
Paget's Disease
Definition
Chronic, non metabolic bone disorder
Characterised by increased bone resorption, bone formation and remodelling
Epidemiology
Rare < 40
1 – 3 % population over 60
M > F
Aetiology
Unknown
Paramyxovirus implicated
- measles
- RSV
- canine distemper virus
Electron Microscope
High ankle sprain / syndesmotic injury
Definition
High ankle sprain
Epidemiology
Uncommon
- often unrecognised or misdiagnosed as lateral ligament injuries
- seen in ice hockey
1-15% of ankle sprains involve the syndesmosis
Mechanism Injury
Hyperdorsiflexion and forced external rotation
Anatomy
Structures
- anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)
Background
Aim 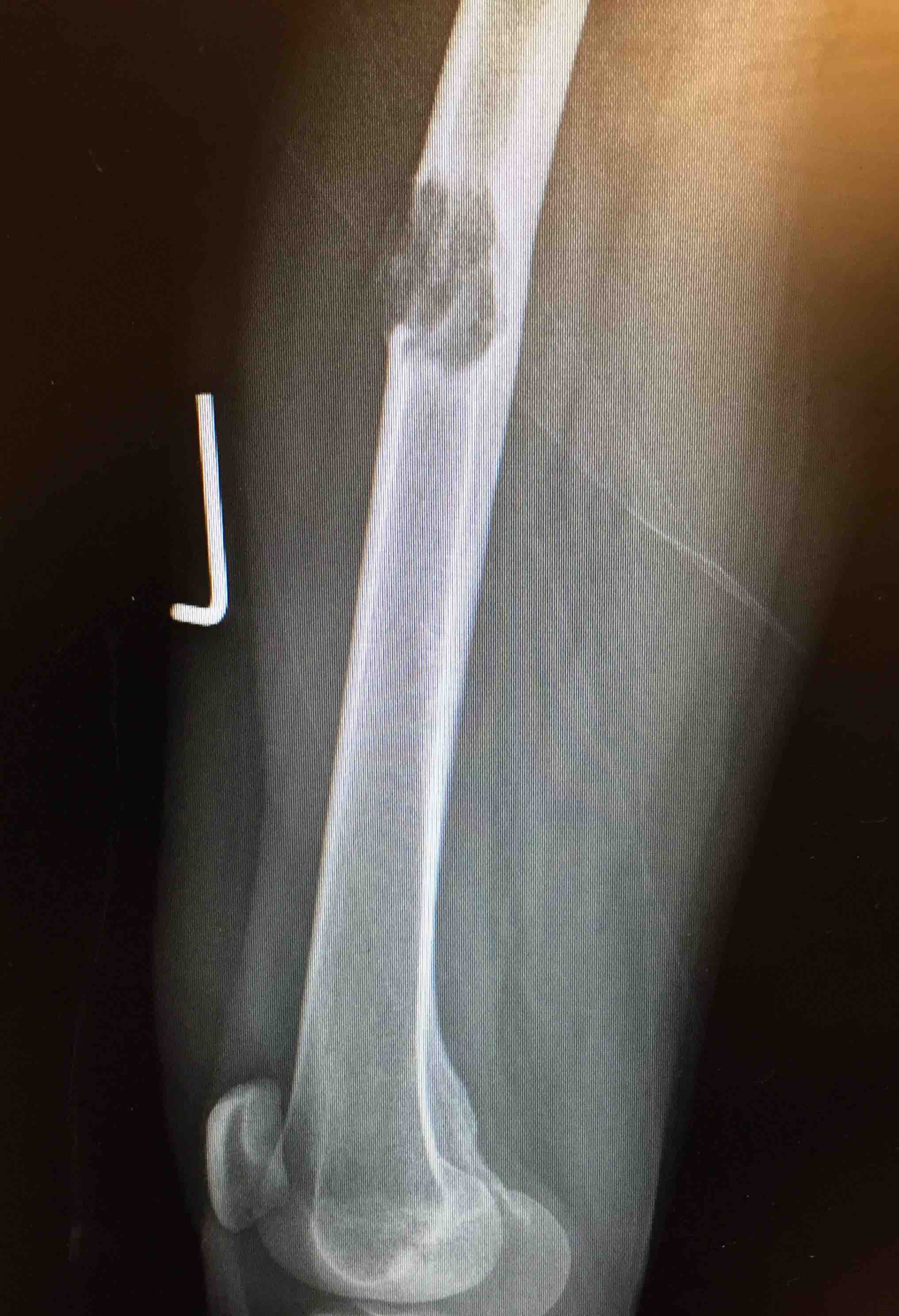
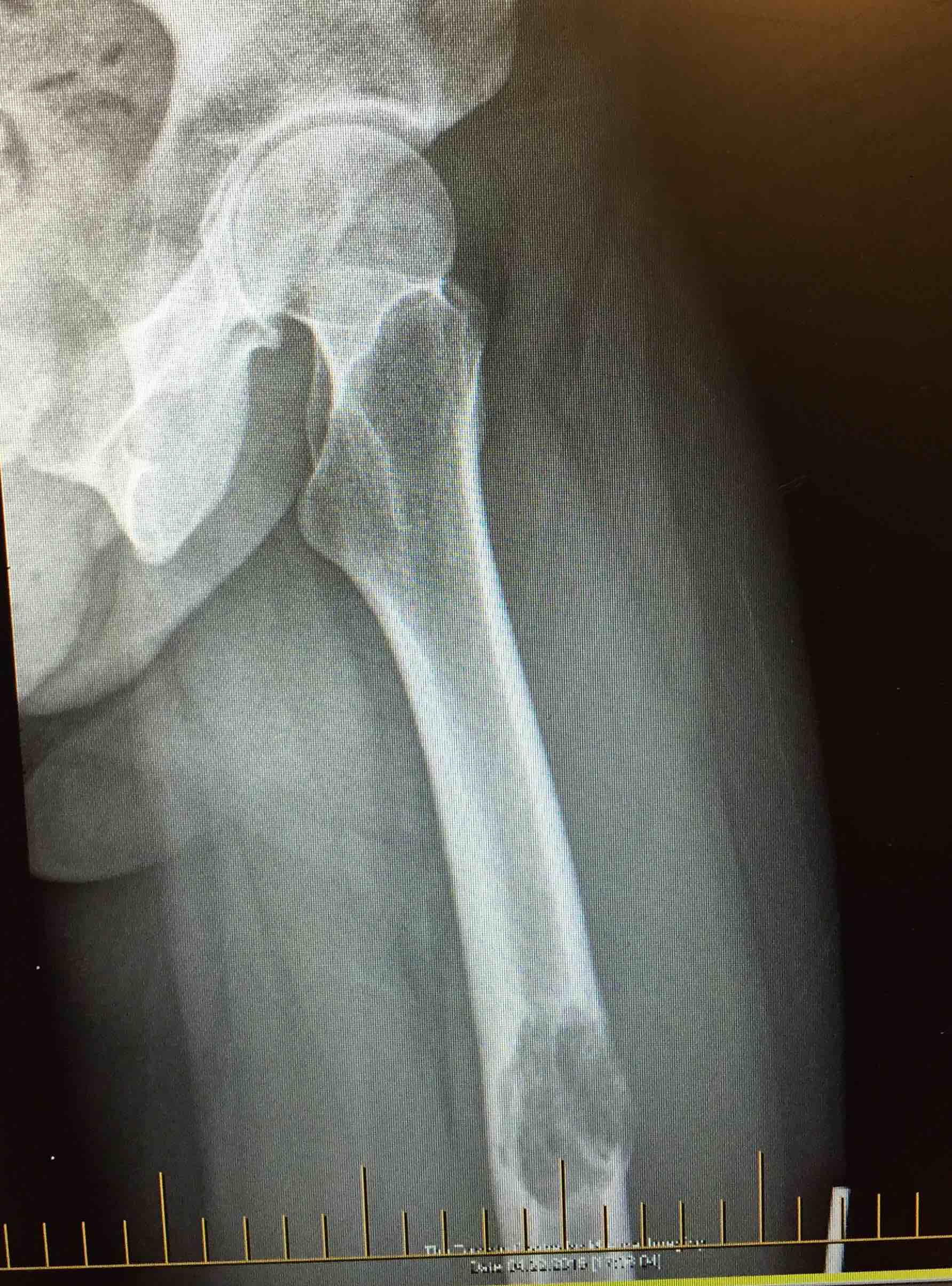
The identification of skeletal metastasis & fixation prior to fracture
Incidence
50% of new cancer cases have metastasis
- 1% have pathological fracture
- increasing with more aggressive palliative care
Mass Behind Knee
DDx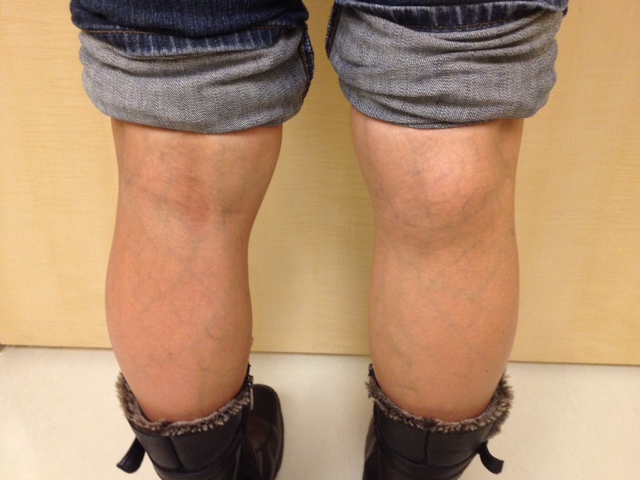
Baker's Cyst
Popliteal Anerysm
Soft tissue sarcoma
Osteosarcoma / Parosteal OS
Hemangioma / AVM
Note:
Always do xray for calcification
A Bakers cyst / aneurysm can be calcified