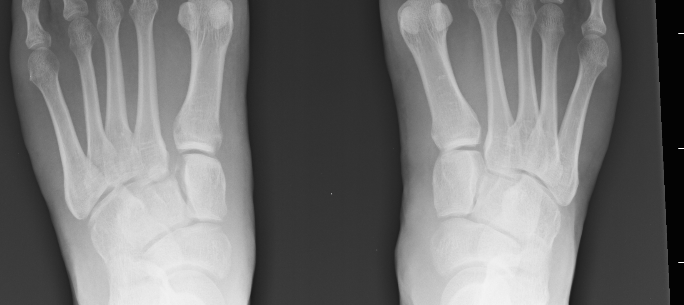
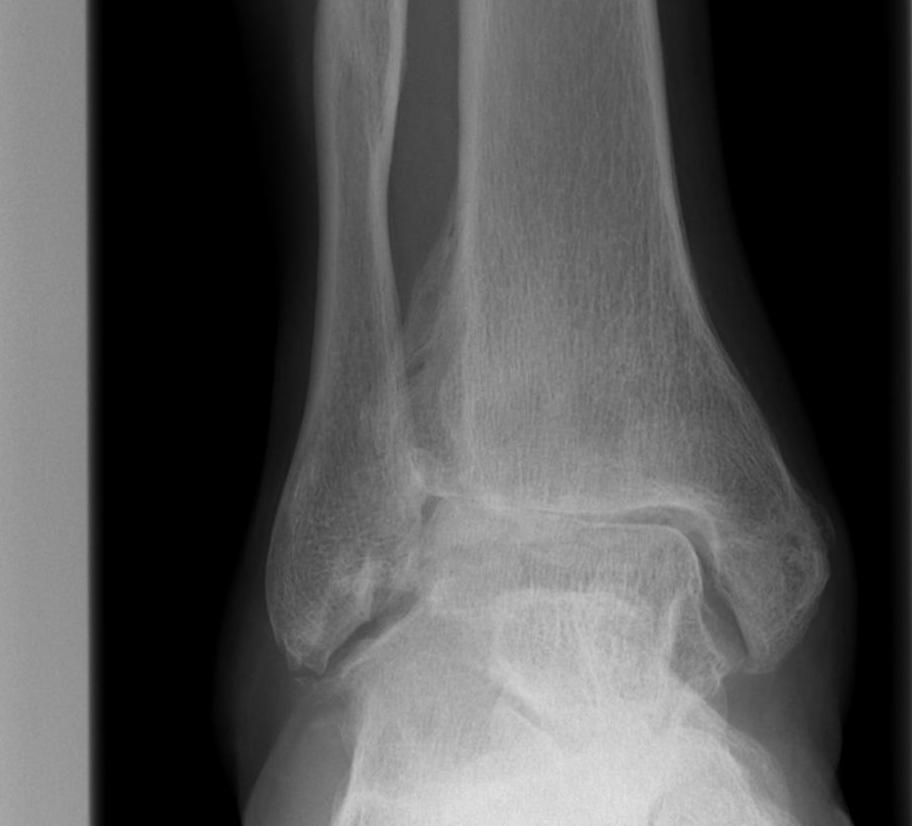
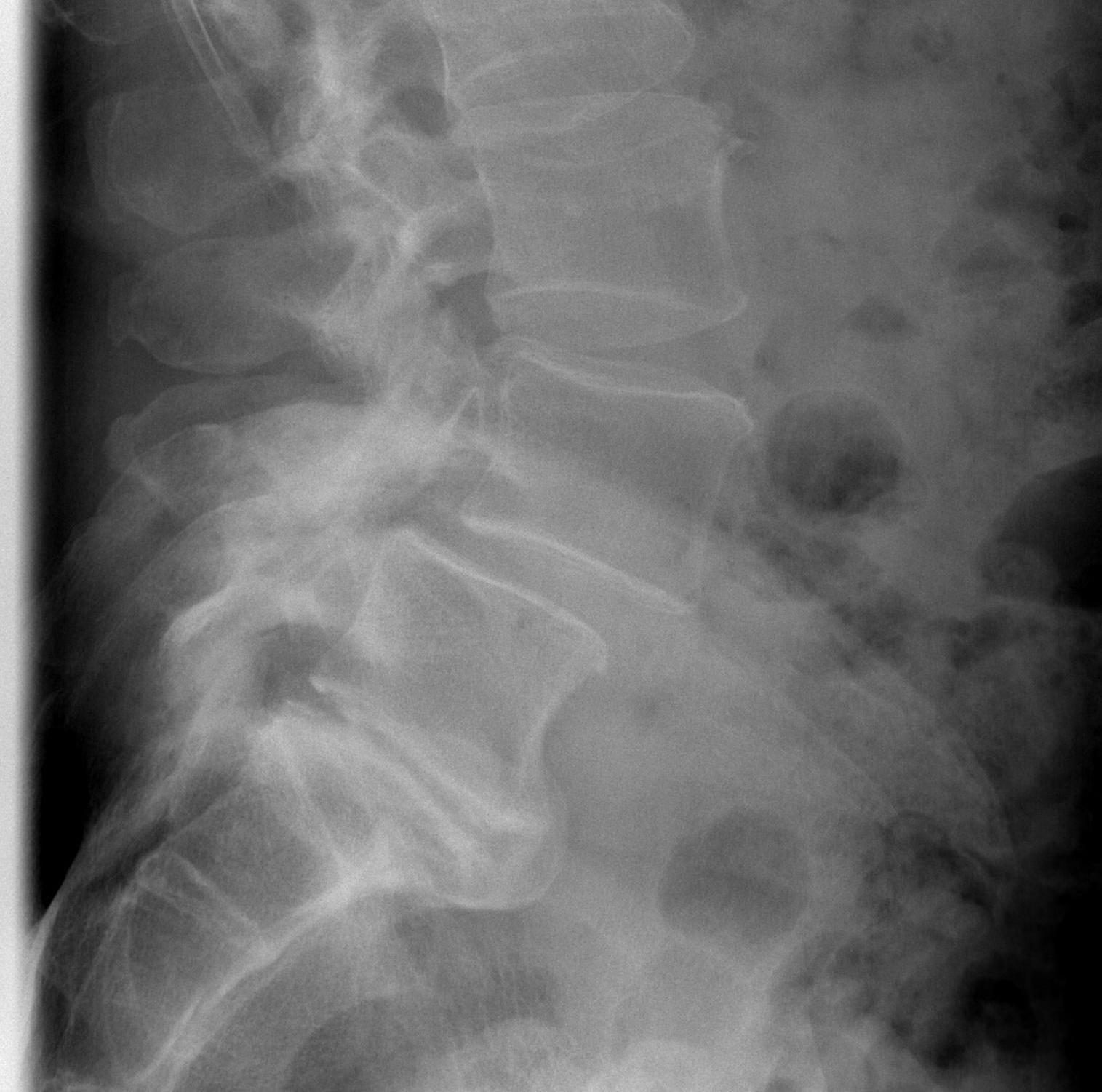
Unicameral Bone Cyst
AKA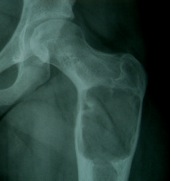
Simple Bone Cyst
Definition
A simple bone cyst is a solitary cavity containing clear fluid
- originating in the metaphysis of growing children
- adjacent to the metaphyseal aspect of the growth plate.
Aetiology
Unknown pathological origin