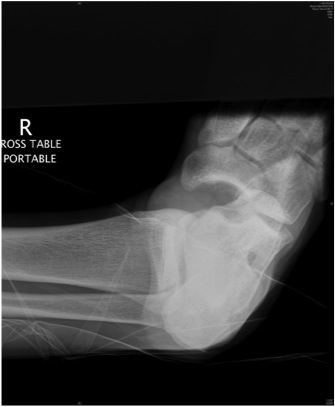
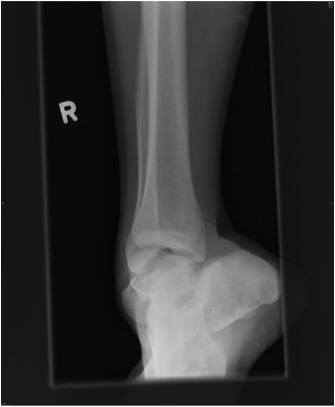
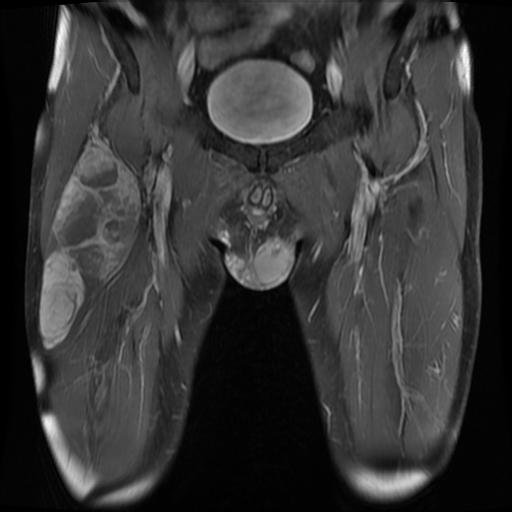
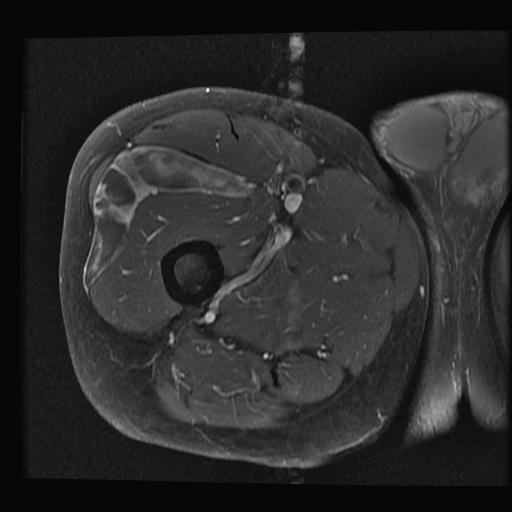
Cuboid Fractures
Types
1. Capsular avulsions
2. Body / Nutcracker fracture
Nutcracker fracture
Epidemiology
- rare
Mechanism
- forced eversion / abduction of forefoot
- cuboid crushed between 4th and 5th MT and calaneum
Pathology
- displaced cuboid fracture with subluxation of tarsus