Perilunate Fractures and Dislocations
Epidemiology
Young men in 20's and 30's
Aetiology
High energy injuries
- fall from heights
- MVA
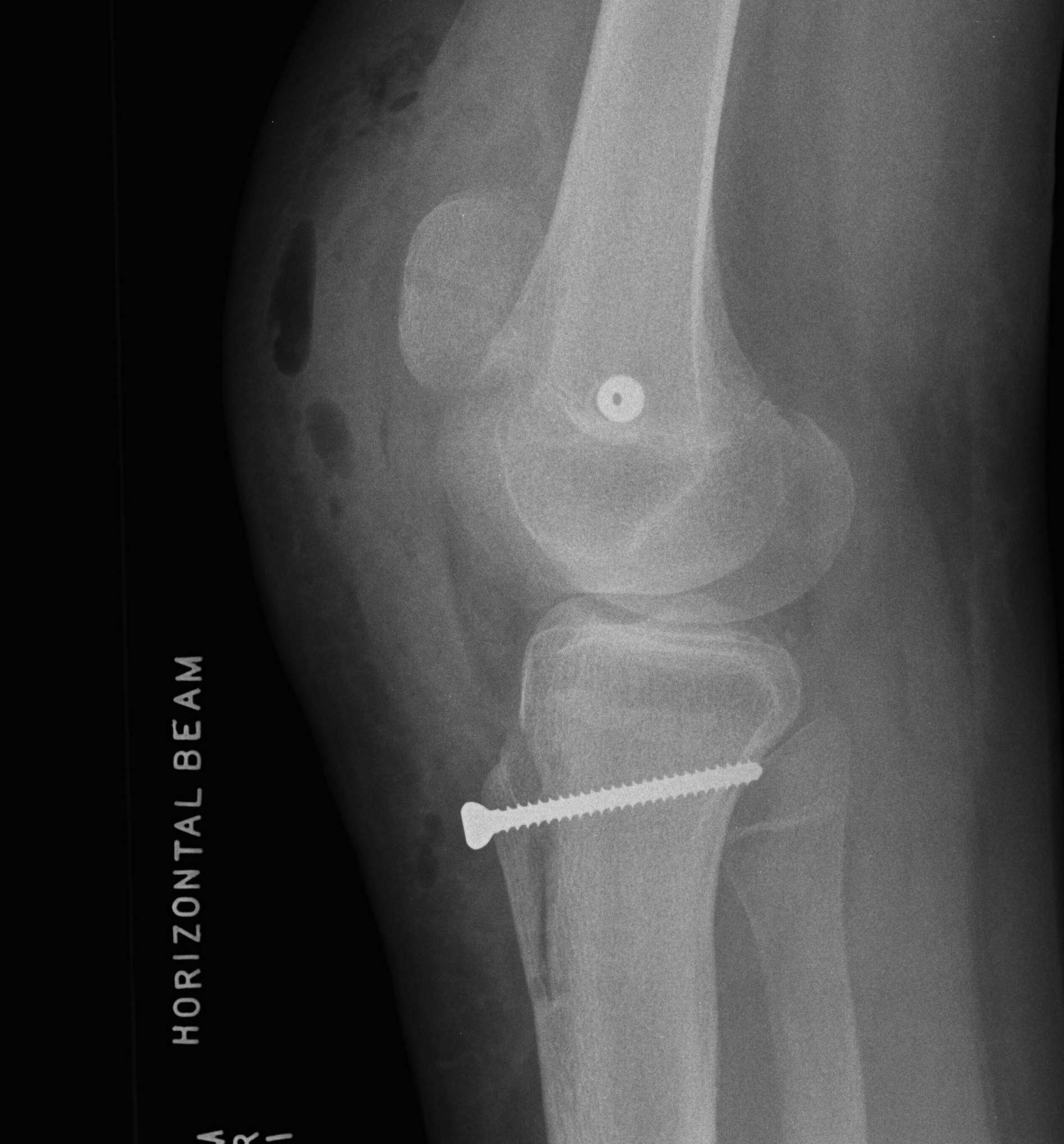
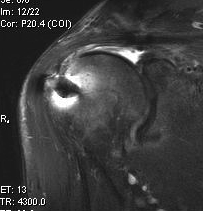
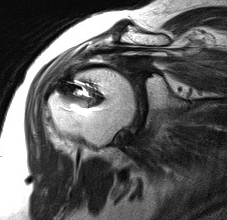
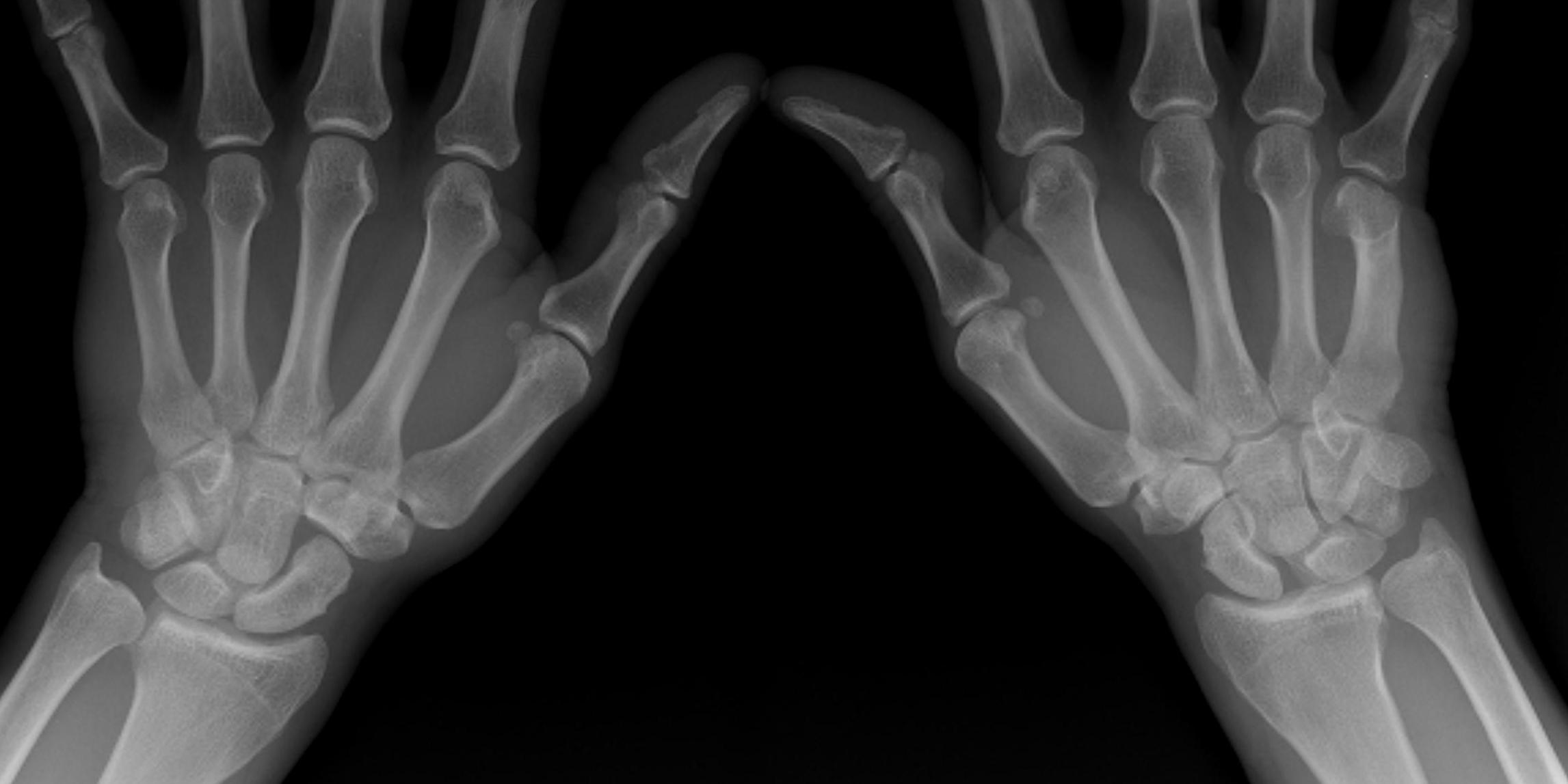
Mayfield Classification
Injury progresses from radial to ulna
- usually disruption proximal row either side of lunate
1. Capitate usually displaces dorsally initially
- volar lunate dislocation is end stage