HAGL
Definition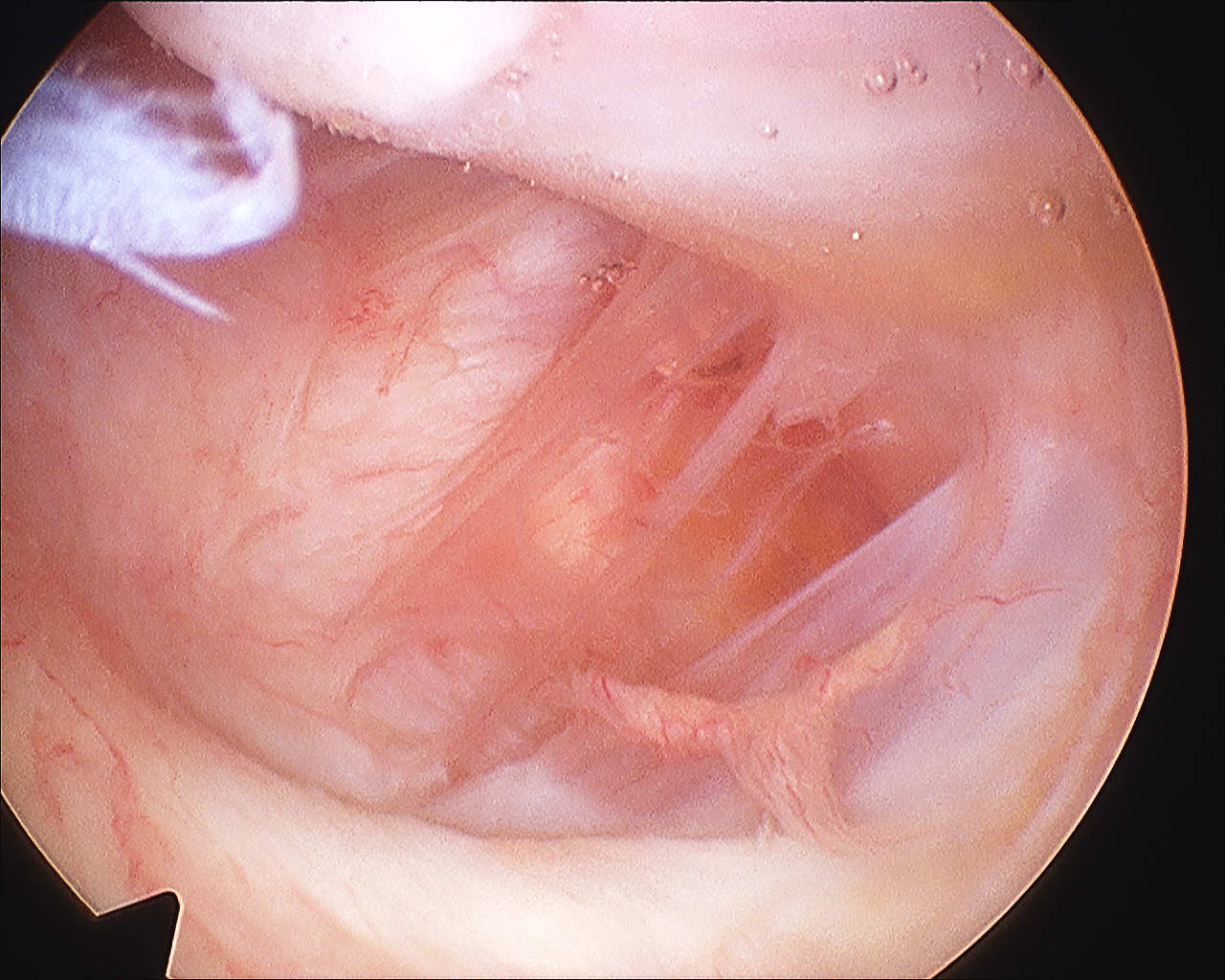
Humeral Avulsion of Glenohumeral Ligament
Incidence
Bokor et al JBJS Br 1999
- 514 cases surgical treatment traumatic instability
- incidence 7.5%
- 25% associated SSC tear
- likelihood of HAGL if no Bankart or MDI 27%

Humeral Avulsion of Glenohumeral Ligament
Bokor et al JBJS Br 1999
- 514 cases surgical treatment traumatic instability
- incidence 7.5%
- 25% associated SSC tear
- likelihood of HAGL if no Bankart or MDI 27%
Concept
Plication subscapularis & capsule
Problems
Loss ER
Secondary OA if ER < 0°
Contraindication
MDI
- will force head out posteriorly
Technique
Divide SSC 2.5cm from insertion
- may divide capsule in same plane
Non-anatomical bony block
- transfer of coracoid process through subscapularis
- dynamic anteroinferior musculotendinous sling
- provides subscapularis tenodesis
- preventing lower portion from displacing proximally as arm abducted
- when shoulder in vulnerable position abduction and ER
Repair of the anterior capsule & avulsed labrum to anterior glenoid
- anatomic repair
Usually combined with a capsular shift
Bony bankart > 25% glenoid
Position
- beach chair position
- arm free
- Mayfield head ring / Spyder and Tmax
Mid-substance calcification of the rotator cuff
- part of a metaplasia secondary to hypoxia
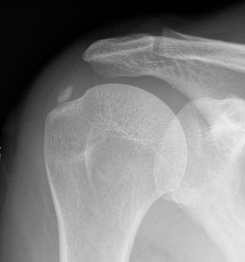
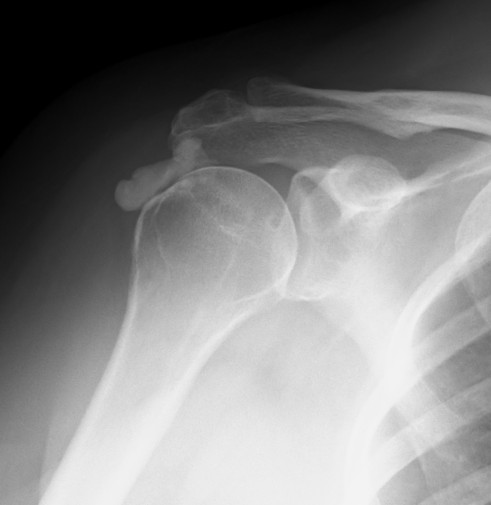
2 groups of patients
Due to scapulothoracic articulation disorder
1. Neurological Origin
A. Spinal Accessory Nerve / Trapezius palsy
B. Long Thoracic Nerve / Serratus Anterior palsy
C. Dorsal Scapular Nerve / Rhomboids palsy (rare)
2. Osseous Origin
Technique
- in plane of thorax
- oblique of GHJ
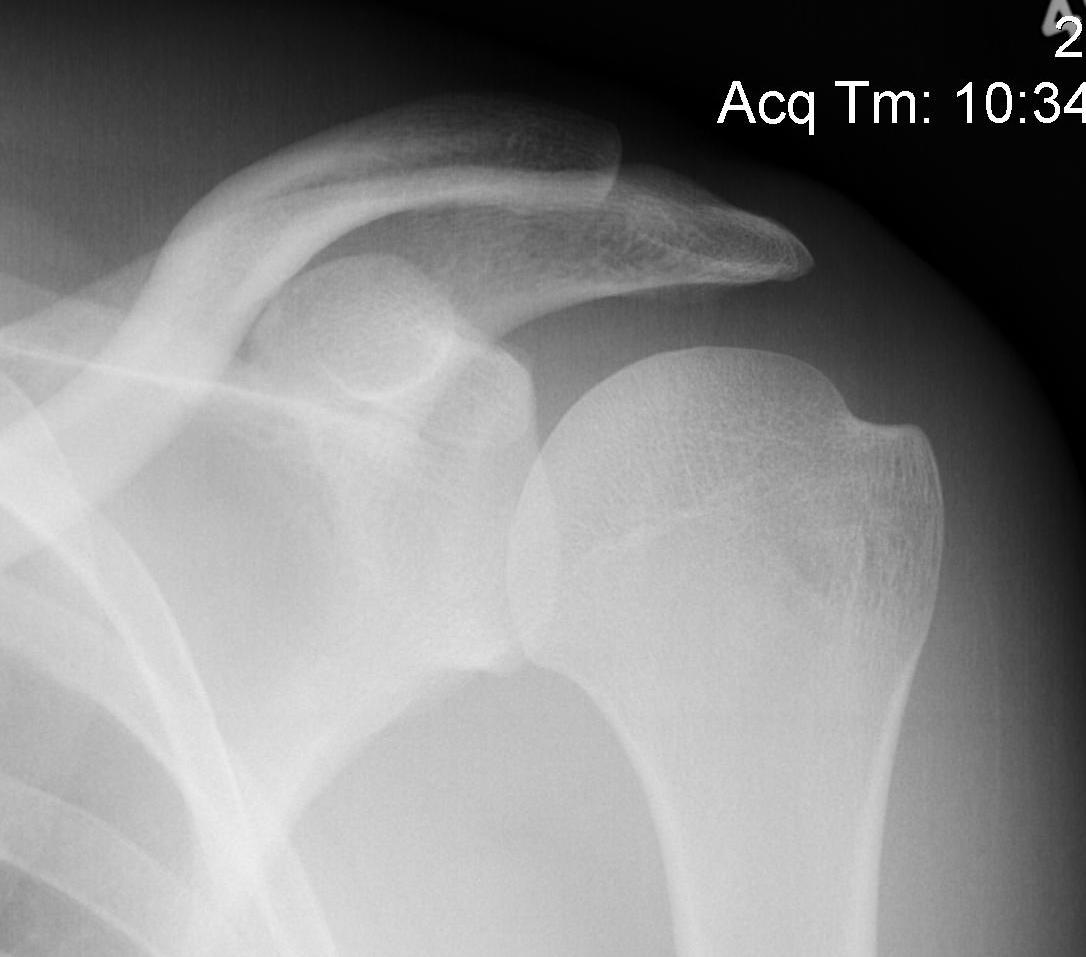
Grashey
- angle 45o lateral
- allows estimation of glenohumeral space
Terminal branch of the posterior cord
- lateral to radial nerve
- behind axillary artery
- runs over inferolateral border of SSC
- enters quadrangular space
Quadrangular space
- SSC superiorly anterior
- T major inferior
- T minor superiorly posterior
- long head triceps and humerus
Divides into anterior and posterior branches
Patients usually complain of subluxation rather than dislocation
- rarely requires reduction
Different entity to acute posterior dislocation usually
Rare
1. Ligamentous laxity > 50%
- commonly associated with MDI
- posterior only 20%
- posterior & inferior 20%
Rare
- 2% of acute dislocations
Often missed
- < 1/ 52 25%
- < 6/52 25%
- < 6/12 25%
- > 6/12 25%