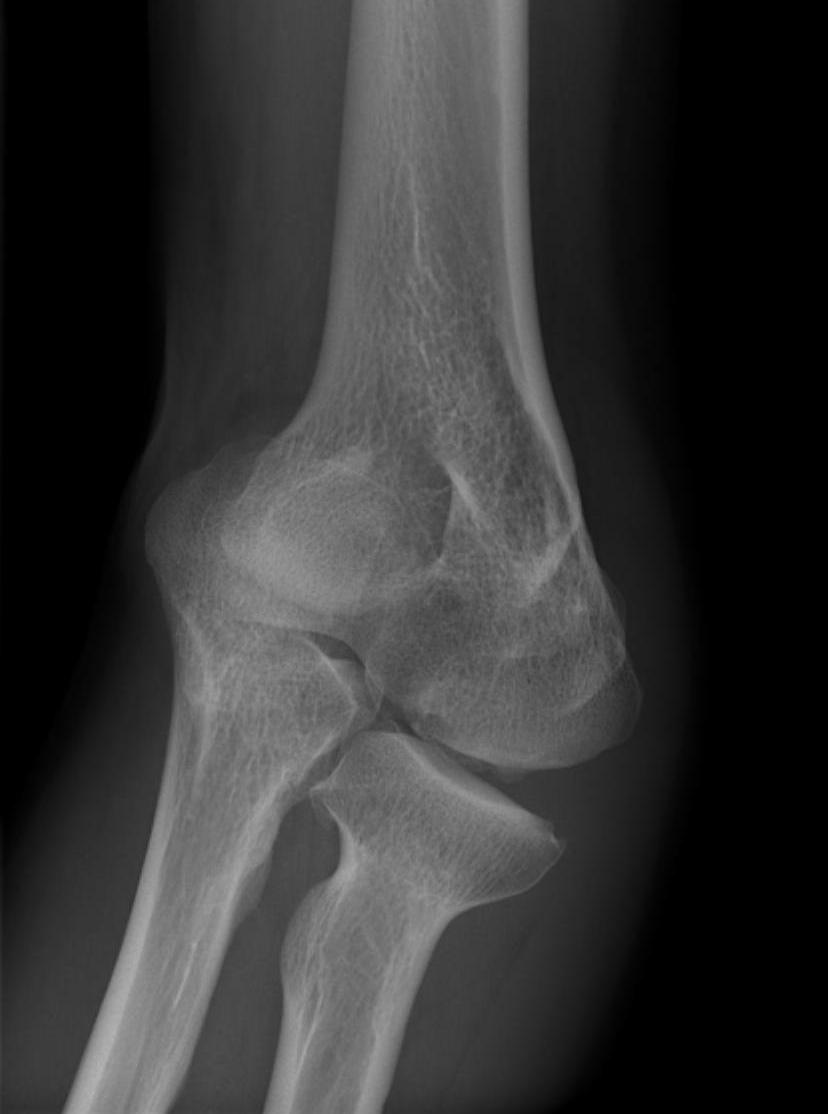
Medial Epicondylitis / Golfers Elbow
Incidence
10% of elbow tendonitis
Aetiology
Overuse injury
- poor swing in golf
- poor throwing technique
- overuse of topspin in tennis
- occupational (repetitive hammering / screwing)
Some patients also have lateral epicondylitis
Examination
Tenderness CFO
Stimulate pain
- flexion of WJ with fingers resisting