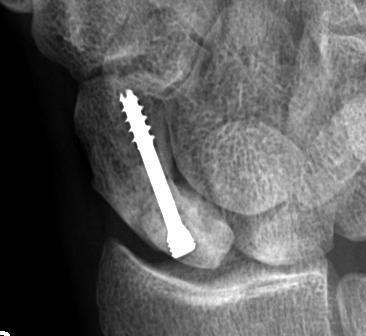
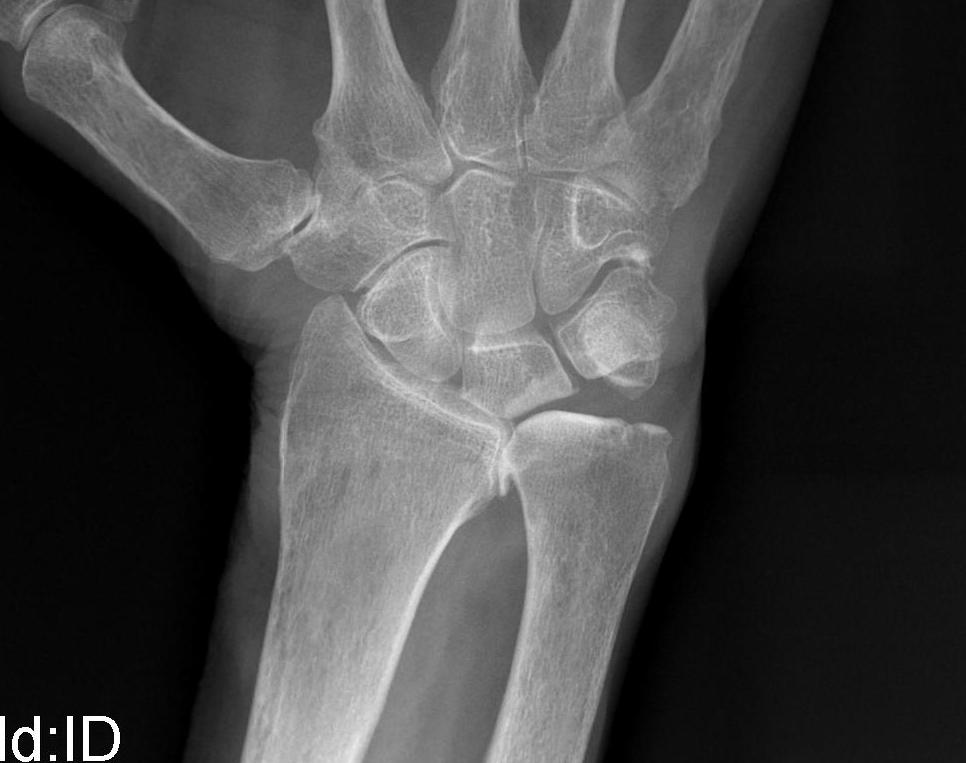
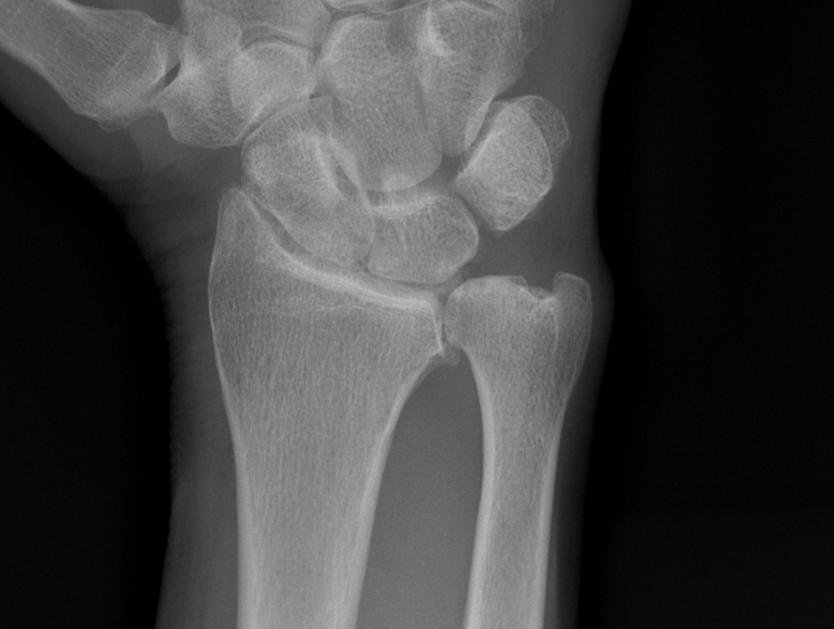
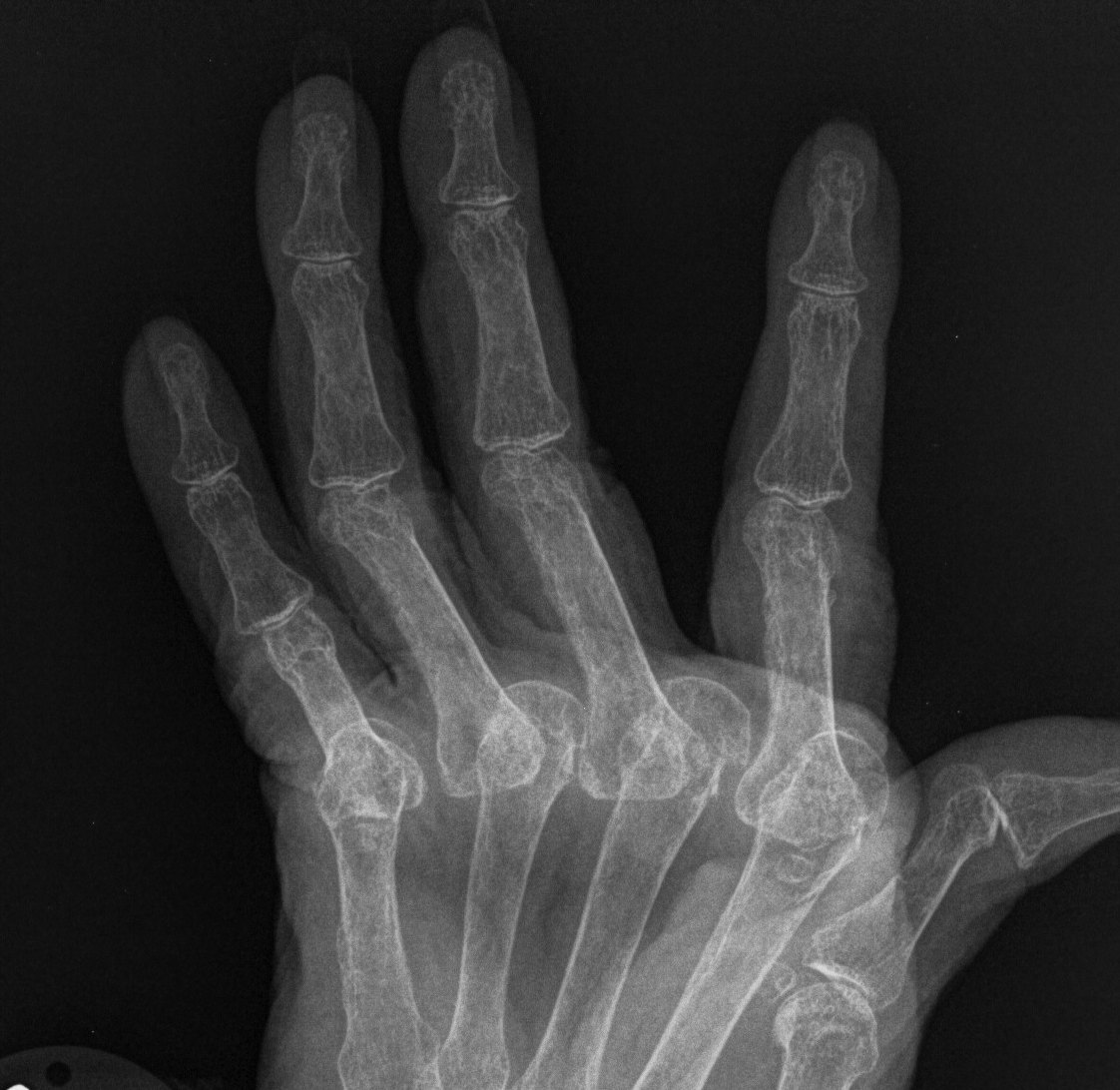
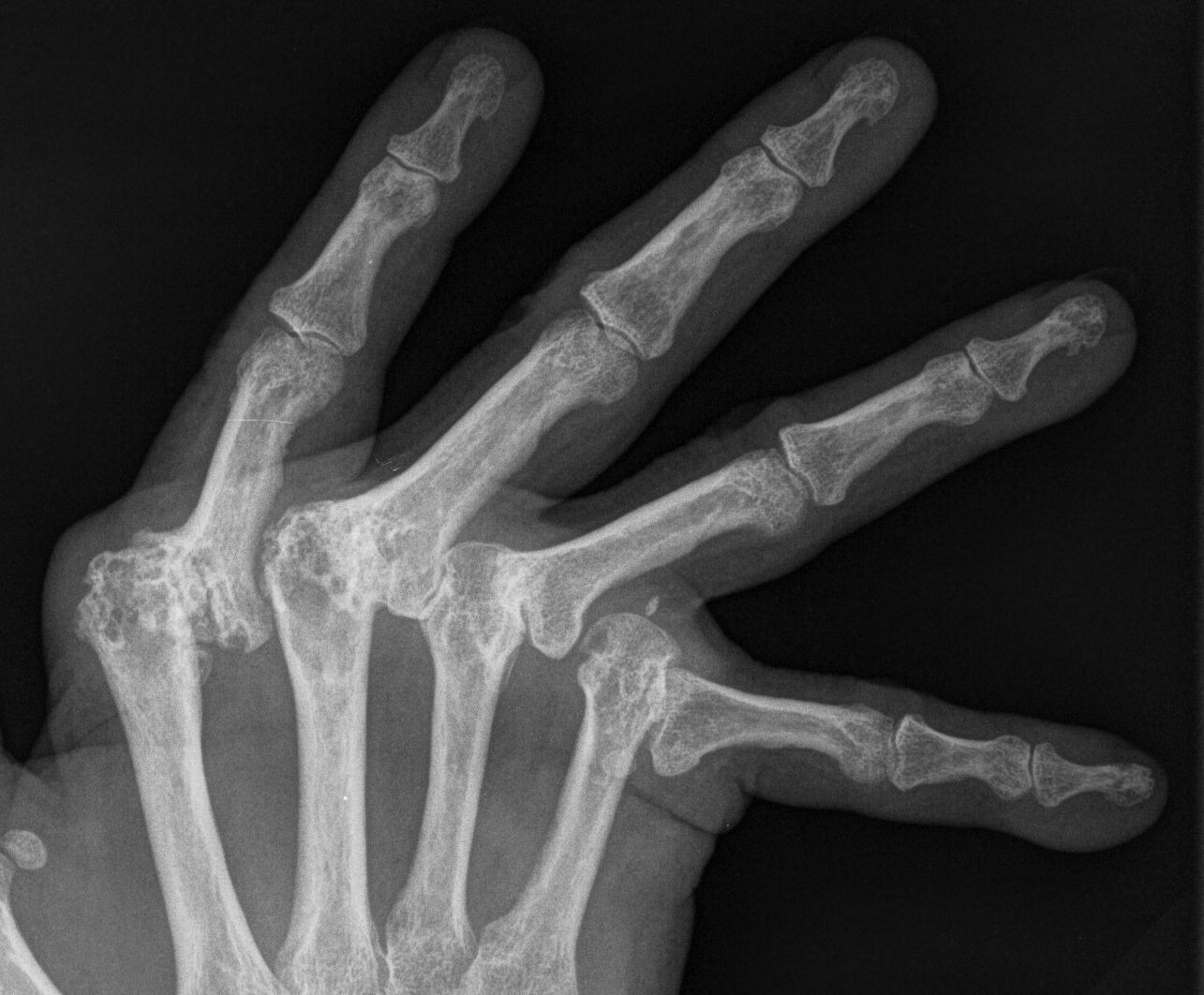
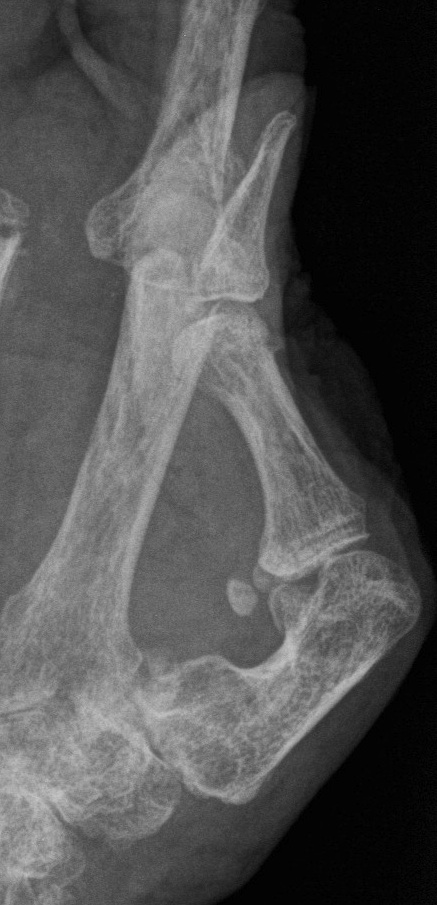
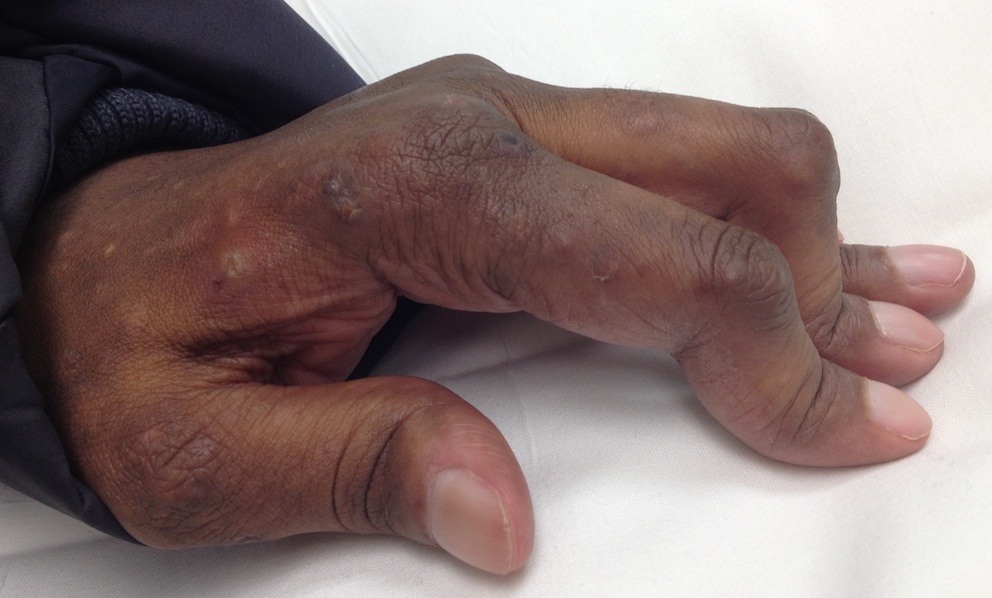
Management
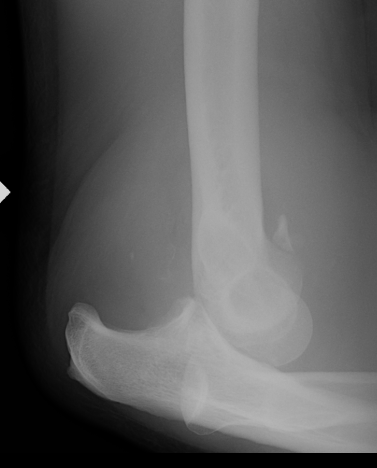
Acute Elbow Dislocation Management
1. Reduction under IV / conscious sedation
- assistant applies traction in slight flexion
- second person corrects lateral displacement by manipulating olecranon medially
- flexion to 90o
2. Post reduction assess stability