Background
Definition 
Palmar Fibromatosis
Aetiology
AD with variable penetration
Pathogenesis
Murrell's Theory of Pathogenesis
1. Microvascular ischaemia
Palmar Fibromatosis
AD with variable penetration
Murrell's Theory of Pathogenesis
1. Microvascular ischaemia
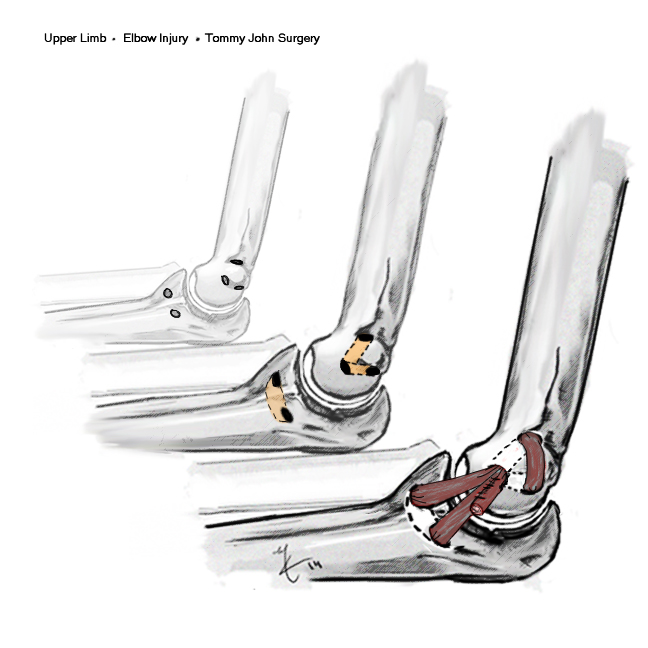
Throwing injury
- seen in the throwing athlete
- repetitive microtrauma / valgus stress
- develop laxity
Initially
- lose velocity / accuracy
Develop medial pain
40% ulna nerve symptoms
Intrinsic
- inflammatory
- degenerative
Extrinsic
- traumatic
- spur
F > 40
Associations 60% of cases
- hypertension
- diabetes
- obese
- trauma
- prior surgery
- steroids
Surgical Diagnosis
1. Prosthetic loosening and failure
2. Infection
3. Patellofemoral tracking problems
4. Instability
5. Recurrent intra-articular soft-tissue impingement / Component overhang
Nonsurgical Diagnoses
1. Referred pain - Hip / Back
Good initial results but unacceptably high failure rate with longer follow-up
Problems
1. Too stiff (low ultimate strain)
- poor resistance to abrasion
- ligament failure by attrition most common
2. Recurrent synovitis, infection, loosening and osteolysis
Lateral : Medial 9:1
4th & 5th decades
- M = F
- 75% dominant arm
50% of regular tennis players
- especially > 2 hrs / week
Insertion pathology / Enthesopathy
Over-extension of the elbow with supination / pronation
Lateral epicondyle
- anconeus from posterior face
- ECRB and EDC from anterior face (CEO)
Any act or failure to act that
- results in or potentially results in harm / death / physical / emotional / sexual abuse
- by a parent or caretaker who is responsible for the child
Neglect
Physical (punch / kick / bite / burn / shake)
Sexual
Emotional
Chronic instability due to rupture of one or more parts of the lateral ligament
Progressive injury
1. Anterolateral capsule
2. ATFL
3. CFL
Can lead to ankle OA over time
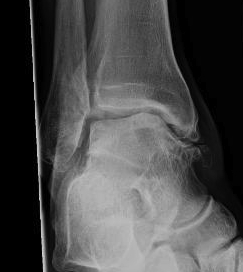
Anterior displacement of peroneal tendons out of peroneal groove
Most common in young adults
Acute injury often missed
Congenital
3 % neonates
- resolves spontaneously
Traumatic
Occurs following sporting activities
Entrapment neuropathy of posterior tibial nerve within the tibial tunnel
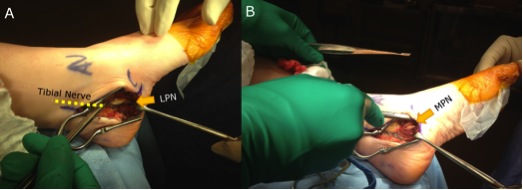
Flexor Retinaculum
- medial malleolus to posterior calcaneum
Tarsal tunnel
- roof is flexor retinaculum
- tibia anteriorly