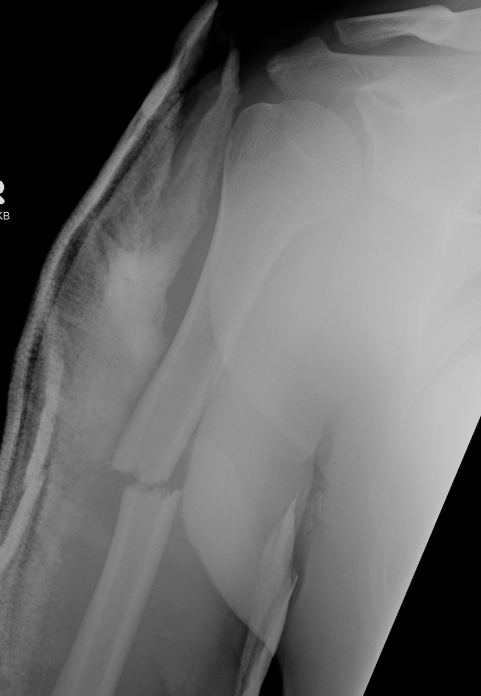
Coronoid Process Fracture
Background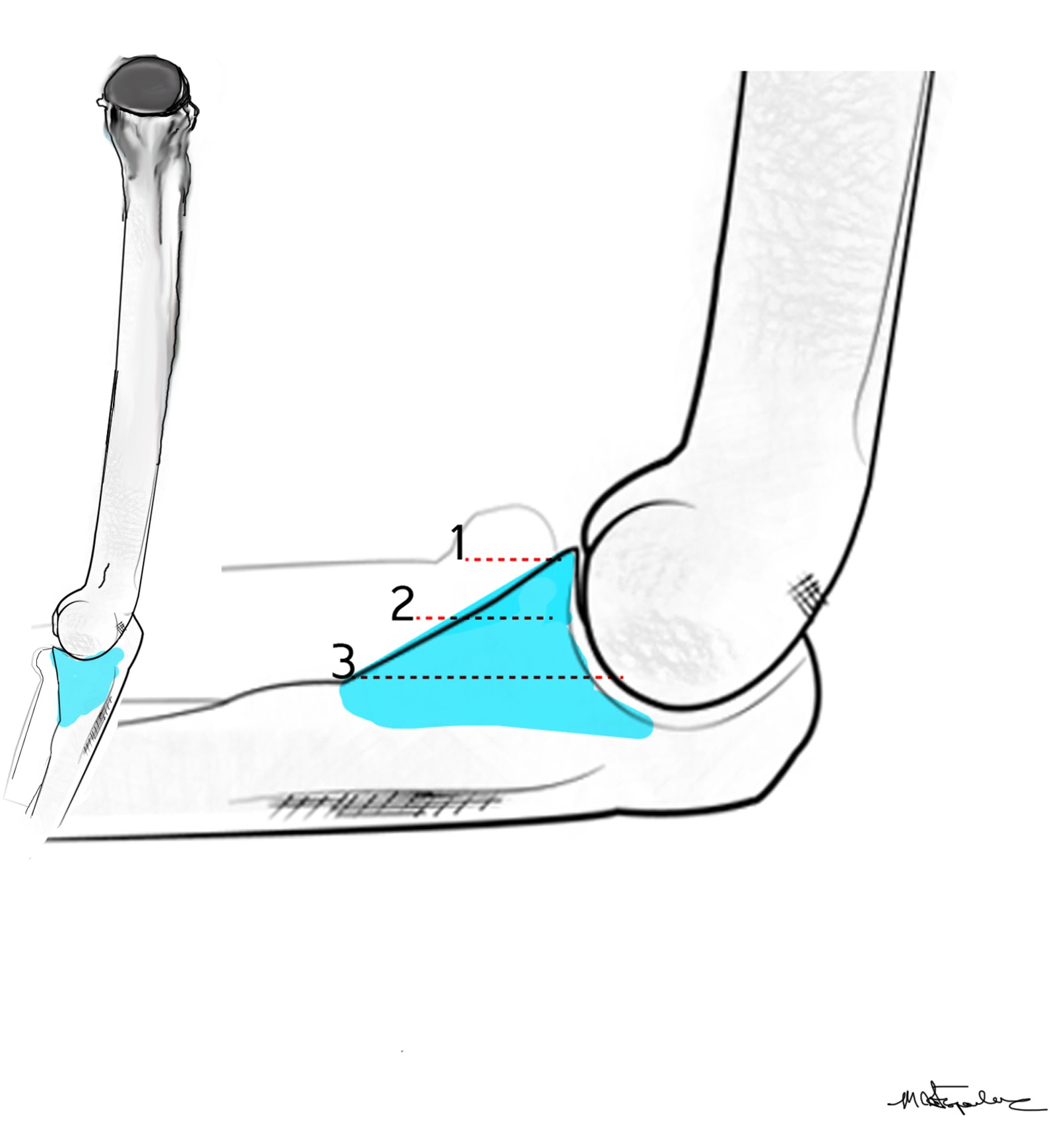
The coronoid is the most important portion of ulno-humeral articulation
Reasons
1. Provides anterior buttress
2. Anterior capsule and brachialis attach to coronoid
2. Anterior band of the MCL attaches to it
- distally and medially on sublime tubercle