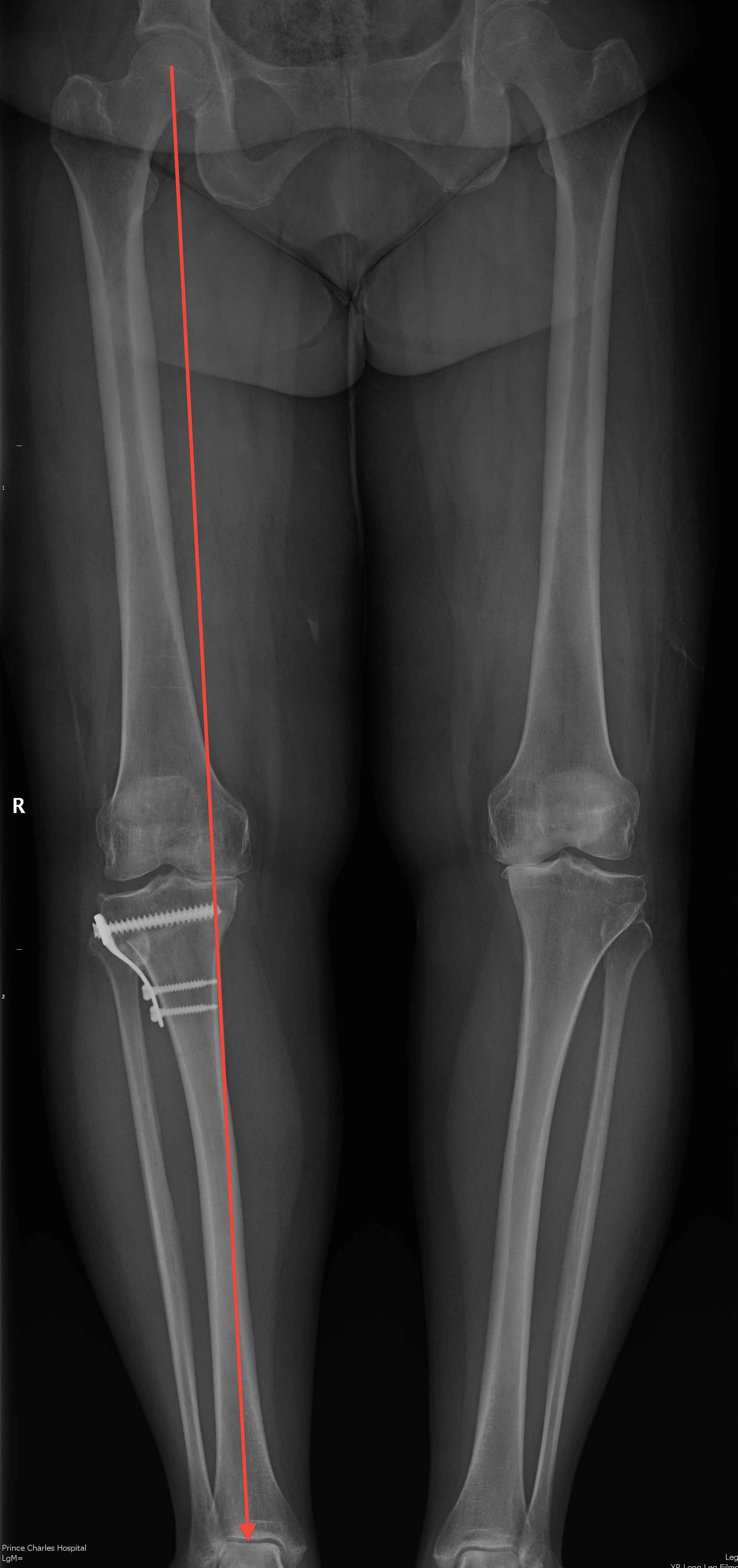
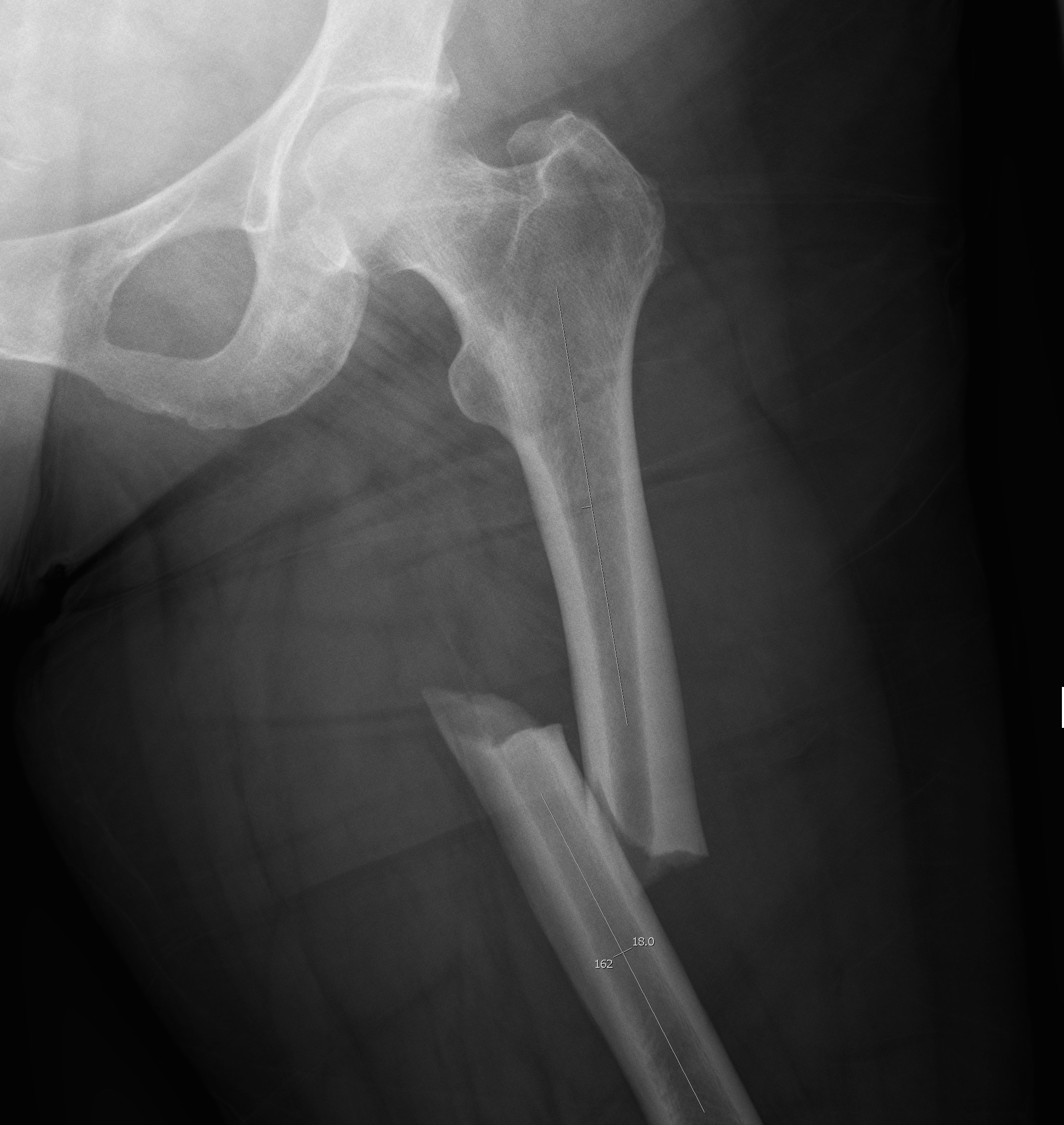
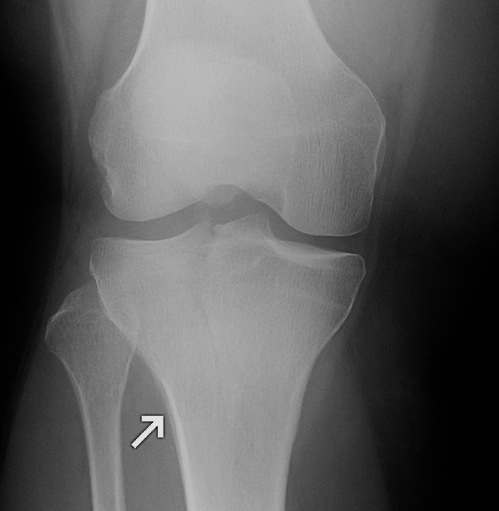
Blood Products
Goal
Ultimate goal of blood management is to AVOID allogenic blood transfusion
Problems
Increased infection rate
- demonstrated in THR
- decreased killer T cells
Increased risk disease transmission
Increased risk transfusion reaction
Increased post-op fever and antibiotic requirements
Increased cost